Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luu, V. N.; Taniguchi, Yoshinori; Udagawa, Yutaka; Katsuyama, Jinya
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 442, p.114222_1 - 114222_15, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00Nguyen, H. H.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 218, p.111361_1 - 111361_9, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study examined the criticality characteristics of a partially damaged reactor model, in which fuels located at the core center melt into fuel debris of varying shapes, while fuels situated at the core edges remain intact. The investigation was conducted using the Serpent code with the JENDL-5 nuclear data library. The results of the calculations indicate that when the volume of fuel debris is small and maintained at a constant level, the shape of the fuel debris does not result in significant alterations in the variation law of k of the system. In contrast, for the scenario in which the volume of the fuel debris is variable, the k
of the system. In contrast, for the scenario in which the volume of the fuel debris is variable, the k variation law can be divided into two groups for the reference case with a system temperature of 300 K and no boron in the water. The first group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are cuboid and cylindrical, while the second group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are spherical, cone-shaped, and truncated cone-shaped.
variation law can be divided into two groups for the reference case with a system temperature of 300 K and no boron in the water. The first group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are cuboid and cylindrical, while the second group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are spherical, cone-shaped, and truncated cone-shaped.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2025-004, 186 Pages, 2025/07
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of a hybrid method for evaluating the long-term structural soundness of nuclear reactor buildings using response monitoring and damage imaging technologies" conducted from FY2021 to FY2023. The present study aims to develop an evaluation method necessary to obtain a perspective on the longterm structural soundness of accident-damaged reactor buildings, where accessibility to work sites is extremely limited due to high radiation dose rate and high contamination. In FY2023, the final year of the three-year project, experimental and analytical research activities were performed to develop, (1) Method for evaluating the building by monitoring the response to earthquakes and other disturbances, (2) Damage detection technology for concrete structures using electromagnetic waves, (3) Evaluation method for concrete materials and structures based on damage detection information, (4) Comprehensive soundness evaluation method and a long-term maintenance plan, (5) Promotion of the research. Expected results and final goals are achieved based on the outcomes including achievements up to FY2022.
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 4 of others*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)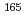 Ho(n,
Ho(n, )
)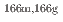 Ho reactions
Ho reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/07
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Motome, Yuiko
JAEA-Research 2025-001, 99 Pages, 2025/06
The detailed computational models for nuclear criticality analyses on the first startup cores of NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), which is categorized as a TRIGA-ACPR (Annular Core Pulse Reactor), were created for the purposes of deeper understandings of safety inspection data on the neutron absorber rod worths of reactivity and improvement of determination technique of the reactivity worths. The uncertainties in effective neutron multiplication factor (k ) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k
) propagated from errors in the geometry, material, and operation data for the present models were evaluated in detail by using the MVP version 3 code with the latest Japanese nuclear data library, JENDL-5, and the previous versions of JENDL libraries. As a result, the overall uncertainties in k for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029
for the present models were evaluated to be in the range of 0.0027 to 0.0029  k
k . It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k
. It is expected that the present models will be utilized as the benchmark on k for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
for TRIGA-ACPR. Moreover, it is confirmed that the overall uncertainties were sufficiently smaller than the values of absorber rod worths determined in NSRR. Thus, it is also considered that the present models are applicable to further analyses on the absorber rod worths in NSRR.
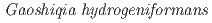 sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation
sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formationUeno, Akio*; Sato, Kiyoshi*; Tamamura, Shuji*; Murakami, Takuma*; Inomata, Hidenori*; Tamazawa, Satoshi*; Amano, Yuki; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Naganuma, Takeshi*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*
International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology, 75(6), p.006802_1 - 006802_11, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Shibahara, Yuji*
KURNS Progress Report 2024, P. 31, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Toyota, Kodai; Onizawa, Takashi; Wakai, Eiichi*
Research & Development in Material Science (Internet), 21(5), p.2632 - 2637, 2025/06
Li, X.; Yamaji, Akifumi*; Sato, Ikken*; Yamashita, Takuya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111217_1 - 111217_13, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Matsumoto, Saori*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Hayashi, Kiichiro*; Endo, Rie*; Bell , M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Volkova, O.*
, M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Volkova, O.*
Steel Research International, 96(5), p.2300766_1 - 2300766_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:75.42(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The density of Ni-based superalloys is measured using the maximum bubble pressure (MBP) method. The viscosity is evaluated using the oscillating crucible method. The surface tension is simultaneously measured using the MBP method.
Neubert, L.*; Bell , M. R.*; Yamamoto, Taisei*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ahrenhold, F.*; Volkova, O.*
, M. R.*; Yamamoto, Taisei*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ahrenhold, F.*; Volkova, O.*
Steel Research International, 96(5), p.202400237_1 - 202400237_8, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.71(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 3 of others*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
Endo, Akira
ESI-News, 43(2), p.37 - 41, 2025/04
The International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements (ICRU) published ICRU Report 95 in 2020, revising the operational quantities for external exposure. This article provides an overview of the developments in the discussions within the ICRU, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP), and experts from Japan, and explores the background and process that led the ICRU to revise the operational quantities, as well as future responses and challenges. The article aims to enhance the understanding of the experts of the new operational quantities and to contribute to their smooth implementation in the future.
Sakurai, Junya*; Torigata, Keisuke*; Matsunaga, Manabu*; Takanashi, Naoto*; Hibino, Shinya*; Kizu, Kenichi*; Morita, Akira*; Inomoto, Masahiro*; Shimohata, Nobuaki*; Toyota, Kodai; et al.
Tetsu To Hagane, 111(5), p.246 - 262, 2025/04
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2024-058, 179 Pages, 2025/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2023 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2024-057, 178 Pages, 2025/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2022 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Nemoto, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Research 2024-018, 16 Pages, 2025/03
The author aimed to contribute to the analysis of the accident behavior of coated cladding with improved oxidation resistance by chromium (Cr) coating on the outer surface of conventional zirconium alloy fuel cladding, and investigated dependence of the oxidation behavior of Cr on the steam flow rate and on temperature. Coated cladding is being developed as one of the Accident Tolerant Fuel (ATF) claddings, and it is important to analyze the behavior of coated cladding under accidental conditions with high accuracy in the purpose of safety evaluation, for which the oxidation kinetics of Cr in high temperature steam is necessary. In this study, based on the results of oxidation tests in high temperature steam using a thermobalance, an oxidation kinetics for Cr in the temperature range and steam flow rate that encompass the conditions of considerable accident was proposed. The results can be used for future analyses in analysis codes such as SAMPSON, thereby contributing to the development of coated cladding.
Scaria, J.*; P drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 59(11), p.5747 - 5755, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:78.93(Engineering, Environmental)Understanding and predicting the interaction mechanisms between chromium and magnetite is of particular interest to elucidate the biogeochemical behavior of Cr in the environment and to develop optimal soil remediation and water treatment strategies. However, while the elimination of the most toxic form of (Cr(VI)) by its reduction to Cr(III) has widely been documented, elucidating the exact mechanism involved in Cr(III) sorption to magnetite has attracted less attention. This study examined the interaction of Cr(III) solution with 10 nm-sized magnetites, whose stoichiometries were carefully defined and preserved in anaerobic conditions. This study reveals the joint effects of pH and magnetite stoichiometry on Cr(III) sorption mechanism, and that Cr(III)-(hydr)oxide precipitation is not necessarily the driving process of Cr(III) elimination from solutions. These results will help predict the fate and transport of chromium, as well as developing magnetite-based chromium remediation processes.
 and -MOX lattice calculations
and -MOX lattice calculationsFujita, Tatsuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study estimated the influence of implicit effect on the k-infinity uncertainty in the PWR-UO and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n,
and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n, ) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO
) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For
and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For  Pu and
Pu and  Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.
Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.