Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Ichiba, Yuta*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(4), p.389 - 400, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Rina; Yoshimura, Kazuya; Sanada, Yukihisa; Mikami, Satoshi; Yamada, Tsutomu*; Nakasone, Takamasa*; Kanaizuka, Seiichi*; Sato, Tetsuro*; Mori, Tsubasa*; Takagi, Marie*
Environment International, 194, p.109148_1 - 109148_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Environmental Sciences)Assessment of individual external doses from ambient dose equivalents is used for predictive and retrospective assessments where personal dosimeters are not applicable. However, it tends to contain more errors than assessment by personal dosimetry due to various parameters. Therefore, in order to accurately assess the individual dose from ambient dose equivalents, a model that estimates effective doses considering life patterns and the shielding effects by buildings and vehicles, were developed in this study. The model parameters were examined using robust datasets of environmental radiation measured in the areas affected by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident in 2020 to 2021. The accuracy of the model was validated by comparison with 106 daily personal doses measured in Fukushima Prefecture in 2020. The measured personal dose was well reproduced by the model-estimated effective dose, showing that the model can be used to assess the individual exposure dose, similar to personal dosimetry. Furthermore, this model is an effective tool for radiation protection, as it can estimate the individual dose predictively and retrospectively by using environmental radiation data.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Okayama University*
JAEA-Review 2024-008, 59 Pages, 2024/07
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Radiation tolerant rapid criticality monitoring with radiation-hardened FPGAs" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. The present study aims to be developing a radiation-hardened optoelectronic FPGA with a 1 Grad total-ionizing-dose tolerance on which optical technologies are introduced onto a semiconductor technology and a radiation hardened FPGA with a 200 Mrad total-ionizing-dose tolerance not using any optical component. Moreover, Japanese research group will support hardware acceleration on FPGAs used for neutron-detection system developed by UK team. Finally, we will provide our radiation-hardened FPGA for the UK neutron-detection system.
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Oura, Masatoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.856 - 870, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:91.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)Endo, Akira
JAEA-Research 2024-002, 90 Pages, 2024/05
This report presents a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between three quantities used for area monitoring - ambient dose equivalent  , maximum dose equivalent
, maximum dose equivalent 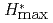 , and ambient dose
, and ambient dose  - and effective dose for external irradiation by photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions, and helium ions. For the analysis, calculations were performed using PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System) and the ICRU sphere. The analysis result shows that
- and effective dose for external irradiation by photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions, and helium ions. For the analysis, calculations were performed using PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System) and the ICRU sphere. The analysis result shows that  and
and 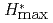 can induce large differences in the estimation of effective dose over a wide energy range for various particle types covered by ICRP Publication 116 while
can induce large differences in the estimation of effective dose over a wide energy range for various particle types covered by ICRP Publication 116 while  can conservatively estimate effective dose within the acceptable range for area monitoring. In other words,
can conservatively estimate effective dose within the acceptable range for area monitoring. In other words,  and
and 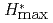 have limitations in estimating effective dose, and using
have limitations in estimating effective dose, and using  is recommended as a more appropriate quantity for the purpose. This conclusion supports the proposal of ICRU Report 95 to use
is recommended as a more appropriate quantity for the purpose. This conclusion supports the proposal of ICRU Report 95 to use  for estimating effective dose in various external exposure situations. The use of ambient dose
for estimating effective dose in various external exposure situations. The use of ambient dose  is particularly important in situations where various types of radiation are encountered, such as the use of radiation in the medical and academic fields and exposure in aviation and can meet the evolving requirements of radiation monitoring for the expansion of the field of radiological protection.
is particularly important in situations where various types of radiation are encountered, such as the use of radiation in the medical and academic fields and exposure in aviation and can meet the evolving requirements of radiation monitoring for the expansion of the field of radiological protection.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Okayama University*
JAEA-Review 2023-038, 48 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Embedded system using a radiation-hardened processor" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to be developing a radiation-hardened optoelectronic processor with a 10 MGy total-ionizing-dose (TID) tolerance, a radiation-hardened processor without any optical component with a 4 MGy TID tolerance, a radiation-hardened memory with a 4 MGy TID tolerance, and a radiation-hardened power supply unit with a 1 MGy TID tolerance. Moreover, Japanese research group will support radiation- hardened field programmable gate arrays, power supply units, and radiation-hardened optical systems for radiation-hardened robot systems and radiation sensor systems developed by UK team.
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.1013 - 1026, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:96.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-063, 86 Pages, 2023/02
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. The samples to be analyzed in this study were collected from wild Japanese macaques exposed in the ex-evacuation zone after the accident of 1F.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Okayama University*
JAEA-Review 2022-017, 56 Pages, 2022/08
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Radiation tolerant rapid criticality monitoring with radiation-hardened FPGAs" conducted in FY2020. This research is developing a radiation-hardened optoelectronic FPGA with a 1 Grad total-ionizing-dose tolerance on which optical technologies are introduced onto a semiconductor technology and a radiation hardened FPGA with a 200 Mrad total-ionizing-dose tolerance not using any optical component. Moreover, Japanese research group will support hardware acceleration on FPGAs used for neutron-detection system developed by UK team.
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(6), p.677 - 687, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:94.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2021-050, 82 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to investigate the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. An interdisciplinary collaborative study discussed the correlation between radiation dose and the biological effect by analyzing the samples of wild Japanese macaques exposed to radiation due to the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station and of animal experiments.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Technology, Kisarazu College*
JAEA-Review 2021-043, 135 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of dosimetry device in reactor cores under severe radiation environment" conducted from FY2018 to FY2020. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2020, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. Since the radiation level in the reactors and buildings of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (1F) is extremely high due to the accident, it is required to develop radiation measurement technology based on the needs at the 1F working site. In this study, we will develop technologies towards practical application of revolutionary radiation measurement system based on the dose measurement technology utilizing solar cell devices.
Nugraha, E. D.*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Kusdiana*; Untara*; Mellawati, J.*; Nurokhim*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Ikram, A.*; Syaifudin, M.*; Yamada, Ryohei; et al.
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.14578_1 - 14578_16, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:83.63(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Mamuju is one of the regions in Indonesia which retains natural conditions but has relatively high exposure to natural radiation. The goals of the present study were to characterize exposure of the entire Mamuju region as a high natural background radiation area (HNBRA) and to assess the existing exposure as a means for radiation protection of the public and the environment. A cross-sectional study method was used with cluster sampling areas by measuring all parameters that contribute to external and internal radiation exposures. It was determined that Mamuju was a unique HNBRA with the annual effective dose between 17 and 115 mSv, with an average of 32 mSv. The lifetime cumulative dose calculation suggested that Mamuju residents could receive as much as 2.2 Sv on average which is much higher than the average dose of atomic bomb survivors for which risks of cancer and non-cancer diseases are demonstrated. The study results are new scientific data allowing better understanding of health effects related to chronic low-dose-rate radiation exposure and they can be used as the main input in a future epidemiology study.
Tamura, Koji; Oba, Hironori; Saeki, Morihisa; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Lim, H. H.*; Taira, Takunori*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(4), p.405 - 415, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:81.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Radiation dose rate effects on the properties of a compact fiber-optic laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) system with a monolithic Nd:YAG/Cr:YAG composite ceramics were investigated for remote analysis in hazardous environment. To investigate radiation effects on the LIBS signal, properties related to the Nd:YAG laser operation such as oscillation threshold, output energy, oscillation timing, temporal pulse shape, and beam profile were measured as a function of the radiation dose rate from 0 to 10 kGy/hr in view of their influences to the signal. LIBS spectra of zirconium metal were measured under irradiation. Although signal intensity decreased considerably by irradiation, informative spectra were well obtained even at the maximum radiation dose rate. From the comparison of the LIBS-related parameters among the laser properties, signal reduction was mainly ascribed to the pulse energy reduction. Scintillation emission spectra were also measured from the ceramics during the irradiation, where the signal intensity increased linearly with the dose rate. The results show that the developed system.
Hashimoto, Makoto; Kinase, Sakae; Munakata, Masahiro; Murayama, Takashi; Takahashi, Masa; Takada, Chie; Okamoto, Akiko; Hayakawa, Tsuyoshi; Sukegawa, Masato; Kume, Nobuhide*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-071, 53 Pages, 2021/03
In the case of a nuclear accident or a radiological emergency, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), as a designated public corporation assigned in the Disaster Countermeasures Basic Act and the Armed Attack Situation Response Law, undertakes technical supports to the national government and local governments. The JAEA is requested to support to evaluate radiation doses to residents in a nuclear emergency, which is specified in the Basic Disaster Management Plan and the Nuclear Emergency Response Manual. For the dose evaluation, however, its strategy, target, method, structure and so on have not been determined either specifically or in detail. This report describes the results of investigation and consideration discussed in the "Working Group for Radiation Dose Evaluation at a Nuclear Emergency" established within the Nuclear Emergency Assistance and Training Center to discuss technical supports for radiation dose evaluation to residents in the case of a nuclear emergency, and aims at contributing to specific and detailed discussion and activities in the future for the national government and local governments, also within the JAEA.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Manabe, Kentaro; Sato, Kaoru
JAEA-Review 2020-068, 114 Pages, 2021/03
Radiation safety regulations have been currently established based on the 1990Recommendation by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) in Japan. Meanwhile, ICRP released the 2007 Recommendation that replaces the 1990 Recommendation. Thus, the Radiation Council, which is established under the Nuclear Regulation Authority (NRA), has made discussions to incorporate the purpose of the 2007 Recommendation into Japanese regulations for radiation safety. As ICRP also has published effective dose coefficients for internal exposure assessment in accordance with the 2007recommendation, the technical standards are to be revised for the internal exposure assessment method in Japan. Currently, not all of the effective doses have been published to revise concentration limits for internal exposure protections of workers and public. The published effective dose coefficients are applied to radionuclides which are important in radiation protection for internal exposure of a worker. Thus, we review new effective dose coefficients as well as basic dosimetry models and data based upon Occupational Intakes of Radionuclides (OIR) parts 2, 3 and 4 that have been published from 2016 to 2019 by ICRP. In addition, issues are sorted out to provide information for revision of the technical standards for internal exposure assessment based on the 2007 Recommendations in future.
Ando, Masaki; Matsuda, Norihiro; Saito, Kimiaki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(1), p.34 - 39, 2021/03
We measured count rates and air dose rates at 11 measurement points where the influence of the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident could be ignored to obtain parameters for a background equation applying to KURAMA-II loaded with the high sensitivity CsI(Tl) detector, C12137-01. It was found that the sensitivity of KURAMA-II (C12137-01) was about 10 times or more for background measurement, compared with KURAMA-II loaded with the standard type CsI(Tl) detector, C12137. A background equation for the energy range of 1400-2000 keV was determined as, y ( Sv/h)=0.062 x (cps). We evaluated background air dose rates using KURAMA-II (C12137-01) for 71 municipalities and compared them with the previous study using KURAMA-II (C12137). Evaluated background air dose rates in this study were almost equal to those in the previous study. We confirmed that the background equation evaluated in this study was applicable for the KURAMA-II (C12137-01).
Sv/h)=0.062 x (cps). We evaluated background air dose rates using KURAMA-II (C12137-01) for 71 municipalities and compared them with the previous study using KURAMA-II (C12137). Evaluated background air dose rates in this study were almost equal to those in the previous study. We confirmed that the background equation evaluated in this study was applicable for the KURAMA-II (C12137-01).
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Technology, Kisarazu College*
JAEA-Review 2020-051, 97 Pages, 2021/02
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Dosimeter for Severe Radiation Environment near Reactor Pressure Vessel" conducted in FY2019.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Shizuoka University*
JAEA-Review 2020-059, 42 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Radiation tolerant rapid criticality monitoring with radiation-hardened FPGAs". This research is developing a radiation-hardened optoelectronic FPGA with a 1 Grad total-ionizing-dose tolerance on which optical technologies are introduced onto a semiconductor technology and a radiation hardened FPGA with a 200 Mrad total-ionizing-dose tolerance not using any optical component. Moreover, Japanese research group will support hardware acceleration on FPGAs used for neutron-detection system developed by UK team. Finally, we will provide our radiation-hardened FPGA for the UK neutron-detection system.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2020-048, 49 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "The study of oxidative stress status in the organs exposed to low dose/low dose-rate radiation". This study investigates the biological effects of low dose/low dose-rate radiation exposure, which is of great social interest, on the oxidative stress status of individual organs and will contribute to the collection of scientific data in a dose range to be required. An interdisciplinary collaborative study discussed the correlation between radiation dose and the biological effect by analyzing the samples of wild Japanese macaques exposed to radiation due to the accident of Fukushima nuclear power station and of animal experiments.