Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kinase, Masami
Radioisotopes, 74(2), p.233 - 238, 2025/07
no abstracts in English
 Cf fission fragments with MRTOF-MS and detailed study of masses of neutron-rich Ce isotopes
Cf fission fragments with MRTOF-MS and detailed study of masses of neutron-rich Ce isotopesKimura, Sota*; Ito, Yuta; 8 of others*
Physical Review C, 110(4), p.045810_1 - 045810_9, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 31(10), p.102504_1 - 102504_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hydrogen isotope mixing phenomena in tokamak plasmas are analyzed using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. Model plasma parameters are chosen based on the hydrogen isotope pellet experiments on JET, in which hydrogen isotope mixing in the time scale of the energy confinement time occurred after injecting deuterium (D) pellets into hydrogen (H) plasmas. Two numerical experiments are conducted using plasma profiles before and after the D pellet injection. In both cases, turbulent fluctuations in the plasma core are characterized by ion temperature gradient driven turbulence, while in the latter case, trapped electron mode turbulence also exists in the outer region. In the former case, the density profile of bulk H ions is kept in a quasi-steady state, and the particle confinement time of bulk H ions is an order of magnitude longer than the energy confinement time. In the latter case, the density profiles of bulk H ions and pellet D ions show transient relaxation in the time scale of the energy confinement time, indicating the fast hydrogen isotope mixing. In the toroidal angular momentum balance, it is found that the hydrogen isotope mixing is driven by the toroidal field stress.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wells, S. R.*; Yamamoto, Yuta*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In this study, triple and double resonance ionization schemes of atomic Ca were developed, aiming for the separation of odd isotopes by (i) laser polarization-dependent selection rules, and (ii) large isotope shifts of odd Ca isotopes in the Rydberg levels. Separation of odd isotopes was confirmed under the orthogonal condition. Suppression of non-resonant ionization of  Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of
Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of  Ca.
Ca.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Kogakuin University*
JAEA-Review 2024-015, 99 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishment of characterization method for small fuel debris using the world's first isotope micro imaging apparatus" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to obtain, for the first time in the world, the important data necessary for clarifying the retrieval of small amounts of fuel debris, and to evaluate and examine them. SEM-EDS and TEM-EDS cannot be used for isotopic identification and analysis of Pu and B. On the other hand, bulk analysis such as ICP-MS lacks the information in a micro region.
Battulga, B.; Munkhbat, D.*; Matsueda, Makoto; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Oyuntsetseg, B.*; Koarashi, Jun; Kawahigashi, Masayuki*
Environmental Pollution, 357, p.124427_1 - 124427_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Environmental Sciences)The occurrence and characteristics of plastic debris in aquatic and terrestrial environments have been extensively studied. However, there is still limited information on the properties and dynamic behavior of plastic-associated biofilms in the environment. In this study, we collected plastic samples from an inland river system in Mongolia and extracted biofilms from the plastics to uncover the characteristics of the biofilms using analytical, isotopic, and thermogravimetric techniques. Mixtures of organic and mineral particles were detected from extracted biofilms, revealing the plastic as a carrier for exogenous substances including contaminants in the river ecosystem. The present study provides insights into the characteristics and environmental behavior of biofilms which are useful to elucidate the impact of plastic-associated biofilms on organic matter and material cycling in the aquatic ecosystems.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Kogakuin University*
JAEA-Review 2024-005, 79 Pages, 2024/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Establishment of characterization method for small fuel debris using the world's first isotope micro imaging apparatus" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to obtain, for the first time in the world, the important data necessary for clarifying the retrieval of small amounts of fuel debris, and to evaluate and examine them. SEM-EDS and TEM-EDS cannot be used for isotopic identification and analysis of Pu and B. On the other hand, bulk analysis such as ICP-MS lacks the information in a micro region.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; i-Lab*
JAEA-Review 2023-029, 77 Pages, 2024/05
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge to advancement of debris composition and direct isotope measurement by microwave-enhanced LIBS" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to increase the emission intensity of LIBS (laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy) by superimposing MW (microwave) and apply it to uranium isotope measurement. In FY2022, we improved the cooling method and reduce unnecessary functions in of the semiconductor microwave oscillator, and apply the optimized conditions obtained from simulations to the LIBS experiment for the microwave antenna gave better results.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Journal of the Optical Society of America B, 41(1), p.119 - 126, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:42.60(Optics)Calcium Rydberg levels are of significant interest for efficient and isotope-selective resonance ionization of trace radionuclides such as calcium-41 ( Ca). In this study, we report novel measurement data on the energy level shifts of calcium-43 (
Ca). In this study, we report novel measurement data on the energy level shifts of calcium-43 (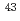 Ca) for 4sns
Ca) for 4sns  S
S and 4s(n-1)d
and 4s(n-1)d  D
D (n=40, 45, 50, 55, 60) Rydberg levels due to hyperfine-induced singlet-triplet mixing specific to isotopes with an odd mass number.
(n=40, 45, 50, 55, 60) Rydberg levels due to hyperfine-induced singlet-triplet mixing specific to isotopes with an odd mass number.
Battulga, B.; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Matsueda, Makoto; Koarashi, Jun
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(31), p.77226 - 77237, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.25(Environmental Sciences)The global survey for the presence of microplastics (MPs) in aquatic environments has attracted widespread scientific attention over the past decade. This study demonstrates a multidimensional analytical approach, including isotopic and thermogravimetric analyses to evaluate characteristics and behavior of MPs in the environment. The MP samples were collected in two contrasting coastal areas of Japan. The 
 C values of field-collected polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS) MPs were ranged from -25.6 to -31.4, -23.4 to -30.9, and -27.3 to -28.6 per mil, respectively. The differences in
C values of field-collected polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polystyrene (PS) MPs were ranged from -25.6 to -31.4, -23.4 to -30.9, and -27.3 to -28.6 per mil, respectively. The differences in 
 C signature between MPs with the same polymer types (i.e., PE and PP) but different colors. Through thermal analysis, the single-step endothermic process was observed for environmental PE and PS-MPs. The results reveal that degradation may play a significant role in the behavior and characteristics of MP debris in the aquatic environment.
C signature between MPs with the same polymer types (i.e., PE and PP) but different colors. Through thermal analysis, the single-step endothermic process was observed for environmental PE and PS-MPs. The results reveal that degradation may play a significant role in the behavior and characteristics of MP debris in the aquatic environment.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; i-Lab*
JAEA-Review 2022-042, 67 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge to advancement of debris composition and direct isotope measurement by microwave-enhanced LIBS" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to increase the emission intensity of LIBS (laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy) by superimposing MW (microwave) and apply it to uranium isotope measurement. In FY2021, after confirming that there was no problem in terms of specifications including noise leakage by downsizing the semiconductor MW oscillator and evaluating it as a single unit, the possibility of uranium isotope measurement was examined by applying it to the LIBS experiment. In addition, the optimized design of the MW antenna was carried out. By applying them, we confirmed the actual performance, …
Battulga, B.; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Nakanishi, Takahiro; Koarashi, Jun
Science of the Total Environment, 849, p.157758_1 - 157758_11, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.72(Environmental Sciences)Characterizing plastic-associated biofilms is key to the better understanding of organic material and mineral cycling in the "Plastisphere"-the thin layer of microbial life on plastics. In this study, we propose a new method to extract biofilms from environmental plastics, in order to evaluate the properties of biofilm-derived organic matter through stable carbon (
 C) and nitrogen (
C) and nitrogen (
 N) isotope signatures and their interactions with radionuclides especially radiocesium (
N) isotope signatures and their interactions with radionuclides especially radiocesium ( Cs). After ultrasound-assisted separation from the plastics, biofilm samples were successfully collected via a sequence of syringe treatments. Biofilm-derived organic matter samples (14.5-65.4 mg) from four river mouths in Japan showed
Cs). After ultrasound-assisted separation from the plastics, biofilm samples were successfully collected via a sequence of syringe treatments. Biofilm-derived organic matter samples (14.5-65.4 mg) from four river mouths in Japan showed  Cs activity concentrations of
Cs activity concentrations of  75 to 820 Bq kg
75 to 820 Bq kg biofilm (dw), providing evidence that environmental plastics, mediated by developed biofilms, serve as a carrier for
biofilm (dw), providing evidence that environmental plastics, mediated by developed biofilms, serve as a carrier for  Cs in the coastal environment. Significant differences in the (
Cs in the coastal environment. Significant differences in the (
 C and
C and 
 N signatures were also obtained for the biofilms, indicating the different sources, pathways, and development processes of biofilms on plastics.
N signatures were also obtained for the biofilms, indicating the different sources, pathways, and development processes of biofilms on plastics.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-014, 106 Pages, 2022/08
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of technology for rapid analysis of strontium-90 with low isotopic abundance using laser resonance ionization" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop a rapid analysis technique for strontium-90 using diode laser-based resonance ionization with elemental and isotopic selectivity. Strontium-90 is one of the major difficult-to-measure nuclides released into the environment due to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.
 Yb for producing
Yb for producing  Lu with high radionuclide purity by
Lu with high radionuclide purity by  Yb(
Yb(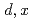 )
) Lu
LuNagai, Yasuki*; Kawabata, Masako*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Motoishi, Shoji*; Saeki, Hideya*; Motomura, Arata*; Minato, Futoshi; Ito, Masatoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(4), p.044201_1 - 044201_10, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:46.56(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recently,  Lu is considered as one of the most important medical RIs for treating neuroendocrine tumors. A plan to produce
Lu is considered as one of the most important medical RIs for treating neuroendocrine tumors. A plan to produce  Lu with high purity by using enriched
Lu with high purity by using enriched  Yb samples with irradiation of deuteron beams in accelerators has been discussed. However, since the other Yb isotopes contained in the Yb sample interacts with deuterons, Lu isotopes other than
Yb samples with irradiation of deuteron beams in accelerators has been discussed. However, since the other Yb isotopes contained in the Yb sample interacts with deuterons, Lu isotopes other than  Lu are produced as impurities. Since the purity of
Lu are produced as impurities. Since the purity of  Lu is important for medical use, a method to evaluate the impurity of Lu has been required. In this study, we proposed a new method to estimate production yields of each Lu isotopes in Yb samples with arbitrary isotopic compositions by using excitation functions of Yb(
Lu is important for medical use, a method to evaluate the impurity of Lu has been required. In this study, we proposed a new method to estimate production yields of each Lu isotopes in Yb samples with arbitrary isotopic compositions by using excitation functions of Yb(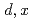 )Lu reactions and the particle transport calculation code PHITS. The method plays an important role in discussing the isotopic composition of enriched samples to produce high-purity
)Lu reactions and the particle transport calculation code PHITS. The method plays an important role in discussing the isotopic composition of enriched samples to produce high-purity  Lu using accelerators.
Lu using accelerators.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; i-Lab*
JAEA-Review 2021-027, 62 Pages, 2021/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge to advancement of debris composition and direct isotope measurement by microwave-enhanced LIBS" conducted in FY2020. Although LIBS (laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy) is commercially available for application to remote composition measurement, it is not suitable for high radiation environment due to loss in optical fibers derived from the influence of radiation, reduction in laser transmission output, and nuclear fuel debris properties. There are general concerns of the signal strength decrease. In addition, since LIBS is generally considered to be unsuitable for isotope measurement, there are problems to be improved.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (Internet), 45A, 4 Pages, 2021/06
This work presents the impacts of the hydrogen isotope mass and the normalized plasma size on confinement of hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven turbulence. Numerical experiments of H and D plasmas with ion and electron heating conditions were conducted using the Gyrokinetic Toroidal 5D full- f Eulerian code GT5D. The energy confinement time in the ion heated numerical experiments was almost independent of isotope mass, and the energy confinement was determined mainly by the normalized plasma size or the plasma size divided by the ion gyro radius, indicating an impact of non-local transport. On the other hand, the electron heated numerical experiments showed a clear isotope mass dependency. In addition to the plasma size effect, the isotope mass dependency of the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions changes the ion heat flux and the turbulence intensity, leading to the degradation of confinement in H plasmas. These results qualitatively agree with the hydrogen isotope scaling in experiments.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2020-074, 105 Pages, 2021/03
The Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3), JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4), NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), Tandem Accelerator, RI Production Facility and TPL (Tritium Process Laboratory). This annual report describes the activities of our department in fiscal year of 2018. We carried out the operation and maintenance, utilization, upgrading of utilization techniques, safety administration and international cooperation. Also contained are lists of publications, meetings, granted permissions on laws and regulations concerning atomic energy, outcomes in service and technical developments and so on.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2020-073, 113 Pages, 2021/03
The Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3), JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4), NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), Tandem Accelerator, RI Production Facility and Tritium Process Laboratory. This annual report describes the activities of our department in fiscal year of 2017. We carried out the operation and maintenance, utilization, upgrading of utilization techniques, safety administration and international cooperation. Also contained are lists of publications, meetings, granted permissions on laws and regulations concerning atomic energy, outcomes in service and technical developments and so on.
Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator
JAEA-Review 2020-072, 102 Pages, 2021/03
The Department of Research Reactor and Tandem Accelerator is in charge of the operation, utilization and technical development of JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3), JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4), NSRR (Nuclear Safety Research Reactor), Tandem Accelerator, RI Production Facility and Tritium Process Laboratory). This annual report describes the activities of our department in fiscal year of 2016. We carried out the operation and maintenance, utilization, upgrading of utilization techniques, safety administration and international cooperation. Also contained are lists of publications, meetings, granted permissions on laws and regulations concerning atomic energy, outcomes in service and technical developments and so on.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2020-024, 75 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Technology for Rapid Analysis of Strontium-90 with Low Isotopic Abundance using Laser Resonance Ionization" conducted in FY2019. In this study, we will develop a rapid analysis technique for strontium-90 using diode laser-based resonance ionization with elemental and isotopic selectivity. Strontium-90 is one of the major difficult-to-measure nuclides released into the environment due to the accident at TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Our method is particularly intended for real samples which contain high concentrations of strontium stable isotopes such as marine samples.