Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kinase, Masami
Radioisotopes, 74(2), p.233 - 238, 2025/07
no abstracts in English
Birkholzer, J. T.*; Graupner, B. J.*; Harrington, J.*; Jayne, R.*; Kolditz, O.*; Kuhlman, K. L.*; LaForce, T.*; Leone, R. C.*; Mariner, P. E.*; McDermott, C.*; et al.
Geomechanics for Energy and the Environment, 42, p.100685_1 - 100685_17, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ozaki, Yusuke; Hayano, Akira; Ono, Hirokazu; Tachi, Yukio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
, 67(6), p.354 - 358, 2025/06
Japan Atomic Energy Agency launched the Horonobe International Project (HIP) utilizing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The main objectives of this project are to develop and demonstrate advanced technologies to be used in repository design, operation and closure and a realistic safety assessment in deep geological disposal, and to encourage and train the next generation of engineers and researchers. In this review, an overview of the HIP is presented.
Tomioka, Dai; Kochiyama, Mami; Ozone, Kenji; Nakata, Hisakazu; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2024-023, 38 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an implementing organization of near-surface disposal for low-level radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial and medical facilities in Japan. Information on the radioactivity concentration of these radioactive wastes is dispensable for the design and conformity assessment of the waste disposal facilities for the licensing application of the disposal project and its safety review. Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center has been improving the radioactivity evaluation procedure for the dismantling waste generated from the research reactors based on the activation calculation. In order to investigate the applicability of the ORIGEN code (included in SCALE6.2.4), which enables more accurate activation calculations using multigroup neutron spectra, we performed activation calculations with the ORIGEN-code and the ORIGEN-S code (included in SCALE6.0), which has been widely used in the past, for the dismantled wastes from the Rikkyo University Research Reactor, where radioactivity analysis data for the structural materials around the reactor core were compiled. As a result, the calculation time difference between ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S was small and the evaluated radioactivity concentrations of the former were in the range of 0.8-1.0 times those of the latter, which was in good agreement with those of radiochemical analysis in the range of 0.5-3.0 times. The applicability of ORIGEN was confirmed. In addition, activation calculations assuming trace elements in structural materials of nuclear reactor were performed with ORIGEN and ORIGEN-S and the results were compared. The causes of the large differences among 170 nuclides that are important for dose assessment in near-surface disposal were assessed each nuclide.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2024-058, 179 Pages, 2025/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2023 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Nuclear Science Research Institute
JAEA-Review 2024-057, 178 Pages, 2025/03
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2022 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)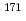 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2024-042, 111 Pages, 2024/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2023, we continued R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D on challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on nearfield system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". The validation of a method for assessing permeability using the Ductility Index and a method for estimating the state of in-situ ground pressure from hydraulic perturbation tests were investigated as part of the study "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". In FY2023, we resumed construction of the subsurface facilities, 3 new tunnels in the 350 m gallery and resumed excavation of the East Access Shaft and the Ventilation Shaft. By the end of FY2023, the 350 m gallery extension (tunnel extension 66 m) had been completed, and the depths of the East Access Shaft and Ventilation Shaft were GL-424 m and GL-393 m respectively.
C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". The validation of a method for assessing permeability using the Ductility Index and a method for estimating the state of in-situ ground pressure from hydraulic perturbation tests were investigated as part of the study "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". In FY2023, we resumed construction of the subsurface facilities, 3 new tunnels in the 350 m gallery and resumed excavation of the East Access Shaft and the Ventilation Shaft. By the end of FY2023, the 350 m gallery extension (tunnel extension 66 m) had been completed, and the depths of the East Access Shaft and Ventilation Shaft were GL-424 m and GL-393 m respectively.
 Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag, and
Ag, and  In
InNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(11), p.1415 - 1430, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)Neutron capture cross-sections of nuclides targeted for decommissioning are necessary to contribute to the evaluation of radioactivity produced. The present study,  Sc,
Sc,  Cu,
Cu,  Zn,
Zn,  Ag and
Ag and  In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18
In nuclides were selected as target ones, and their thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were measured by an activation method at Kyoto University Research Reactor. The thermal-neutron capture cross-sections were obtained as follows: 27.18 0.28 barn for
0.28 barn for  Sc(n,
Sc(n,  )
)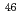 Sc, 4.34
Sc, 4.34 0.06 barn for
0.06 barn for  Cu(n,
Cu(n,  )
) Cu, 0.719
Cu, 0.719 0.011 barn for
0.011 barn for  Zn(n,
Zn(n,  )
) Zn, 4.05
Zn, 4.05 0.05 barn for
0.05 barn for  Ag(n,
Ag(n,  )
)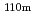 Ag and 8.53
Ag and 8.53 0.27 barn for
0.27 barn for  In(n,
In(n,  )
) 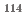 In
In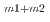 . The results for
. The results for  Sc and
Sc and  Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Zn nuclides supported evaluated values within the limits of uncertainties, while those for the other nuclides were slightly different from evaluated ones. The obtained results are useful not only for the evaluation of production amount, but also for the monitor selection other than Au and Co by considering those nuclides as flux monitors.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2024-001, 40 Pages, 2024/10
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the medium- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which evaluates and advises toward the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2023 (April 1st, 2023 - March 31st, 2024) and their evaluation by the committee.
Licensing Application Group, Fuels and Materials Department
JAEA-Testing 2024-002, 20 Pages, 2024/08
The contamination accident occurred at Plutonium Fuel Research Facility (PFRF) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) Oarai Research and Development Institute on June 6, 2017. During the work of opening the fuel storage container and checking the properties of the contents, the plastic bag that double-packed the inner container burst. The scattering of the fuels contaminated the work room and exposed the worker. The cause of the plastic bag burst was that the enclosed epoxy resin was decomposed by  -rays and the internal pressure increased due to the generated hydrogen gas. The 54 storage containers containing plutonium held at PFRF also at risk of increasing internal pressure. Therefore, an opening inspection was conducted to confirm the contents of the storage container in the hot cell. In addition, the contents of storage containers that may generate gas were stabilized. We are planning to transport the fuel storage containers out to another facility for the decommission of PFRF. The other 9 storage containers include oxide raw material powder: Pu +
-rays and the internal pressure increased due to the generated hydrogen gas. The 54 storage containers containing plutonium held at PFRF also at risk of increasing internal pressure. Therefore, an opening inspection was conducted to confirm the contents of the storage container in the hot cell. In addition, the contents of storage containers that may generate gas were stabilized. We are planning to transport the fuel storage containers out to another facility for the decommission of PFRF. The other 9 storage containers include oxide raw material powder: Pu +  U in excess of 220 g. In order to decrease to less than 220 g (the limit of transport cask), the metal inner containers in the storage container were taken out and repacked in another storage container. This report describes advance measures such as permit application and the details of about storage container opening inspection and metal inner container repacking.
U in excess of 220 g. In order to decrease to less than 220 g (the limit of transport cask), the metal inner containers in the storage container were taken out and repacked in another storage container. This report describes advance measures such as permit application and the details of about storage container opening inspection and metal inner container repacking.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2023-032, 159 Pages, 2024/02
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to enhance the reliability of relevant technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through investigating the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rocks at Horonobe Town in Hokkaido, north Japan. In the fiscal year 2022, we continued R&D on "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". These are identified as key R&D on challenges to be tackled in the Horonobe underground research plan for the fiscal year 2020 onwards. Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near- field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
C" were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The Horonobe International Project (HIP) was initiated in February 2023 to promote research and development in collaboration with national and international organizations.
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysisNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)The thermal-neutron capture cross section (
 ) and resonance integral (I
) and resonance integral (I ) for
) for  Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of
Nb among nuclides for decommissioning were measured by an activation method and the half-life of  Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25-
Nb by mass analysis. Niobium-93 samples were irradiated with a hydraulic conveyer installed in the research reactor in Institute for Integral Radiation and Nuclear Science, Kyoto University. Gold-aluminum, cobalt-aluminum alloy wires were used to monitor thermal-neutron fluxes and epi-thermal Westcott's indexes at an irradiation position. A 25- m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of
m-thick gadolinium foil was used to sort out reactions ascribe to thermal-and epi-thermal neutrons. Its thickness provided a cut-off energy of 0.133 eV. In order to attenuate radioactivity of 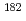 Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by
Ta due to impurities, the Nb samples were cooled for nearly 2 years. The induced radio activity in the monitors and Nb samples were measured by  -ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the
-ray spectroscopy. In analysis based on Westcott's convention, the 
 and I
and I values were derived as 1.11
values were derived as 1.11 0.04 barn and 10.5
0.04 barn and 10.5 0.6 barn, respectively. After the
0.6 barn, respectively. After the  -ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both
-ray measurements, mass analysis was applied to the Nb sample to obtain the reaction rate. By combining data obtained by both  -ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of
-ray spectroscopy and mass analysis, the half-life of  Nb was derived as (2.00
Nb was derived as (2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 years.
years.
Center for Computational Science & e-Systems
JAEA-Evaluation 2023-001, 38 Pages, 2023/07
Research on advanced computational science for nuclear applications, based on "the plan to achieve the medium- and long-term goal of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency", has been performed by Center for Computational Science & e-Systems (CCSE), Japan Atomic Energy Agency. CCSE established a committee consisting of external experts and authorities which evaluates and advises toward the future research and development. This report summarizes the results of the R&D performed by CCSE in FY2022 (April 1st, 2022 - March 31st, 2023) and their evaluation by the committee.
Nuclear Science Research Institute, Sector of Nuclear Science Research
JAEA-Review 2023-009, 165 Pages, 2023/06
Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) is composed of Planning and Management Department and six departments, namely Department of Operational Safety Administration, Department of Radiation Protection, Engineering Services Department, Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator, Department of Criticality and Hot Examination Technology and Department of Decommissioning and Waste Management, and each department manages facilities and develops related technologies to achieve the "Medium- to Long-term Plan" successfully and effectively. And, four research centers which are Advanced Science Research Center, Nuclear Science and Engineering Center, Nuclear Engineering Research Collaboration Center and Materials Sciences Research Center, belong to NSRI. In order to contribute the future research and development and to promote management business, this annual report summarizes information on the activities of NSRI of JFY 2020 as well as the activity on research and development carried out by Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science, Nuclear Safety Research Center and activities of Nuclear Human Resource Development Center, using facilities of NSRI.
Sakai, Akihiro
Dai-33-Kai Genshiryoku Shisetsu Dekomisshoningu Gijutsu Koza Tekisuto, p.31 - 63, 2023/02
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is promoting the project for concrete-vault disposal and landfill-type disposal of radioactive waste generated from research facilities, etc. This report introduces current status of technical development for JAEA's disposal project as following items; (1) kinds of research facilities and characteristics of radioactivity inventory of the waste, (2) the structures of the disposal facilities which JAEA conceptually designed, (3) development of waste acceptance criteria for major radioactive waste for the JAEA disposal facilities, (4) the concept of the criteria for disposal of uranium bearing waste, that has been established in 2021.
Wu, P.*; Murai, Naoki; Li, T.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Xia, K.*; Peng, K.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 25(1), p.013032_1 - 013032_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Review 2022-025, 164 Pages, 2022/11
The Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) Project is being pursued by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The main aim of this project is to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste through a comprehensive research and development (R&D) program in the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary rock at Horonobe in Hokkaido, north Japan. In fiscal year 2021, we continued R&D on three important issues specified in the "Horonobe Underground Research Plan from Fiscal Year 2020", which involve "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment", "Demonstration of repository design options", and "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations". Specifically, "full-scale engineered barrier system (EBS) performance experiment" and "solute transport experiment with model testing" were carried out as part of "Study on near-field system performance in geological environment". "Demonstration of engineering feasibility of repository technology" and "evaluation of EBS behaviour over 100 C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
C' were addressed for "Demonstration of repository design options". A study on "Understanding of buffering behaviour of sedimentary rock to natural perturbations" was also implemented in two areas, "evaluation of intrinsic buffering against endogenic and exogenic processes" and "development of techniques for evaluating excavation damaged zone (EDZ) self-sealing behaviour after backfilling". The results of the R&D, along with those obtained in other departments of JAEA, will reinforce the technical basis for both repository implementation and safety regulation. For the sake of this, we will steadily proceed with this project in collaboration with relevant organizations and universities both domestically and internationally and also widely publish the plans and results of the R&D to ensure their transparency and technical reliability.
Planning and Co-ordination Office, Sector of Nuclear Safety Research and Emergency Preparedness
JAEA-Evaluation 2022-008, 68 Pages, 2022/11
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) consulted an assessment committee, "Evaluation Committee of Research and Development (R&D) Activities for Nuclear Safety Research", for post-review and pre-review assessments of Nuclear Safety Research, in accordance with "General Guideline for Evaluation of Government R&D Activities" by Cabinet Office, Government of Japan, "Guideline for Evaluation of R&D in Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology" and "Regulation on Conduct for Evaluation of R&D Activities" by JAEA. In response to the JAEA's consult, the Committee assessed the results and outcomes of the R&D programs during the 3rd mid-/long-term plan (from April 2015 to March 2022, including the expected results and outcomes) and the validity of the 4th mid-/long-term plan (7 years from FY2022), according to the above-mentioned guidelines. The Committee concluded that the rationale behind the R&D programs, the relevance of the program outcome and the efficiency of the program implementation during the 3rd mid-/long-term plan are comprehensively evaluated as "A", and the R&D programs for the 4th mid-/long-term plan is generally appropriate. This report summarizes the results of the assessment by the Committee. In addition, the appendices of the report contain the responses from JAEA on the comments and suggestions by the Committee and the presentation materials submitted to the Committee.