Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Kazuo; Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2025-003, 24 Pages, 2025/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (RuO ) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. RuO
) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. RuO is expected to be absorbed chemically into water dissolving nitrous acid. Condensation of mixed vapor plays an important role for Ru transporting behavior in the facility building. The thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code. The latent heat, which is a governing factor for vapor condensing behavior, has almost same value for nitric acid and water at the temperature range under 120 centigrade. Considering this thermal characteristic, it is assumed that the amount of nitric acid is substituted with mole-equivalent water in MELCOR simulation. Compensating modeling induced deviation by this assumption have been assembled with control function features of MELCOR. The comparison results have been described conducted between original simulation and modified simulation with compensating model in this report. It has been revealed that the total amount of pool water in the facility was as same as both simulations.
is expected to be absorbed chemically into water dissolving nitrous acid. Condensation of mixed vapor plays an important role for Ru transporting behavior in the facility building. The thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code. The latent heat, which is a governing factor for vapor condensing behavior, has almost same value for nitric acid and water at the temperature range under 120 centigrade. Considering this thermal characteristic, it is assumed that the amount of nitric acid is substituted with mole-equivalent water in MELCOR simulation. Compensating modeling induced deviation by this assumption have been assembled with control function features of MELCOR. The comparison results have been described conducted between original simulation and modified simulation with compensating model in this report. It has been revealed that the total amount of pool water in the facility was as same as both simulations.
Wilson, J.*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Tachi, Yukio; Kawama, Daisuke*
Applied Clay Science, 275, p.107862_1 - 107862_15, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0High-Level Radioactive Waste (HLW) repositories include iron or steel-based containers/overpack and bentonite buffers. Over the last 25 years or so, research efforts have attempted to elucidate the nature of iron-bentonite interactions, especially the potential for the deleterious alteration of the swelling clay component (smectite), to iron-rich layer silicates, some of which lack the capacity for intracrystalline swelling. This could result in a reduction or loss in swelling pressure in the bentonite buffer which is designed to protect waste containers from shear forces and also acts to restrict water and solute transport, as part of an engineered barrier system. Most data on iron-bentonite interactions come from experimental and geochemical modelling studies, as natural analogue data are lacking. The data suggests that there is the potential for the development of an iron-rich bentonite alteration zone with smectite (generally present as the aluminous montmorillonite type) undergoing alteration to iron-rich solids, including layer silicates and steel corrosion products such as green rust or magnetite. The evidence available is complex, arguably incomplete, with many potential complex couplings. Many uncertainties remain despite efforts taken over the last 25 years, but plausible scenarios for iron-bentonite interactions have been identified and possible implications for buffer properties have been suggested.
Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.195 - 198, 2025/05
Extraction chromatgraphy technology for trivalent minor actinide (MA(III) ; Am(III) and Cm(III)) recovery from the solution generated by an extraction process in reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel has been developed. A fine particle is generated in the solution. The fine particle must be removed before MA recovery operation, because that leads clogging of the extraction chlomatography column. In order to prevent clogging the column, filtration system utilizing porous silica beads packed column has been designed. In this study, a fine particle trapping system was developed and particle removal performance of the system was experimentally evaluated using alumina particles as simulated fine particle. Column experiments revealed that the fine particle with the particle size from 0.12 to 15  m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2024-042, 111 Pages, 2024/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2023, we continued R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D on challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on nearfield system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". The validation of a method for assessing permeability using the Ductility Index and a method for estimating the state of in-situ ground pressure from hydraulic perturbation tests were investigated as part of the study "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". In FY2023, we resumed construction of the subsurface facilities, 3 new tunnels in the 350 m gallery and resumed excavation of the East Access Shaft and the Ventilation Shaft. By the end of FY2023, the 350 m gallery extension (tunnel extension 66 m) had been completed, and the depths of the East Access Shaft and Ventilation Shaft were GL-424 m and GL-393 m respectively.
C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". The validation of a method for assessing permeability using the Ductility Index and a method for estimating the state of in-situ ground pressure from hydraulic perturbation tests were investigated as part of the study "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". In FY2023, we resumed construction of the subsurface facilities, 3 new tunnels in the 350 m gallery and resumed excavation of the East Access Shaft and the Ventilation Shaft. By the end of FY2023, the 350 m gallery extension (tunnel extension 66 m) had been completed, and the depths of the East Access Shaft and Ventilation Shaft were GL-424 m and GL-393 m respectively.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2024-033, 64 Pages, 2024/09
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2024, we continue R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. In the "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", we continue to obtain data from the full-scale engineered barrier system performance experiment, and work on the specifics of the full-scale engineered barrier system dismantling experiment. We summarise the solute transport experiments for the excavation damaged zone and the effects of organic matter, micro-organisms and colloids, and develop the assessment methodology. We summarise the evaluation methodology using the deep Wakkanai Formation as a case study for block-scale solute transport experiments. As for "Demonstration of repository design options", we summarise the results of investigations and experiments on changes in the geological environment after tunnel excavation and closure, and summarise the applicability and technical challenges of the closure technology for boreholes excavated from tunnels. The systematic integration of technologies towards EBS emplacement, including the organisation of investigation and evaluation methods and analysis, will be promoted. Experiments to confirm the performance of the engineered barrier system under critical conditions, such as high temperatures ( 100
100 C), continue the in-situ tests started in 2023.
C), continue the in-situ tests started in 2023.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2024-007, 24 Pages, 2024/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. It has been observed experimentally that volatility of RuO is suppressed by HNO
is suppressed by HNO generated by HNO
generated by HNO radiolysis. The analysis of chemical reactions of NO
radiolysis. The analysis of chemical reactions of NO including HNO
including HNO and HNO
and HNO in the waste tank is essential to simulate of these phenomena. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been attempted to couple dynamically two computer codes SHAWED and SCHERN. The simulation of boiling behavior in the tank is conducted with SHAWED. SCHERN simulates chemical behaviors of HNO
in the waste tank is essential to simulate of these phenomena. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been attempted to couple dynamically two computer codes SHAWED and SCHERN. The simulation of boiling behavior in the tank is conducted with SHAWED. SCHERN simulates chemical behaviors of HNO , HNO
, HNO and NO
and NO in the tank. A programmatic coupling algorithm and a trial simulation of the accident are presented in this report.
in the tank. A programmatic coupling algorithm and a trial simulation of the accident are presented in this report.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-032, 159 Pages, 2024/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2022, we continued R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D on challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near- field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-019, 70 Pages, 2023/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2023, we continue R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. In the "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", we conduct the coupled analysis on the full-scale engineered barrier system performance experiment and test the coupled simulation code through comparison with different simulation codes in the international DECOVALEX-2023 collaboration project. Borehole investigations are also carried out for solute transport experiments in the Koetoi Formation. As for "Demonstration of repository design concept", we carry out in situ experiments and data analysis on concrete deterioration under the subsurface conditions. Geophysical surveys are also carried out around an experimental tunnel to be newly excavated at the 350m gallery and characterise the initial conditions of the excavation damaged zone. For the "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations", we analyse the results of the hydraulic disturbance tests conducted in previous years and understand the relationship between rock stress / stress state and fault / fracture hydraulic connectivity. Concerning the construction and maintenance of the subsurface facilities, the 350 m gallery is extended and shafts are sank to a depth of 500 m.
Yokoyama, Miki*; Onuma, Susumu*; Osawa, Hideaki; Otomo, Shoji*; Hirose, Yukio*
Humanities & Social Sciences Communications (Internet), 10(1), p.623_1 - 623_10, 2023/09
This study demonstrates that a decision-making process utilising "the veil of ignorance" concept, defined in process terms as beginning from a blank slate encompassing the entire country as potential sites and shortlisting candidate sites based on scientific (geological) safety, promotes public acceptance of siting a repository for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and fosters procedural fairness.
Minari, Eriko*; Kabasawa, Satsuki; Mihara, Morihiro; Makino, Hitoshi; Asano, Hidekazu*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takeshita, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.793 - 803, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:41.50(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2023-001, 26 Pages, 2023/05
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been developed using computer simulation programs to assess the radioactive source term from those facilities. The proposed approach consists analyses with three computer programs. At first, the simulation of boiling behavior in the HLLW tank is conducted with SHAWED code. Next step, the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code based on the results at the first step simulation such as flowed out mixed steam flow rate, temperature and volatilized Ru from the tank. The final analysis step is carried out for estimating amount of released radioactive materials with SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitric acid, nitrogen oxide and Ru based on the condition also simulated MELCOR. Series of sample simulations of the accident at a hypothetical typical facility are presented with the data transfer between those codes in this report.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2022-011, 37 Pages, 2022/12
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. Two major mechanisms are expected for fission products (FPs) transfer from liquid to vapor phase. One is non-volatiles FPs transfer in the form of mists to the vapor phase in the tank, the other is volatilization of such as Ruthenium. These FPs transferred to the vapor phase in the tank could be released with water and nitric-acid mixed steam and NO gas flow to the environment. NO
gas flow to the environment. NO is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (
is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (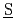 imulation of
imulation of 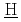 igh-level radio
igh-level radio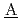 ctive
ctive 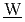 aste
aste 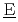 vaporation and
vaporation and 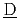 ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2022-026, 66 Pages, 2022/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2022, we continue to conduct research on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rocks to natural perturbations", which are the important issues shown in the Horonobe underground research plan from fiscal year 2020. The main studies to be conducted in fiscal year 2022 are as follows. As "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", we will continue to the test under the simulated condition in which the heat generation by the high-level radioactive waste has subsides in the full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment. We will also conduct solute transport experiment with model testing that take into account the effects of organic matter, microbes, and colloids, and initiate borehole investigation to evaluate solute transport experiments on fractures distribute in Koetoi formation. As "Demonstration of repository design concept", we will continue experiment and analysis of concrete deterioration in the underground environment as a demonstration of remote technique for emplacement and retrievable. As a demonstration of the closure techniques, laboratory tests will be continued to investigate the mechanism of bentonite runoff behaviour, which could be a factor in changing the performance of backfill material, and to expand data on swelling and deformation behaviour. In addition, in-situ borehole closure tests will be conducted to evaluate the applicability of the closure method. As "Understanding of buffering behaviour of
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2022-025, 164 Pages, 2022/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The main aim of this project is to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program in the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2021, we continued R&D on three important issues specified in the "Horonobe Underground Research Plan from Fiscal Year 2020", which involve "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
Yamaguchi, Akinori*; Yokotsuka, Muneyuki*; Furuta, Masayo*; Kubota, Kazuo*; Fujine, Sachio*; Mori, Kenji*; Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 21(4), p.173 - 182, 2022/09
Risk information obtained from probabilistic risk assessment (PRA) can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of measures against severe accidents in nuclear facilities. The PRA methods used for reprocessing facilities are considered immature compared to those for nuclear power plants, and to make the methods mature, reducing the uncertainty of accident scenarios becomes crucial. In this paper, we summarized the results of literature survey on the event progression of evaporation to dryness caused by boiling of high-level liquid waste (HLLW) which is a severe accident in reprocessing facilities and migration behavior of associated radioactive materials. Since one of the important characteristics of Ru is its tendency to form volatile compounds over the course of the event progression, the migration behavior of Ru is categorized into four stages based on temperature. Although no Ru has been released in the waste in the high temperature region, other volatile elements such as Cs could be released. Sufficient experimental data, however, have not been obtained yet. It is, therefore, necessary to further clarify the migration behavior of radioactive materials that predominantly depends on temperature in this region.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2021-053, 133 Pages, 2022/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The main aim of this project is to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program in the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2020, JAEA continued R&D on three important issues specified in the "Horonobe Underground Research Plan from Fiscal Year 2020", which involve "Study on nearfield system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". Specifically, 'full scale engineered barrier system (EBS) experiment' and 'solute transport experiment' were carried out as part of "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment". 'Development and testing of EBS emplacement / retrieval and tunnel closure technologies' and 'evaluation of EBS behavior over 100 C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, 'evaluation of hydromechanical responses of faults to water pressure changes' and 'development of techniques for evaluating self-sealing behavior of an excavation damaged zone after backfilling'. The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, JAEA will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behavior of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, 'evaluation of hydromechanical responses of faults to water pressure changes' and 'development of techniques for evaluating self-sealing behavior of an excavation damaged zone after backfilling'. The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, JAEA will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-013, 20 Pages, 2022/01
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. An idea has been proposed to implement a steam condenser as an accident countermeasure. This measure is expected to prevent nitric acid steam diffusing in facility building and to increase gaseous Ru trapping ratio into condensed water. A simulation study has been carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building to analyze the efficiency of steam condenser. In this study, SCHERN computer code simulates chemical behaviors of Ru in nitrogen oxide, nitric acid and water mixed vapor based on the conditions obtained from simulation with thermal-hydraulic computer code MELCOR. The effectiveness of steam condenser has been analyzed quantitively in preventing mixed vapor diffusion and gaseous Ru trapping effect. Some issues to be solved in analytical model has been also clarified in this study.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-005, 25 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an empirical correlation equation of Ru mass transfer coefficient across the vapor-liquid surface, which can be useful for quantitative simulation of Ru mitigating behavior, has been obtained from data analyses of small-scale experiments conducted to clarify gaseous Ru migrating behavior under steam-condensing condition. A simulation study has been also carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building successfully to demonstrate the feasibility of quantitative estimation of amount of Ru migrating in the facility using the obtained correlation equation implemented in SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitrogen oxide based on the condition also simulated thermal-hydraulic computer code.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-008, 35 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides (NO ) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO
) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2021-009, 54 Pages, 2021/07
The Horonobe URL Project is being pursued by the JAEA to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In 2021 fiscal year (2021/2022), JAEA continue to conduct research on "Demonstration of EBS in geological environment", "Demonstration of disposal concept", and "Validation of buffer capacity of the sedimentary rock to tectonism", which are the important issues shown in the Horonobe underground research plan after 2020 fiscal year. The main studies to be conducted in 2021 fiscal year are as follows. As "Demonstration of EBS in geological environment", we will shift to the test under the condition that the influence of heating is eliminated in the full scale EBS experiment. As "Demonstration of disposal concept", as a demonstration of the closure techniques, it details the conditions under which long-term transitions in the tunnel and surrounding bedrock have a significant impact on safety assessments. And we will continue engineering scale experiment to confirm the workability and performance of plugs and laboratory tests to examine the interaction between backfilling materials and buffer materials. As "Validation of buffer capacity of the sedimentary rock to tectonism", we will analyze the results of the hydraulic disturbance test and continue to study the hydraulic disconnection of faults/fissures in the Wakkanai Formation. As an advancement of technology for investigating and evaluating areas where the flow of groundwater is extremely slow, a boring exploration will be conducted to confirm the three-dimensional distribution of the fossil seawater area.