Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Co
CoLokotko, T.*; Leblond, S.*; Lee, J.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Poves, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Authelet, G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(3), p.034314_1 - 034314_7, 2020/03
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:73.32(Physics, Nuclear)中性子過剰核である Coに対する(
Coに対する( )ノックアウト反応が理化学研究所RIBFで測定された。
)ノックアウト反応が理化学研究所RIBFで測定された。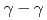 coincidenceの方法で準位構造が決定され、測定された包括的断面積および排他的断面積から暫定的ではあるがスピン・パリティが決定された。殻模型計算との比較により、
coincidenceの方法で準位構造が決定され、測定された包括的断面積および排他的断面積から暫定的ではあるがスピン・パリティが決定された。殻模型計算との比較により、 Coの低励起状態には球形核と変形核が共存することが示唆された。
Coの低励起状態には球形核と変形核が共存することが示唆された。
 Ni from the (
Ni from the ( ,
,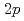 ) reaction
) reactionElekes, Z.*; Kripk ,
, 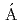 *; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; 馬場 秀忠*; et al.
*; Sohler, D.*; Sieja, K.*; 緒方 一介*; 吉田 数貴; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Authelet, G.*; 馬場 秀忠*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(1), p.014312_1 - 014312_7, 2019/01
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:70.85(Physics, Nuclear)( ,
,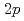 )反応による
)反応による Niの核構造の探索実験を行った。Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, Sieja相互作用を用いた殻模型計算では実験結果を説明しうる陽子空孔状態が得られており、理論的な断面積計算は実験値とよい一致を与えた。実験で得られたすべての状態を理論的に一意に決定することはできなかったが、過去の実験結果と同様にNi同位体でのZ = 28の大きなshell gapを示す結果が得られた。
Niの核構造の探索実験を行った。Lenzi, Nowacki, Poves, Sieja相互作用を用いた殻模型計算では実験結果を説明しうる陽子空孔状態が得られており、理論的な断面積計算は実験値とよい一致を与えた。実験で得られたすべての状態を理論的に一意に決定することはできなかったが、過去の実験結果と同様にNi同位体でのZ = 28の大きなshell gapを示す結果が得られた。
 Sc and development of the
Sc and development of the 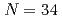 subshell closure
subshell closureSteppenbeck, D.*; 武内 聡*; 青井 考*; Doornenbal, P.*; 松下 昌史*; Wang, H.*; 馬場 秀忠*; 郷 慎太郎*; Holt, J. D.*; Lee, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(6), p.064310_1 - 064310_10, 2017/12
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:80.34(Physics, Nuclear)理化学研究所のRIBFにて、中性子過剰核 Scの励起状態を
Scの励起状態を Tiからの1陽子ノックアウト反応および
Tiからの1陽子ノックアウト反応および Scの非弾性散乱によって生成し、そこからの脱励起
Scの非弾性散乱によって生成し、そこからの脱励起 線を観測することによってエネルギー準位を得た。その結果、第一励起状態が695keVと低く現れることがわかった。
線を観測することによってエネルギー準位を得た。その結果、第一励起状態が695keVと低く現れることがわかった。 Caで知られているように中性子数34の閉殻構造が成り立っているとすると、第一励起状態は約2MeVと高く現れるはずであり、この結果は
Caで知られているように中性子数34の閉殻構造が成り立っているとすると、第一励起状態は約2MeVと高く現れるはずであり、この結果は Scでは中性子数34の新魔法数が消滅していることを示している。殻模型計算でもこの結果は得られ、中性子数34の殻ギャップが陽子数に応じて強く変化していることがその原因であることがわかった。
Scでは中性子数34の新魔法数が消滅していることを示している。殻模型計算でもこの結果は得られ、中性子数34の殻ギャップが陽子数に応じて強く変化していることがその原因であることがわかった。
 =28 and
=28 and  =50; Spectroscopy of
=50; Spectroscopy of 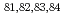 Zn
ZnShand, C. M.*; Podoly k, Zs.*; G
k, Zs.*; G rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
rska, M.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Nowacki, F.*; Otsuka, T.*; Sieja, K.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Tsunoda, T.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 773, p.492 - 497, 2017/10
被引用回数:28 パーセンタイル:87.55(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Low-lying states in neutron-rich 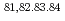 Zn nuclei were measured for the first time via in-beam
Zn nuclei were measured for the first time via in-beam  -ray spectroscopy at RIKEN. These include the 4
-ray spectroscopy at RIKEN. These include the 4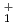 to 2
to 2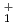 in
in 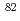 Zn and the 2
Zn and the 2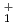 to 0
to 0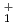 and 4
and 4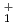 to 2
to 2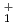 in
in 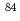 Zn. The reduced E(
Zn. The reduced E(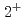 ) energies and increased E(4
) energies and increased E(4 )/E(2
)/E(2 ) ratios at
) ratios at  =52,54 compared to
=52,54 compared to  Zn attest that the magicity is confined just on the neutron number
Zn attest that the magicity is confined just on the neutron number  =50 only. The levels observed in
=50 only. The levels observed in  Zn suggest the onset of deformation towards heavier Zn isotopes. The data were compared to state-of-the-art shell model calculations.
Zn suggest the onset of deformation towards heavier Zn isotopes. The data were compared to state-of-the-art shell model calculations.
 Kr
KrFlavigny, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Delaroche, J.-P.*; Girod, M.*; Libert, J.*; Rodriguez, T. R.*; Authelet, G.*; 馬場 秀忠*; Calvet, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_6, 2017/06
被引用回数:40 パーセンタイル:86.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The first  -ray spectroscopy of very neutron rich
-ray spectroscopy of very neutron rich  Kr isotopes was carried out at the RIBF at RIKEN Nishina center. Excited states in these isotopes were populated via (p,2p) reactions using radioactive
Kr isotopes was carried out at the RIBF at RIKEN Nishina center. Excited states in these isotopes were populated via (p,2p) reactions using radioactive  Rb beams accelerated to 220 MeV/nucleon. The new data show a significant increase in deformation beyond N=60, as well as competing configurations (shape-coexistence) at low energy. The data were compared with beyond-mean-field calculations which predict level energies in good agreement with observation, and suggest oblate-prolate shape coexistence.
Rb beams accelerated to 220 MeV/nucleon. The new data show a significant increase in deformation beyond N=60, as well as competing configurations (shape-coexistence) at low energy. The data were compared with beyond-mean-field calculations which predict level energies in good agreement with observation, and suggest oblate-prolate shape coexistence.
 decay of unbound neutron-hole states in
decay of unbound neutron-hole states in  Sn
SnVaquero, V.*; Jungclaus, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Wimmer, K.*; Gargano, A.*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Chen, S.*; N cher, E.*; Sahin, E.*; 志賀 慶明*; et al.
cher, E.*; Sahin, E.*; 志賀 慶明*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(20), p.202502_1 - 202502_5, 2017/05
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:76.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excited states in  Sn were populated following one-neutron knockout reaction from an unstable
Sn were populated following one-neutron knockout reaction from an unstable  Sn beam at the RIBF laboratory in RIKEN. In addition to the already known
Sn beam at the RIBF laboratory in RIKEN. In addition to the already known  rays, additional
rays, additional  strength was observed for the first time in the excitation-energy range 3.5-5.5 MeV. Since the neutron separation energy of
strength was observed for the first time in the excitation-energy range 3.5-5.5 MeV. Since the neutron separation energy of  Sn is low, this observation provides direct evidence for the radioactive decay of neutron-unbound states in this nucleus. The ability of
Sn is low, this observation provides direct evidence for the radioactive decay of neutron-unbound states in this nucleus. The ability of  decay to compete with neutron emission was attributed to a mismatch between the wave functions of the initial and final states in the neutron emission case. These findings suggest that in the region south-east of
decay to compete with neutron emission was attributed to a mismatch between the wave functions of the initial and final states in the neutron emission case. These findings suggest that in the region south-east of  Sn, nuclear structure effects play a significant role in the decay of unbound states, which are instead usually ignored in the evaluation of neutron-emission probabilities in astrophysical simulations.
Sn, nuclear structure effects play a significant role in the decay of unbound states, which are instead usually ignored in the evaluation of neutron-emission probabilities in astrophysical simulations.
Chen, S.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Rodriguez, T. R.*; Authelet, G.*; 馬場 秀忠*; Calvet, D.*; Ch teau, F.*; Corsi, A.*; Delbart, A.*; et al.
teau, F.*; Corsi, A.*; Delbart, A.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 95(4), p.041302_1 - 041302_6, 2017/04
被引用回数:31 パーセンタイル:89.26(Physics, Nuclear)Neutron-rich isotopes of selenium, 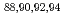 Se, where studied via in beam
Se, where studied via in beam  -ray spectroscopy after nucleon removal reactions at RIBF in RIKEN. The low-energy excitations of these nuclei were investigated using
-ray spectroscopy after nucleon removal reactions at RIBF in RIKEN. The low-energy excitations of these nuclei were investigated using  -
- coincidences, and the first and second excited 2
coincidences, and the first and second excited 2 states were found at remarkably low energies. The analysis and comparison with self-consistent beyond-mean field calculations suggest that both shape coexistence and triaxiality are needed to describe these isotopes.
states were found at remarkably low energies. The analysis and comparison with self-consistent beyond-mean field calculations suggest that both shape coexistence and triaxiality are needed to describe these isotopes.
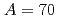 isobars from the
isobars from the 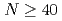 island of inversion
island of inversionMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; 角田 佑介*; Otsuka, T.*; 西村 俊二*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 765, p.328 - 333, 2017/02
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:92.29(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The level schemes of neutron-rich isotopes  Co and
Co and  Ni were populated in the
Ni were populated in the  decay of
decay of  Fe and studied using
Fe and studied using  -delayed
-delayed  -ray spectroscopy of the
-ray spectroscopy of the  decay, at the RIBF in RIKEN, Japan. The experimental results were compared to state-of-the-art shell-model calculations, and indicate a dominance of prolate deformation in the low-lying states, coexisting with spherical states. The
decay, at the RIBF in RIKEN, Japan. The experimental results were compared to state-of-the-art shell-model calculations, and indicate a dominance of prolate deformation in the low-lying states, coexisting with spherical states. The  decay of the
decay of the 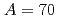 isobars is shown to progress in accordance to a new type of shell evolution, the so-called Type II, which involves many particle-hole excitations across energy gaps.
isobars is shown to progress in accordance to a new type of shell evolution, the so-called Type II, which involves many particle-hole excitations across energy gaps.
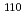 Zr
ZrPaul, N.*; Corsi, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Authelet, G.*; 馬場 秀忠*; Bally, B.*; Bender, M.*; Calvet, D.*; Ch teau, F.*; et al.
teau, F.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(3), p.032501_1 - 032501_7, 2017/01
被引用回数:46 パーセンタイル:88.07(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The first measurement of  rays emitted by the very neutron rich nuclei
rays emitted by the very neutron rich nuclei 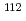 Mo (Z=42) and
Mo (Z=42) and 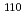 Zr (Z=40) was carried out at the RIBF facility at RIKEN. These data shine light on the postulated N=70 harmonic oscillator shell. If the spin-orbit splitting which gives rise to the N=82 shell gap is reduced in very neutron-rich nuclei, the harmonic oscillator gap at N=70 should open instead. However, both the measured energy of the first excited state
Zr (Z=40) was carried out at the RIBF facility at RIKEN. These data shine light on the postulated N=70 harmonic oscillator shell. If the spin-orbit splitting which gives rise to the N=82 shell gap is reduced in very neutron-rich nuclei, the harmonic oscillator gap at N=70 should open instead. However, both the measured energy of the first excited state 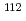 Mo and
Mo and 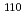 Zr, respectively 235(7) keV and 185(11) keV, and their E(4
Zr, respectively 235(7) keV and 185(11) keV, and their E(4 )/E(2
)/E(2 ) ratio, indicate that these nuclei are good rotors, and exclude the shell stabilization scenario at Z=40 and N=70. These results were compared to state-of-the-art density functional theoretical calculations using Gogny and Skyrme effective interactions.
) ratio, indicate that these nuclei are good rotors, and exclude the shell stabilization scenario at Z=40 and N=70. These results were compared to state-of-the-art density functional theoretical calculations using Gogny and Skyrme effective interactions.
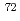 Ni
NiMorales, A. I.*; Benzoni, G.*; Watanabe, H.*; 西村 俊二*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; Lorusso, G.*; Patel, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(3), p.034328_1 - 034328_14, 2016/03
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:83.29(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying excited states in 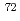 Ni have been investigated at RIKEN by studying the
Ni have been investigated at RIKEN by studying the  decay of
decay of 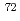 Co to
Co to 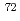 Ni.
Ni. 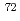 Co was separated with BigRIPS, implanted into the WaS3ABi Silicon array, and the
Co was separated with BigRIPS, implanted into the WaS3ABi Silicon array, and the  ray measured using the EURICA
ray measured using the EURICA  spectrometer. From the analysis, 60 new
spectrometer. From the analysis, 60 new  -ray transitions and 21 new levels in
-ray transitions and 21 new levels in 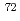 Ni were observed. The new experimental information is compared to shell-model calculations which include neutron excitation across the
Ni were observed. The new experimental information is compared to shell-model calculations which include neutron excitation across the 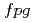 shell. The calculations reproduce rather well the observed states, implying that a clear understanding of these low-lying excitations has been achieved.
shell. The calculations reproduce rather well the observed states, implying that a clear understanding of these low-lying excitations has been achieved.
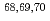 Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chain
Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chainBenzoni, G.*; Morales, A. I.*; Watanabe, H.*; 西村 俊二*; Coraggio, L.*; Itaco, N.*; Gargano, A.*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 751, p.107 - 112, 2015/12
被引用回数:20 パーセンタイル:75.16(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The  decays of
decays of 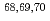 Mn have been measured at the RIBF facility at RIKEN using the EURICA
Mn have been measured at the RIBF facility at RIKEN using the EURICA  spectrometer combined with an active stopper consisting of a stack of Si detectors. Half-lives and
spectrometer combined with an active stopper consisting of a stack of Si detectors. Half-lives and  -delayed neutron emission probabilities have been extracted for these decays, together with first experimental information on excited states populated in
-delayed neutron emission probabilities have been extracted for these decays, together with first experimental information on excited states populated in 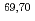 Fe. The data indicate a continuously increasing deformation for Fe isotopes up to A=70, and interpreted to be due to the interplay between quadrupole correlation of specific neutron orbitals and the monopole component of the proton-neutron interaction.
Fe. The data indicate a continuously increasing deformation for Fe isotopes up to A=70, and interpreted to be due to the interplay between quadrupole correlation of specific neutron orbitals and the monopole component of the proton-neutron interaction.