Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Li, X.; 山路 哲史*; 佐藤 一憲*; 山下 拓哉
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 214, p.111217_1 - 111217_13, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi NPP Unit-2 requires understanding of reactor damage and fuel debris distribution for effective debris retrieval. This study numerically analyzes potential Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV) boundary failure due to eutectic melting of Control Rod Drive (CRD) housings during reheating after debris bed dryout. The Moving Particle Semi-implicit (MPS) method, with an enthalpy-based temperature algorithm and Boussinesq approximation, is applied to simulate melt/solid interactions in a 2-D model of the lower plenum. The CRD housing melting temperature is set at 1523 K based on a quasi-binary phase diagram of 304 Stainless Steel (SS) and Zirconium (Zr) and ELSA experiments. Results suggest local RPV failure at CRD housings, leading to melt release and refreezing. The estimated failure occurs 8-12 hours post-dryout (ca. 12:00-16:00 on 3/15/2011), providing insights into melt progression and boundary breach scenarios in Unit-2.
相原 純; 植田 祥平; 本田 真樹*; 笠原 清司; 岡本 孝司*
JAEA-Research 2024-012, 98 Pages, 2025/02
Pu燃焼高温ガス炉とは、再処理Puの量を安全に減らすための高温ガス炉である。Pu燃焼高温ガス炉では、PuO -イットリア安定化ジルコニア(PuO
-イットリア安定化ジルコニア(PuO -YSZ)の微小球にZrC層を被覆し、更にSiC-TRISO被覆を施した核拡散抵抗性の高い被覆燃料粒子(CFP)を用いる計画である。ZrC層の役割は酸素ゲッターである。平成26-29年に行われたPu燃焼高温ガス炉研究プロジェクトでは、Puの模擬物質としてCeを用いて模擬CFPが製造され、更に、この模擬CFPがHTTR燃料と同様に黒鉛母材で焼き固められ模擬燃料コンパクトが製造された。本報告では、模擬燃料コンパクト製造までの各段階におけるCeO
-YSZ)の微小球にZrC層を被覆し、更にSiC-TRISO被覆を施した核拡散抵抗性の高い被覆燃料粒子(CFP)を用いる計画である。ZrC層の役割は酸素ゲッターである。平成26-29年に行われたPu燃焼高温ガス炉研究プロジェクトでは、Puの模擬物質としてCeを用いて模擬CFPが製造され、更に、この模擬CFPがHTTR燃料と同様に黒鉛母材で焼き固められ模擬燃料コンパクトが製造された。本報告では、模擬燃料コンパクト製造までの各段階におけるCeO -YSZ核及びZrC層の微細構造観察の結果を報告する。
-YSZ核及びZrC層の微細構造観察の結果を報告する。
山田 剛司*; Li, X.; 山下 拓哉; 山路 哲史*
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2024/11
本研究では、MPS法によるMCCI対応溶融物挙動解析コードに、長期間のコンクリート浸食挙動の解析を可能とするような新たなクラストモデルを開発した。新クラストモデルでは、長時間にわたるクラスト粒子の物理的移動の累積を可能にしつつ、数値的移動の累積(数値的クリープ)を防ぐことができる。CEAで実施されたVULCANO VBS-U3実験の公開文献を参考に試解析を実施し、模擬炉心物質とコンクリート壁との境界にクラストが形成された後も継続するコンクリートの溶融浸食(アブレーション)挙動を定性的に解析できることを示した。
寺田 敦彦; 永石 隆二
Nuclear Technology, 210(10), p.1871 - 1887, 2024/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)表面の平滑なガラスビーズ層と細孔を有する真砂土層中に漏洩した水素の拡散挙動について、CFDによる実験結果の照合解析を行い、流れの特性を明らかにした。ガラスビーズ層と真砂土層において、漏洩点からの表層(空気層と粒子層の境界面)までの濃度の広がり方は同様な傾向を示すが、真砂土層の方が表層面近傍での空気層中の水素濃度は低下する傾向がみられた。真砂土層中の拡散挙動シミュレーションでは、透気係数や拡散係数の感度が実験結果の再現性に影響することが示唆された。また、空気層中に流出した水素の滞留を抑制する簡易な自然換気プロセスの検証を試計算し、見通しを示した。
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 東京工業大学*
JAEA-Review 2024-022, 59 Pages, 2024/09
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和4年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和4年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「マイクロ・ナノテクノロジーを利用したアルファ微粒子の溶解・凝集分散に及ぼすナノ界面現象の探求」の令和4年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。安全で合理的な燃料デブリ取出しを進めるためには、デブリ加工時に発生するアルファ微粒子の溶解や変性挙動の把握は不可欠であることに鑑み、本研究は、金属酸化物ナノ粒子の凝集、溶解、変性挙動を熱力学的・速度論的に解明し得るマイクロ・ナノデバイスを創出すると共に、数理科学と組み合わせることで、アルファ微粒子の溶解・凝集・変性プロセスのメカニズム解明と反応モデル化を実現することを目的としている。具体的には、(1)ナノ粒子溶解特性評価、(2)溶解ダイナミクス分析、(3)凝集ダイナミクス分析、(4)表面微構造解析、(5)数理科学的モデリングの5項目を日本側・英国側で分担し、互いに有機的に連携しながら推し進める。令和4年度には、マイクロ限外ろ過分離法を用いて金属酸化物ナノ粒子(TiO 、CeO
、CeO 、ZrO
、ZrO 、ZnO)の溶解特性を調べ、これら金属酸化物ナノ粒子と反応溶媒(純水、硝酸、H
、ZnO)の溶解特性を調べ、これら金属酸化物ナノ粒子と反応溶媒(純水、硝酸、H O
O )との組み合わせによって、個々のナノ粒子の変性挙動は異なっており、特に、H
)との組み合わせによって、個々のナノ粒子の変性挙動は異なっており、特に、H O
O 処理がナノ粒子の変性と溶解の促進を引き起こすことを見出した。また、金属酸化物ナノ粒子と反応溶媒との衝突反応を観測できるマイクロデバイスを創出し、観察画像の輝度変化からナノ粒子の凝集速度を求めることに成功した。
処理がナノ粒子の変性と溶解の促進を引き起こすことを見出した。また、金属酸化物ナノ粒子と反応溶媒との衝突反応を観測できるマイクロデバイスを創出し、観察画像の輝度変化からナノ粒子の凝集速度を求めることに成功した。
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 工学院大学*
JAEA-Review 2024-015, 99 Pages, 2024/09
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和4年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和3年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「世界初の同位体分析装置による少量燃料デブリの性状把握分析手法の確立」の令和4年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、少量燃料デブリの取り出し把握に必要な直接的なデータを世界で初めて取得して評価・検討を行っていくことを目的とする。SEM-EDS等やTEM-EDSでは同位体識別やPu、Bの分析ができない。一方、ICP-MS等のバルク分析では微小視野での情報が欠落する。つまり、既存の方法では、燃焼率指標情報(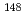 NdとUの組成比)、中性子毒物Gdや中性子吸収物質Bの存在比などの局所分析データを含めて燃料デブリ性状を把握するための分析手段がないことが大きな課題である。JAEA大洗研究所に導入した同位体マイクロイメージング装置(工学院大学開発)は放射性の微小試料に断面加工を行いながら同位体組成などの局所的な定量データが多量に得られ、燃料デブリの性状を正しくかつ迅速に把握できる。令和4年度は、ホット試料の分析と併せて、同位体マイクロイメージング装置の実用性の向上のための改良を令和3年度に引き続き行った。具体的には、同位体マイクロイメージング内にホット試料を導入し、数十
NdとUの組成比)、中性子毒物Gdや中性子吸収物質Bの存在比などの局所分析データを含めて燃料デブリ性状を把握するための分析手段がないことが大きな課題である。JAEA大洗研究所に導入した同位体マイクロイメージング装置(工学院大学開発)は放射性の微小試料に断面加工を行いながら同位体組成などの局所的な定量データが多量に得られ、燃料デブリの性状を正しくかつ迅速に把握できる。令和4年度は、ホット試料の分析と併せて、同位体マイクロイメージング装置の実用性の向上のための改良を令和3年度に引き続き行った。具体的には、同位体マイクロイメージング内にホット試料を導入し、数十 m程度の粒子に対して複数回FIB断面加工を行い、粒子の表面から内部にかけて、成分イメージングを行った。その結果、
m程度の粒子に対して複数回FIB断面加工を行い、粒子の表面から内部にかけて、成分イメージングを行った。その結果、 Zrと
Zrと U
U Oが同じ分布で存在していることが確認された。また、CとFe、Uの分布がそれぞれ分離して存在していることが確認された。また、
Oが同じ分布で存在していることが確認された。また、CとFe、Uの分布がそれぞれ分離して存在していることが確認された。また、 U、
U、 Uの同位体比についてもホット試料から粒子単位で測定することに世界で初めて成功した。
Uの同位体比についてもホット試料から粒子単位で測定することに世界で初めて成功した。
田中 琢朗*; 福岡 将史*; 戸田 賀奈子*; 中西 貴宏; 寺島 元基; 藤原 健壮; 庭野 佑真*; 加藤 弘亮*; 小林 奈通子*; 田野井 慶太朗*; et al.
ACS ES&T Water (Internet), 4(8), p.3579 - 3586, 2024/08
Radioactive cesium released by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in March 2011 remains in the forest environment and is being transported to the ocean via residential areas by runoff into river systems. Most of the  Cs in river water exists as suspended forms, being strongly fixed by micaceous clay minerals. If this fraction can change its form into dissolved forms, this results in additional input of bioavailable
Cs in river water exists as suspended forms, being strongly fixed by micaceous clay minerals. If this fraction can change its form into dissolved forms, this results in additional input of bioavailable  Cs. In this study, in-situ sampling of
Cs. In this study, in-situ sampling of  Cs at multiple rivers in Fukushima Prefecture was conducted using the DGT (diffusive gradient in thin film) devices to investigate the dynamics of radioactive cesium in river environments. At almost all sampling points, the DGT
Cs at multiple rivers in Fukushima Prefecture was conducted using the DGT (diffusive gradient in thin film) devices to investigate the dynamics of radioactive cesium in river environments. At almost all sampling points, the DGT  Cs concentrations exceeded dissolved
Cs concentrations exceeded dissolved  Cs concentrations, revealing the existence of a flux from the suspended to the dissolved forms. This additional input was found to have higher
Cs concentrations, revealing the existence of a flux from the suspended to the dissolved forms. This additional input was found to have higher  Cs/
Cs/  Cs ratios, compared those of Cs in the dissolved form. This study demonstrates that the bioavailability of
Cs ratios, compared those of Cs in the dissolved form. This study demonstrates that the bioavailability of  Cs can be underestimated by assessing only the dissolved form due to
Cs can be underestimated by assessing only the dissolved form due to  Cs flux from the suspended particles likely caused by their dissolution.
Cs flux from the suspended particles likely caused by their dissolution.
酒瀬川 英雄; 中島 基樹*; 加藤 太一朗*; 野澤 貴史*; 安堂 正己*
Materials Today Communications (Internet), 40, p.109659_1 - 109659_8, 2024/08
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:30.18(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)酸化物分散強化型鋼鋼のナノメートルサイズの酸化物粒子はクリープ強度の向上に対して重要な役割を持つ。以前の研究では旧粉末境界という焼結前に機械的合金粉末の表面であった組織因子に注目した。その結果、より小さなサイズの粉末で製作され微細な旧粉末境界を持つ酸化物分散強化型鋼は、より大きなサイズの粉末で製作され粗大な旧粉末境界を持つ酸化物分散強化型鋼よりも、短いクリープ寿命を示すことを確かめた。これより、機械的合金粉末の大きさがクリープ強度特性に影響を及ぼすことを明らかとなった。本研究では非球状である機械的合金粉末の形状がクリープ強度特性に及ぼす影響に注目した。このような形状がクリープ強度特性に異方性を生じさせる可能性が考えられたからである。ここでは異なった切り出し方位を持つ試験片に対してスモールパンチクリープ試験を実施することで異方性に注目した。これより、クリープ寿命は試験片の切り出し方位によって変化することを確かめて、形状がクリープ強度特性に及ぼす影響を明らかとした。
安部 諭; 柴本 泰照
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 202, p.110461_1 - 110461_16, 2024/07
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)During a severe accident in a nuclear containment vessel, jets released from the primary system exhibit complex thermohydraulic behavior due to buoyancy effects and impingement on internal obstacles such as inner walls and floors. Thus, the obstacle-influenced jets are of interest in recent research activities. This paper describes an experimental investigation of the behavior of jets passing through a grid-type obstacle. The flow field was acquired by a particle image velocimetry system. The experiment captured the jet fragmentation by the grid-type obstacle and their recoupling. The mean velocity field obtained by postprocessing indicates a "Rectifying effect," with the axial velocity increasing at the center and the magnitude of the radial velocity decreasing. The meandering flow was suppressed due to this effect. In the near grid-obstacle region, the axial turbulence intensity was relatively large at the edge of each fragmented region due to shear stress. Moreover, the spatial distribution of the radial turbulence fluctuation became more complex. Further investigation is required to clarify the budget of the transport equation for turbulence fluctuation. The experimental data shown in this paper is useful for computational fluid dynamics validation.
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 工学院大学*
JAEA-Review 2024-005, 79 Pages, 2024/06
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和3年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等を始めとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和3年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「世界初の同位体分析装置による少量燃料デブリの性状把握分析手法の確立」の令和3年度の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、少量燃料デブリの取り出し把握に必要な直接的なデータを世界で初めて取得して評価・検討を行っていくことを目的とする。SEM-EDS等やTEM-EDSでは同位体識別やPu、Bの分析ができない。一方、ICP-MS等のバルク分析では微小視野での情報が欠落する。つまり、既存の方法では、燃焼率指標情報(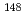 NdとUの組成比)、中性子毒物Gdや中性子吸収物質Bの存在比などの局所分析データを含めて燃料デブリ性状を把握するための分析手段がないことが大きな課題である。JAEA大洗研究所に導入した同位体マイクロイメージング装置(工学院大学開発)は放射性の微小試料に断面加工を行いながら同位体組成などの局所的な定量データが多量に得られ、燃料デブリの性状を正しくかつ迅速に把握できる。令和3年度は、同位体マイクロイメージング装置の実用性の向上のための改良を行った。具体的には、高線量試料への対応として、検出器の放射線シールドや安全な試料導入機構の開発を行った。また、分析スループットや実用性向上のため、手動で調整が必要だった機構の自動化・遠隔化を行い、併せて重要核種について、最適な共鳴イオン化スキームの開発を行った。
NdとUの組成比)、中性子毒物Gdや中性子吸収物質Bの存在比などの局所分析データを含めて燃料デブリ性状を把握するための分析手段がないことが大きな課題である。JAEA大洗研究所に導入した同位体マイクロイメージング装置(工学院大学開発)は放射性の微小試料に断面加工を行いながら同位体組成などの局所的な定量データが多量に得られ、燃料デブリの性状を正しくかつ迅速に把握できる。令和3年度は、同位体マイクロイメージング装置の実用性の向上のための改良を行った。具体的には、高線量試料への対応として、検出器の放射線シールドや安全な試料導入機構の開発を行った。また、分析スループットや実用性向上のため、手動で調整が必要だった機構の自動化・遠隔化を行い、併せて重要核種について、最適な共鳴イオン化スキームの開発を行った。
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 大阪大学*
JAEA-Review 2023-040, 104 Pages, 2024/05
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和4年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和3年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「アルファ微粒子の実測に向けた単一微粒子質量分析法の高度化」の令和4年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、燃料デブリ取り出しの際に発生するウランやプルトニウムを含むアルファ微粒子のリアルタイムモニタリングに向け、単一微粒子質量分析法の高度化を目的とする。令和4年度において、改良型ATOFMSの試作装置を製作し、粒子検出部の捕集効率、検出効率の測定、TOFスペクトル測定を実施した。捕集効率が約85%、検出効率が約60%、粒子検出効率は約6%と見積もられた。レーザー光のビームプロファイルが均質となるように光学系を構築すれば、より高い効率で微粒子を検出することができると考えられる。肥大化濃縮法では、濃縮部ならびに肥大化の試験を行い、微粒子を高効率で溶液中に濃縮捕集できること、製作したエアーアシスト型アトマイザでは肥大微粒化効率が非常に低いことがわかった。冷却型捕集装置や超音波アトマイザの使用などの改良策を提案した。(U,Zr)O ペレットから生成した微粒子についてICP-MS分析を実施し、肥大化濃縮装置で捕集した微粒子は捕集の際にUの一部が超純水に溶解することを見出した。肥大化装置の効率を算出し、効率が約0.1%であると定量した。(U,Zr)O
ペレットから生成した微粒子についてICP-MS分析を実施し、肥大化濃縮装置で捕集した微粒子は捕集の際にUの一部が超純水に溶解することを見出した。肥大化装置の効率を算出し、効率が約0.1%であると定量した。(U,Zr)O 微粒子の表面状態をSEMEDSを用いて観察し、大きさが100nm程度のUを含んだ粒子による集合体が観測され、一部の微粒子は肥大化に成功していることが示唆された。
微粒子の表面状態をSEMEDSを用いて観察し、大きさが100nm程度のUを含んだ粒子による集合体が観測され、一部の微粒子は肥大化に成功していることが示唆された。
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 大阪大学*
JAEA-Review 2023-039, 71 Pages, 2024/03
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和3年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等を始めとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、令和3年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「アルファ微粒子の実測に向けた単一微粒子質量分析法の高度化」の令和3年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである。本研究は、燃料デブリ取り出しの際に発生するウランやプルトニウムを含むアルファ微粒子のリアルタイムモニタリングに向け、単一微粒子質量分析法の高度化を目的とする。令和3年度において、質量分解能を向上する改良型単一微粒子質量分析計(ATOFMS)の開発に向けて、シミュレーションによりイオン軌道や飛行距離を最適化した結果、市販ATOFMSと比べて10倍以上の質量分解能ならびに9倍以上のイオン透過率が得られる構造を得、さらにそれに適合する粒子検出部の設計を完了した。また、検出効率を改善するために新たに開発する肥大化濃縮装置を設計し、それに必要な装置や部品を購入した。試作した肥大化部を用いて予備実験を行い、溶液から乾燥微粒子を製造できること等を確認した。模擬アルファ微粒子の粒径ならびに含有元素分布に関する研究。さらに、模擬アルファ微粒子の表面状態観測を実施し、気化・凝縮を経て生成したと考えられるサブ mの粒径を持つ球状微粒子と、原料が飛散したと考えられる不定形の粒子が存在することを見出した。また、濃縮肥大化した粒子に対する表面状態等の性状分析も可能であることを見出した。
mの粒径を持つ球状微粒子と、原料が飛散したと考えられる不定形の粒子が存在することを見出した。また、濃縮肥大化した粒子に対する表面状態等の性状分析も可能であることを見出した。
廃炉環境国際共同研究センター; 茨城大学*
JAEA-Review 2023-021, 112 Pages, 2024/02
日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)廃炉環境国際共同研究センター(CLADS)では、令和2年度英知を結集した原子力科学技術・人材育成推進事業(以下、「本事業」という。)を実施している。本事業は、東京電力ホールディングス株式会社福島第一原子力発電所の廃炉等をはじめとした原子力分野の課題解決に貢献するため、国内外の英知を結集し、様々な分野の知見や経験を、従前の機関や分野の壁を越えて緊密に融合・連携させた基礎的・基盤的研究及び人材育成を推進することを目的としている。平成30年度の新規採択課題から実施主体を文部科学省からJAEAに移行することで、JAEAとアカデミアとの連携を強化し、廃炉に資する中長期的な研究開発・人材育成をより安定的かつ継続的に実施する体制を構築した。本研究は、平成30年度に採択された研究課題のうち、「放射性微粒子の基礎物性解明による廃炉作業リスク低減への貢献」の平成30年度から令和3年度分の研究成果について取りまとめたものである(令和3年度まで契約延長)。本研究は、東京電力株式会社福島第一原子力発電所事故で環境へ放出された放射性セシウム(Cs)を高濃度に含有する、不溶性の性状を持つシリカ(SiO )主材微粒子の基礎的な物性(粒径、組成、同位体組成、静電特性、光学特性)や
)主材微粒子の基礎的な物性(粒径、組成、同位体組成、静電特性、光学特性)や 放射体の濃度等について、一定の成果をもつ我が国の放射化学、分析化学、エアロゾルの科学者らが英知を集め英国側と協力して更に研究を進め、炉内事故事象の解明、生成要因の解明を行い、廃炉手順の確立、溶融燃料等の回収、作業員、現場・周辺環境の安全確保等の達成に寄与することをねらいとした。
放射体の濃度等について、一定の成果をもつ我が国の放射化学、分析化学、エアロゾルの科学者らが英知を集め英国側と協力して更に研究を進め、炉内事故事象の解明、生成要因の解明を行い、廃炉手順の確立、溶融燃料等の回収、作業員、現場・周辺環境の安全確保等の達成に寄与することをねらいとした。
宮川 晃尚*; 林 直輝*; 岩本 響*; 新井 剛*; 長友 重紀*; 宮崎 康典; 長谷川 健太; 佐野 雄一; 中谷 清治*
Analytical Sciences, 40(2), p.347 - 352, 2024/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:23.37(Chemistry, Analytical)複数のランタノイドイオンを含む錯体溶液中における単一抽出剤含浸高分子被覆シリカ粒子中のEu(III)分配機構を蛍光顕微分光法を用いて調べた。律速段階はEu(III)と2つの抽出剤分子との反応であった。得られた機構と速度定数は、Eu(III)溶液中でEu(III)が粒子に分配される単元素系の機構と一致した。
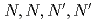 -tetraoctyldiglycolamide-impregnated polymer-coated silica particle using fluorescence microspectroscopy; Transfer mechanism and effect of polymer crosslinking degree
-tetraoctyldiglycolamide-impregnated polymer-coated silica particle using fluorescence microspectroscopy; Transfer mechanism and effect of polymer crosslinking degree宮川 晃尚*; 高橋 拓海*; 崩 愛昌*; 岩本 響*; 新井 剛*; 長友 重紀*; 渡部 創; 佐野 雄一; 中谷 清治*
Analytical Sciences, 39(11), p.1929 - 1936, 2023/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:10.71(Chemistry, Analytical)本研究では、単一のジグリコールアミド誘導体抽出剤(TODGA)を含浸させたポリマー被覆シリカ粒子におけるEu(III)分布を明らかにした。Eu(III)とポリマー層中の2つのTODGA分子との反応が律速過程であることが、速度定数(k and k
and k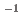 )とEu(III)とHNO
)とEu(III)とHNO の濃度との間に相関がないことから明らかとなった。
の濃度との間に相関がないことから明らかとなった。
Tei, C.; 大高 雅彦; 桑原 大介*
Chemical Physics Letters, 829, p.140755_1 - 140755_6, 2023/10
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.83(Chemistry, Physical)固体金属粒子の界面に付着した液体ナトリウムの核磁気共鳴(NMR)信号を初めて検出することに成功した。本研究では、液体ナトリウムと液体ナトリウム中に浮遊する金属粒子との相互作用の違いによる緩和時間の違いを確認した。その結果、微小チタン粒子表面と液体金属ナトリウムは化学的ではなく物理的に相互作用していることが明らかとなった。
宮川 晃尚*; 林 直輝*; 岩本 響*; 新井 剛*; 長友 重紀*; 宮崎 康典; 長谷川 健太; 佐野 雄一; 中谷 清治*
Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 96(9), p.1019 - 1025, 2023/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:41.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)本研究では、ニトリロトリアセトアミド(NTA)抽出液を含浸させたポリマーコートシリカ単粒子において、Eu(III)とSm(III)のこれらのイオンを含む溶液中での物質移動機構を明らかにした。質量移動の律速過程は、NO
 イオンが関与しないイオンとNTA分子の反応過程であり、これは単一イオン分配系で得られたものと一致した。
イオンが関与しないイオンとNTA分子の反応過程であり、これは単一イオン分配系で得られたものと一致した。
 Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant
Cs occurring near the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant太田 雅和; 高原 省五; 吉村 和也; 長久保 梓; 廣内 淳; 林 奈穂; 阿部 智久; 舟木 泰智; 永井 晴康
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 264, p.107198_1 - 107198_15, 2023/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)福島第一原子力発電所(FDNPP)事故時に環境中に放出され、陸面に沈着した放射性核種について、大気中に再浮遊した Csの吸引は現在における主要な被ばく経路の一つである。再浮遊では、風による土壌粒子の巻き上げが主なメカニズムとされてきた。一方、FDNPP事故後の研究から、帰宅困難区域(DRZ)などの農村部においては、真菌類による胞子放出が大気中
Csの吸引は現在における主要な被ばく経路の一つである。再浮遊では、風による土壌粒子の巻き上げが主なメカニズムとされてきた。一方、FDNPP事故後の研究から、帰宅困難区域(DRZ)などの農村部においては、真菌類による胞子放出が大気中 Cs濃度に影響を及ぼす可能性が示唆されてきた。本研究は、土壌粒子および真菌類胞子としての
Cs濃度に影響を及ぼす可能性が示唆されてきた。本研究は、土壌粒子および真菌類胞子としての Cs再浮遊を計算するモデルを開発し、これをDRZ内に適用することで、これら再浮遊過程の大気中濃度への影響評価を試みた。モデル計算の結果から、土壌粒子の再浮遊は冬から春に観測された大気中
Cs再浮遊を計算するモデルを開発し、これをDRZ内に適用することで、これら再浮遊過程の大気中濃度への影響評価を試みた。モデル計算の結果から、土壌粒子の再浮遊は冬から春に観測された大気中 Csの主要因となったものの、夏から秋に観測された高濃度を再現できないことが示された。真菌類からの胞子状
Csの主要因となったものの、夏から秋に観測された高濃度を再現できないことが示された。真菌類からの胞子状 Csの放出を考慮することで、この夏から秋の高濃度事象は概ねモデルで再現された。解析結果から、真菌類胞子への
Csの放出を考慮することで、この夏から秋の高濃度事象は概ねモデルで再現された。解析結果から、真菌類胞子への Csの蓄積と、農村部に特徴づけられる高い胞子放出率が夏から秋の大気中
Csの蓄積と、農村部に特徴づけられる高い胞子放出率が夏から秋の大気中 Csに寄与している可能性が見出された。DRZ内には依然として未除染の森林が存在しているため、この真菌類胞子の大気中
Csに寄与している可能性が見出された。DRZ内には依然として未除染の森林が存在しているため、この真菌類胞子の大気中 Csへの寄与は今後将来も継続する可能性がある。
Csへの寄与は今後将来も継続する可能性がある。
小坂 亘; 内堀 昭寛; 岡野 靖; 柳沢 秀樹*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.1150 - 1163, 2023/08
ナトリウム冷却型高速炉における蒸気発生器(SG)の安全性評価及び設計について、SG内伝熱管からの加圧水のリーク及びその後の事象進展の評価は重要である。解析コードLEAP-IIIは半経験式や1次元保存式などの低計算コストなモデルで構成されるために短い計算時間で水リーク率等を評価でき、革新炉開発における多様なSG設計の探求を加速させることが期待される。しかし、現在の温度分布評価モデルには、過度な保守性を示す場合があること、及びチューニングのために予備的な実験又は詳細な数値解析が必要とされて準備に時間がかかることに課題がある。これらを改善するため、より単純な計算原理に従い、機構論的な側面を持ちつつも高速計算可能なラグランジュ粒子法コードの開発に取り組んでいる。今回は、本粒子法コードに実装されている粒子ペア探索手法の効率化、及び粒子ペア探索を用いずに同等の結果を得るためのモデルの開発を行った。テスト解析を通して、これらのモデル改良による計算時間短縮効果を確認し、また、伝熱管破損判定に重要な伝熱管周囲の代表温度について、詳細な機構論的解析コード(SERAPHIM)による評価結果とよい一致を示すことを確認した。
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; 内堀 昭寛; 岡野 靖; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; 高田 孝*; 岡本 孝司*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:36.16(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For a sodium-cooled fast reactor, the capability for stable cooling and avoiding re-criticality on the debris bed is essential for achieving in-vessel retention when severe accidents occur. However, an unexploited uncertainty still existed regarding the compound effect of the heterogeneous configuration and dynamic particle redistribution for the debris bed's criticality and cooling safety assessment. Therefore, this research aims to develop a numerical tool for investigating the effects of the different transformations of the heterogeneous configurations on the debris bed's criticality/cooling assessment. Based on the newly proposed methodology in this research, via integrating the Discrete Element Method (DEM) with Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Monte-Carlo-based Neutronics (MCN), the coupled CFD-DEM-MCN solver was constructed with the originally created interface to integrate two existing codes. The effects of the different bed configurations' transformations on the bed safety assessments were also quantitively confirmed, indicating that the effect of the particle-centralized fissile material had the dominant negative effect on the safety margin of avoiding re-criticality and particle re-melting accidents and had a more evident impact than the net bed-centralized effect. This coupled solver can serve to further assess the debris bed's safety via a multi-physics simulation approach, leading to safer SFR design concepts.