Decay properties of 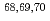 Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chain
Mn; Probing collectivity up to N=44 in Fe isotopic chain
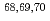 Mnの崩壊の性質; 鉄同位体における中性子数44までの集団性の探索
Mnの崩壊の性質; 鉄同位体における中性子数44までの集団性の探索
Benzoni, G.*; Morales, A. I.*; Watanabe, H.*; 西村 俊二*; Coraggio, L.*; Itaco, N.*; Gargano, A.*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; Lorusso, G.*; Patel, Z.*; Rice, S.*; Sinclair, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; 炭竃 聡之*; Wu, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Yokoyama, R.*; 馬場 秀忠*; Avigo, R.*; Bello Garrote, F. L.*; Blasi, N.*; Bracco, A.*; Camera, F.*; Ceruti, S.*; Crespi, F. C. L.*; De Angelis, G.*; Delattre, M.-C.*; Dombr
m, P.-A.*; 炭竃 聡之*; Wu, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Yokoyama, R.*; 馬場 秀忠*; Avigo, R.*; Bello Garrote, F. L.*; Blasi, N.*; Bracco, A.*; Camera, F.*; Ceruti, S.*; Crespi, F. C. L.*; De Angelis, G.*; Delattre, M.-C.*; Dombr di, Zs.*; Gottardo, A.*; Isobe, T.*; Kuti, I.*; Matsui, K.*; Melon, B.*; Mengoni, D.*; Miyazaki, T.*; Modamio-Hoybjor, V.*; Momiyama, S.*; Napoli, D. R.*; 新倉 潤*; Orlandi, R.
di, Zs.*; Gottardo, A.*; Isobe, T.*; Kuti, I.*; Matsui, K.*; Melon, B.*; Mengoni, D.*; Miyazaki, T.*; Modamio-Hoybjor, V.*; Momiyama, S.*; Napoli, D. R.*; 新倉 潤*; Orlandi, R. 

 ; 櫻井 博儀*; Sahin, E.*; Sohler, D.*; 谷内 稜*; Taprogge, J.*; Vajta, Zs.*; Valiente-Dob
; 櫻井 博儀*; Sahin, E.*; Sohler, D.*; 谷内 稜*; Taprogge, J.*; Vajta, Zs.*; Valiente-Dob n, J. J.*; Yalcinkaya, M.*; Wieland, O.*
n, J. J.*; Yalcinkaya, M.*; Wieland, O.*
Benzoni, G.*; Morales, A. I.*; Watanabe, H.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Coraggio, L.*; Itaco, N.*; Gargano, A.*; Browne, F.*; Daido, R.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Fang, Y.*; Lorusso, G.*; Patel, Z.*; Rice, S.*; Sinclair, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Wu, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Yokoyama, R.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Avigo, R.*; Bello Garrote, F. L.*; Blasi, N.*; Bracco, A.*; Camera, F.*; Ceruti, S.*; Crespi, F. C. L.*; De Angelis, G.*; Delattre, M.-C.*; Dombr
m, P.-A.*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; Wu, J.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Yokoyama, R.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Avigo, R.*; Bello Garrote, F. L.*; Blasi, N.*; Bracco, A.*; Camera, F.*; Ceruti, S.*; Crespi, F. C. L.*; De Angelis, G.*; Delattre, M.-C.*; Dombr di, Zs.*; Gottardo, A.*; Isobe, T.*; Kuti, I.*; Matsui, K.*; Melon, B.*; Mengoni, D.*; Miyazaki, T.*; Modamio-Hoybjor, V.*; Momiyama, S.*; Napoli, D. R.*; Niikura, Megumi*; Orlandi, R.; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Sahin, E.*; Sohler, D.*; Taniuchi, Ryo*; Taprogge, J.*; Vajta, Zs.*; Valiente-Dob
di, Zs.*; Gottardo, A.*; Isobe, T.*; Kuti, I.*; Matsui, K.*; Melon, B.*; Mengoni, D.*; Miyazaki, T.*; Modamio-Hoybjor, V.*; Momiyama, S.*; Napoli, D. R.*; Niikura, Megumi*; Orlandi, R.; Sakurai, Hiroyoshi*; Sahin, E.*; Sohler, D.*; Taniuchi, Ryo*; Taprogge, J.*; Vajta, Zs.*; Valiente-Dob n, J. J.*; Yalcinkaya, M.*; Wieland, O.*
n, J. J.*; Yalcinkaya, M.*; Wieland, O.*
The  decays of
decays of 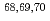 Mn have been measured at the RIBF facility at RIKEN using the EURICA
Mn have been measured at the RIBF facility at RIKEN using the EURICA  spectrometer combined with an active stopper consisting of a stack of Si detectors. Half-lives and
spectrometer combined with an active stopper consisting of a stack of Si detectors. Half-lives and  -delayed neutron emission probabilities have been extracted for these decays, together with first experimental information on excited states populated in
-delayed neutron emission probabilities have been extracted for these decays, together with first experimental information on excited states populated in 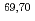 Fe. The data indicate a continuously increasing deformation for Fe isotopes up to A=70, and interpreted to be due to the interplay between quadrupole correlation of specific neutron orbitals and the monopole component of the proton-neutron interaction.
Fe. The data indicate a continuously increasing deformation for Fe isotopes up to A=70, and interpreted to be due to the interplay between quadrupole correlation of specific neutron orbitals and the monopole component of the proton-neutron interaction.