Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-001, 94 Pages, 2025/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2023, along with the verification of each system, a three-dimensional reconstruction model was generated using images acquired from a moving camera on the monitoring platform in a simulated environment, and an integrated experiment was conducted to demonstrate that it is possible to present images from the optimal viewpoint for the visualization target, with the cooperation of each research theme.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Sawahata, Yoshiro*; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-022, 170 Pages, 2025/03
On March 11, 2011, the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake caused a tsunami that led to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, releasing radioactive material into the environment. Since then, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) using manned helicopters has been employed to measure radiation distribution. As a commissioned project from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) utilizes this technology for emergency monitoring during nuclear facility accidents, aiming to provide prompt results by pre-arranging information on background radiation, topography, and control airspaces around nuclear power plants nationwide. In fiscal year 2023, the commissioned project included conducting ARM around the Sendai Nuclear Power Station and preparing related information. To enhance effectiveness during emergencies, ARM and the first domestic training flight of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) were conducted during the FY2023 Nuclear Energy Disaster Prevention Drill. Furthermore, UAVs radiation monitoring technology was advanced by selecting UAVs and investigating their performance. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified providing insights to improve emergency preparedness.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nakama, Shigeo; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ochi, Kotaro; Nagakubo, Azusa; Sawahata, Yoshiro*; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-021, 232 Pages, 2025/03
The 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on March 11, 2011, caused a tsunami that led to the TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) accident, releasing a large amount of radioactive material into the surrounding environment. Since the accident, Aerial Radiation Monitoring (ARM) has been used to quickly and widely measure radiation distribution. As a commissioned project from the Nuclear Regulation Authority, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has continuously conducted ARM around FDNPS using manned and unmanned helicopters. This report summarizes the monitoring results for fiscal year 2023, evaluates changes in dose rate from past results, and discusses the factors contributing to these changes. Additionally, an analysis considering terrain undulation was conducted to improve accuracy for converting ARM data into dose rate. Furthermore, a method to discriminate airborne radon progeny was applied for ARM results to evaluate its impact. Moreover, to perform wide-area monitoring more efficiently, we advanced the development of unmanned airplane monitoring technology.
Endo, Akira
JAEA-Research 2024-002, 90 Pages, 2024/05
This report presents a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between three quantities used for area monitoring - ambient dose equivalent  , maximum dose equivalent
, maximum dose equivalent 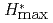 , and ambient dose
, and ambient dose  - and effective dose for external irradiation by photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions, and helium ions. For the analysis, calculations were performed using PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System) and the ICRU sphere. The analysis result shows that
- and effective dose for external irradiation by photons, neutrons, electrons, positrons, protons, muons, pions, and helium ions. For the analysis, calculations were performed using PHITS (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System) and the ICRU sphere. The analysis result shows that  and
and 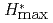 can induce large differences in the estimation of effective dose over a wide energy range for various particle types covered by ICRP Publication 116 while
can induce large differences in the estimation of effective dose over a wide energy range for various particle types covered by ICRP Publication 116 while  can conservatively estimate effective dose within the acceptable range for area monitoring. In other words,
can conservatively estimate effective dose within the acceptable range for area monitoring. In other words,  and
and 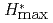 have limitations in estimating effective dose, and using
have limitations in estimating effective dose, and using  is recommended as a more appropriate quantity for the purpose. This conclusion supports the proposal of ICRU Report 95 to use
is recommended as a more appropriate quantity for the purpose. This conclusion supports the proposal of ICRU Report 95 to use  for estimating effective dose in various external exposure situations. The use of ambient dose
for estimating effective dose in various external exposure situations. The use of ambient dose  is particularly important in situations where various types of radiation are encountered, such as the use of radiation in the medical and academic fields and exposure in aviation and can meet the evolving requirements of radiation monitoring for the expansion of the field of radiological protection.
is particularly important in situations where various types of radiation are encountered, such as the use of radiation in the medical and academic fields and exposure in aviation and can meet the evolving requirements of radiation monitoring for the expansion of the field of radiological protection.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nagakubo, Azusa; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-027, 146 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been applied as a method to quickly and extensively measure the distribution of radiation. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has continuously conducted ARM via manned helicopter around FDNPS. In this report, we summarize the results of the ARM around FDNPS in the fiscal year 2022, evaluate the changes of ambient dose rates and other parameters based on the comparison to the past ARM results, and discuss the causes of such changes. In order to contribute to improve the accuracy of ambient dose rate conversion, we analyzed the ARM data taking into account undulating topography, and evaluated the effect of this method. Furthermore, the effect of radon progenies in the air on the ARM was evaluated by applying the discrimination method to the measurement results.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-026, 161 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been utilized as a method to quickly and extensively measure radiation distribution surrounding FDNPS. In order to utilize ARM and to promptly provide the results during a nuclear emergency, information on background radiation levels, topographical features, and controlled airspace surrounding nationwide nuclear facilities have been prepared in advance. In the fiscal year 2022, we conducted ARM around the Mihama Nuclear Power Station of Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO), the Tsuruga Power Station of Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC), and the Ikata Power Station of Shikoku Electric Power Company (YONDEN), and prepared information on background radiation doses and controlled airspace. In addition, we have developed an aerial radiation detection system via unmanned airplane, which is expected to be an alternative to ARM, during a nuclear emergency. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2023-023, 99 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human Resource Development Related to Remote Control Technology for Monitoring Inside RPV Pedestal during Retrieval of Fuel Debris" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2022, each system was improved and expanded toward the final year, and verification experiments were conducted in simulated environments.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; High Energy Accelerator Research Organization*
JAEA-Review 2023-020, 90 Pages, 2023/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Technology development of diamond-base neutron sensors and radiation-resistive integrated-circuits for shielding-free criticality approach monitoring system" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to develop key components of neutron detection system without a radiation shield for a criticality approach monitoring system with high neutron detection efficiency (a few count/nv) under high gamma ray background (1kGy/h). Developed components are neutron detection devices based on diamond sensors and a high radiation resistive signal-processing data-transfer system based on radiation resistive integrated circuit technologies.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Hokama, Tomonori; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-028, 127 Pages, 2023/02
A large amount of radioactive material was released by the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company, caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring via manned helicopter has been utilized to grasp rapidly and widely the distribution of the radioactive materials surrounding FDNPS. We prepare the data of background radiation dose, geomorphic characteristics and the controlled airspace surrounding nuclear facilities of the whole country in order to make effective use of the monitoring technique as a way of emergency radiation monitoring and supply the results during an accident of a facility. This report has summarized the knowledge noted above achieved by the aerial radiation monitoring around Ohi and Takahama nuclear power stations. In addition, the examination's progress aimed at introducing airborne radiation monitoring via an unmanned plane during a nuclear disaster and the technical issues are summarized in this report.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Nagakubo, Azusa; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Urabe, Yoshimi*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-027, 148 Pages, 2023/02
By the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011, a large amount of radioactive material was released from the FDNPS. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring via manned helicopter has been conducted around FDNPS. The results of the airborne radiation monitoring and the evaluation for temporal change of dose rate in the fiscal 2021 were summarized in this report. Analysis considering topographical effects was applied to the result of the airborne monitoring to improve the accuracy of the conventional method. In addition, technique for discriminating gamma rays from the ground and those from the airborne Rn-progenies was also utilized to evaluate their effect on airborne radiation monitoring.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-032, 102 Pages, 2022/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2021, we mainly worked on improving the base design and technology development that we had worked on in the previous year, and we also prepared for integration experiments.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; High Energy Accelerator Research Organization*
JAEA-Review 2022-031, 89 Pages, 2022/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Technology development of diamond-base neutron sensors and radiation-resistive integrated-circuits for shielding-free criticality approach monitoring system" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to develop key components of neutron detection system without a radiation shield for a criticality approach monitoring system. It is required high neutron detection efficiency for a few cps/nv under 1 kGy/h and compact-light-weight to fit constraints of the penetration size and the payload. The project aims to design and evaluate neutron detection devices based on diamond sensors and a high radiation resistive signal-processing data-transfer system based on radiation resistive integrated circuit technologies …
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Ishizaki, Azusa; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Kikuchi, Hikaru*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-029, 132 Pages, 2022/02
By the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011, a large amount of radioactive material was released from the FDNPS. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring using manned helicopter has been conducted around FDNPS. The results of the airborne radiation monitoring and the evaluation for temporal change of dose rate in the fiscal 2020 were summarized in this report. Analysis considering topographical effects was applied to the result of the airborne monitoring to improve the accuracy of conventional method. In addition, technique for discriminating gamma rays from the ground and those from the airborne Rn-progenies was also utilized to evaluate their effect on airborne radiation monitoring.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; High Energy Accelerator Research Organization*
JAEA-Review 2021-038, 65 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Technology development of diamond-base neutron sensors and radiation-resistive integrated-circuits for shielding-free criticality approach monitoring system" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to develop key components of neutron detection system without a radiation shield for a criticality approach monitoring system. It is required high neutron detection efficiency for a few cps/nv under high gamma ray radiation environment (i.e. 1 kGy/h maximum) and compact-light-weight to fit constraints of the penetration size and the payload.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2021-030, 79 Pages, 2021/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted in FY2020. This study deals with construction of a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2020, the main activities were base design and underlying technology development.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Kikuchi, Hikaru*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2021-020, 138 Pages, 2021/11
A large amount of radioactive material was released by the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company, caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring via manned helicopter has been utilized to grasp rapidly and widely the distribution of the radioactive materials surrounding FDNPS. We prepare the data of background radiation dose, geomorphic characteristics and the controlled airspace surrounding nuclear facilities of the whole country in order to make effective use of the monitoring technique as a way of emergency radiation monitoring and supply the results during an accident of a facility. This report is summarized that the knowledge as noted above achieved by the aerial radiation monitoring around Tsuruga and Mihama nuclear power station, research reactors in Kindai University Atomic Energy Research Institute and Institute for Integrated Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. In addition, examination's progress aimed at introduction of airborne radiation monitoring via unmanned plane during nuclear disaster and the technical issues are summarized in this report.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Kikuchi, Hikaru*; Ishizaki, Azusa; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-019, 128 Pages, 2021/02
A large amount of radioactive material was released by the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company, caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring using manned helicopter has been utilized to grasp rapidly and widely the distribution of the radioactive materials around FDNPS. We prepare the data of background radiation dose, geomorphic characteristics and the controlled airspace around nuclear facilities of the whole country in order to make effective use of the monitoring technique as a way of emergency radiation monitoring and supply the results during accidents of the facilities. Furthermore, the airborne radiation monitoring has been conducted in Integrated Nuclear Emergency Response Drill to increase effectiveness of the monitoring. This report is summarized that the knowledge as noted above achieved by the aerial radiation monitoring around Higashidori nuclear power station, the nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Rokkasho village and Shika nuclear power station, the full details of the aerial radiation monitoring in Integrated Nuclear Emergency Response Drill in the fiscal 2019. In addition, examination's progress aimed at introduction of airborne radiation monitoring using unmanned helicopter during nuclear disaster and the technical issues are summarized in this report.
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Ishizaki, Azusa; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Sato, Kazuhiko*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Kikuchi, Hikaru*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2020-018, 121 Pages, 2021/02
By the nuclear disaster of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake and the following tsunami on March 11, 2011, a large amount of radioactive material was released from the FDNPS. After the nuclear disaster, airborne radiation monitoring using manned helicopter has been conducted around FDNPS. The results in the fiscal 2019 were summarized in this report. Analysis taken topographical effects into consideration was applied to the result of airborne monitoring to improve the precision of conventional method. In addition, discrimination method of gamma rays from Rn-progenies was also utilized to evaluate their effect on aerial radiation monitoring.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2020-028, 68 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human Resource Development Related to Remote Control Technology for Monitoring Inside RPV Pedestal during Retrieval of Fuel Debris". This study deals with construction of a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2019, the main activities were conceptual design, prototyping, and conceptual planning.
Malins, A.; Ochi, Kotaro; Machida, Masahiko; Sanada, Yukihisa
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.147 - 154, 2020/10