Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
福田 航大; 小原 徹*; 須山 賢也
Nuclear Technology, 211(5), p.963 - 973, 2025/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)An application of the boiling water reactor (BWR) to an offshore floating nuclear power plant (OFNP) is discussed in Japan. The BWR-type OFNP has some challenges for practical use, although it has high economic efficiency because of downsizing and simplification. One challenge is understanding reactor kinetics under conditions specific to the marine environment. This study quantitatively clarifies the total and spatial changes in power when the BWR is inclined during regular operation. Therefore, the TRAC/RELAP Advanced Computational Engine (TRACE) and Purdue Advanced Reactor Core Simulator (PARCS) codes were used to perform a three-dimensional neutronics-thermal-hydraulics-coupled transient analysis. The calculation model is based on Peach Bottom II. This study clarifies the changing trend in total and local BWR power by inclination with simplified modeling and conditions. Reasons for such changes are discussed based on changes in several thermal-hydraulic parameters. The difference in BWR power against the inclinations is small. Thus, it was implied that the BWR-type OFNP is expected to have a stable power supply capability during natural disasters. Finally, requires further studies to support the obtained conclusions are discussed.
福田 航大; 小原 徹*
Nuclear Technology, 12 Pages, 2025/00
Offshore floating nuclear power plants (OFNPs) are gaining attention as safe and location-flexible means for nuclear energy utilization. Although platform motion in the marine environment may affect reactor kinetics, particularly in boiling water reactors (BWRs), BWR-type OFNPs are expected to have high economic efficiency. This study investigated the reactor power behavior of a BWR-type OFNP using three-dimensional transient neutronics-thermal hydraulics coupled analysis. Heave and pitch motions were considered under realistic wave conditions using a typical BWR model. The results show that the reactor power and its distribution can vary because of the wave-induced platform motion; however, the amplitude of these variations is sufficiently small to ensure normal operation, even under the extreme wave conditions of a one-in-10,000-year storm. Although the results of the present study demonstrate the ability of BWR-type OFNPs to provide a safe and stable energy supply, they also suggest the need for further research. Further studies are needed to address the complex wave conditions and assess the effects of the platform motion on ancillary systems, such as recirculation systems.
土井 大輔
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 91, p.1245 - 1252, 2024/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:31.33(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrogen is a major nonmetallic impurity in the coolant of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs) during normal operation. A higher hydrogen concentration than the gas-liquid equilibrium has been transiently detected in the gas space of actual SFR plants. The presence of several sodium compounds can increase hydrogen generation; however, a thorough understanding of the thermal behavior of candidate reactions is lacking. Herein, thermal analysis reveals the hydrogen release behavior of sodium hydride. Mass spectrometry indicates hydrogen generation with decreasing sample mass, indicating thermal decomposition. Detailed kinetic analysis based on master plot methods indicates that the hydrogen release reaction occurred through a mechanism involving random nucleation and growth of nuclei. Furthermore, the reaction rate was newly formulated based on a kinetic model function representing the above mechanism and the Arrhenius-type reaction rate constant comprising an activation energy of 119.0  0.8 kJ mol
0.8 kJ mol and a frequency factor of 1.8
and a frequency factor of 1.8  10
10 s
s . These findings will enable the numerical simulation of the hydrogen release behavior in SFRs.
. These findings will enable the numerical simulation of the hydrogen release behavior in SFRs.
 Nb by activation method and half-life of
Nb by activation method and half-life of  Nb by mass analysis
Nb by mass analysis中村 詔司; 芝原 雄司*; 遠藤 駿典; 木村 敦
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1361 - 1371, 2023/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:62.75(Nuclear Science & Technology)廃止措置の対象核種の中から Nbについて、熱中性子捕獲断面積(
Nbについて、熱中性子捕獲断面積(
 )および共鳴積分(I
)および共鳴積分(I )を放射化法により測定した。また、
)を放射化法により測定した。また、 Nbの半減期を質量分析により測定した。ニオブ93試料は、京都大学複合原子力科学研究所の研究炉に整備されている水圧輸送艦を用いて照射した。金-アルミ合金線、およびコバルト-アルミ合金線を用いて、照射位置における中性子束成分を測定した。厚さ25
Nbの半減期を質量分析により測定した。ニオブ93試料は、京都大学複合原子力科学研究所の研究炉に整備されている水圧輸送艦を用いて照射した。金-アルミ合金線、およびコバルト-アルミ合金線を用いて、照射位置における中性子束成分を測定した。厚さ25 mのガドリニウム箔を用いた照射も行って、熱および熱外中性子による反応率の寄与をより分けた。ガドリニウムの厚さから、カットオフ・エネルギーは0.133eVに設定した。ニオブ試料中に含まれている不純物により生成される
mのガドリニウム箔を用いた照射も行って、熱および熱外中性子による反応率の寄与をより分けた。ガドリニウムの厚さから、カットオフ・エネルギーは0.133eVに設定した。ニオブ試料中に含まれている不純物により生成される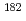 Taの放射能を減衰させるために、約2年間ニオブ試料を冷却した。
Taの放射能を減衰させるために、約2年間ニオブ試料を冷却した。 線スペクトロスコピーにより照射されたニオブ試料およびモニタの生成放射能を測定した。Westcottコンベンションに基づいて解析を行い、
線スペクトロスコピーにより照射されたニオブ試料およびモニタの生成放射能を測定した。Westcottコンベンションに基づいて解析を行い、
 およびI
およびI を、それぞれ1.11
を、それぞれ1.11 0.04barnおよび10.5
0.04barnおよび10.5 0.6barnと導出することができた。
0.6barnと導出することができた。 線測定の後に、ニオブ試料の質量分析を行い、反応率を導出した。
線測定の後に、ニオブ試料の質量分析を行い、反応率を導出した。 線スペクトロスコピーと質量分析で得られたデータを組み合わせることにより、
線スペクトロスコピーと質量分析で得られたデータを組み合わせることにより、 Nbの半減期を、(2.00
Nbの半減期を、(2.00 0.15)
0.15) 10
10 年と導出することができた。
年と導出することができた。
山崎 泰広*; 篠宮 啓介*; 奥村 忠晴*; 鈴木 賢治*; 菖蒲 敬久; 中村 唯我*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
The suspension plasma spray (SPS) technique has attracted attention because of its various microstructures, which can be achieved by mixing submicron spray particles with a solvent to form a suspension. Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) with a columnar structure, which might achieve high strain tolerance, can be obtained using the SPS technique. In this study, the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC with different columnar structures was evaluated by hybrid measurement using high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis and laboratory low-energy X-rays. The effect of microstructure on the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC was discussed on the basis of the experimental results. In addition, the in-plane internal stress was decreased by decreasing the column diameter. The thin columnar microstructure of the SPS-TBC has superior strain tolerance. The internal stresses in the column of the SPS-TBC are periodic decrements caused by stress relaxation in porous layers.
土井 大輔
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2022/08
In sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs), hydrogen is a major nonmetallic impurity in the coolant during normal operation. A higher hydrogen concentration than the gas-liquid equilibrium had been transiently detected in the gas space of the actual SFR plant. However, the chemical reactions that caused hydrogen generation, which involve several sodium compounds, have not been identified. Furthermore, the thermal behavior of these hydrogen release reactions has not been thoroughly investigated. In this study, the hydrogen release behavior of sodium hydride, which could be involved in all of these reactions, was clarified by two experimental methods dealing with different sample quantities. In the thermal analysis with a semi-micro sample of about 1mmol, the hydrogen generation was demonstrated by mass spectrometry as the sample mass decreased, suggesting thermal decomposition. A monomodal hydrogen release curve similar to the thermal analysis result was obtained in the heating experiment with a macro amount sample of about 1mol. These experimental results showed consistent activation energies within the standard error. Therefore, it was elucidated that the ideal reaction behavior obtained by thermal analysis could be sufficiently extrapolated to the reaction behavior occurring in a larger amount of sample. These findings provide fundamental insights into the thermal decomposition of sodium hydride and are indispensable for analyzing hydrogen release behavior in other hydrogen release reactions involving sodium hydride.
加藤 匠馬*; 永岡 美佳; Guo, H.*; 藤田 博喜; 相田 卓*; Smith, R. L. Jr.*
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(39), p.55725 - 55735, 2021/10
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Environmental Sciences)本研究では、土壌中のSrを無添加でスクリーニングする方法の開発を目的として、模擬土壌(粘土鉱物のバーミキュライト,モンモリロナイト,カオリナイト)及び実際の土壌(照沼)に熱水浸出を行い、有機酸を生成した。安定ストロンチウム(SrCl )を土壌に吸着させ、10種類の有機酸を用いて、水熱条件下(120
)を土壌に吸着させ、10種類の有機酸を用いて、水熱条件下(120 200
200 C)での模擬土壌からのSrの溶出量を0.3Mまで評価した。ストロンチウムを吸着したバーミキュライト(Sr-V)については、0.1Mのクエン酸が150
C)での模擬土壌からのSrの溶出量を0.3Mまで評価した。ストロンチウムを吸着したバーミキュライト(Sr-V)については、0.1Mのクエン酸が150 C、1時間の処理でSrの溶出に有効であることがわかった。これらの結果をもとに、照沼土壌の有機物からの有機酸の生成について検討した。照沼土壌の水熱処理では、200
C、1時間の処理でSrの溶出に有効であることがわかった。これらの結果をもとに、照沼土壌の有機物からの有機酸の生成について検討した。照沼土壌の水熱処理では、200 C、0.5hの反応時間で最大量の有機酸が生成された。照沼土壌からのSrの溶出の可能性を確認するために、ストロンチウムを吸着した照沼土壌(Sr-S)を調べた。Sr-Sでは、200
C、0.5hの反応時間で最大量の有機酸が生成された。照沼土壌からのSrの溶出の可能性を確認するために、ストロンチウムを吸着した照沼土壌(Sr-S)を調べた。Sr-Sでは、200 Cで0.5hの反応時間で水熱処理を行うと、室温でSrの40%が溶出し、土壌中のSrのスクリーニングに無添加の方法が使えることがわかった。無添加の水熱浸出法は、化学分析の第一段階で固体を焼成する必要がないため、土壌中の金属の日常的なモニタリングや緊急時の対応にも応用できる。
Cで0.5hの反応時間で水熱処理を行うと、室温でSrの40%が溶出し、土壌中のSrのスクリーニングに無添加の方法が使えることがわかった。無添加の水熱浸出法は、化学分析の第一段階で固体を焼成する必要がないため、土壌中の金属の日常的なモニタリングや緊急時の対応にも応用できる。
Lu, K.; 勝山 仁哉; Li, Y.
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 142(5), p.051501_1 - 051501_10, 2020/10
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:17.10(Engineering, Mechanical)Structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) is essential for the safe operation of nuclear power plants. For RPVs in pressurized water reactors (PWRs), the assessment should be performed by considering neutron irradiation embrittlement and pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events. To assess the structural integrity of an RPV, a traditional method is usually employed by comparing fracture toughness of the RPV material with the stress intensity factor ( ) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,
) of a crack postulated near the RPV inner surface. When an underclad crack (i.e., a crack beneath the cladding of an RPV) is postulated,  of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on
of this crack can be increased owing to the plasticity effect of cladding. This is because the yield stress of cladding is lower than that of base metal and the cladding may yield earlier than base metal. In this paper, detailed three-dimensional (3D) finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed in consideration of the plasticity effect of cladding for underclad cracks postulated in Japanese RPVs. Based on the 3D FEA results, a plasticity correction method was proposed on  calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for
calculations of underclad cracks. In addition, the effects of RPV geometries and loading conditions were investigated using the proposed plasticity correction method. Moreover, the applicability of the proposed method to the case which considers the hardening effect of materials after neutron irradiation was also investigated. All of these results indicate that the proposed plasticity correction method can be used for  calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
calculations of underclad cracks and is applicable to structural integrity assessment of Japanese RPVs containing underclad cracks.
中山 雅
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-009, 98 Pages, 2020/09
幌延深地層研究センターの地下施設において、原子力機構が開発した低アルカリ性セメント(Highly Fly-ash contained Silicafume Cement: HFSC)を用いた吹付けコンクリート(深度140m, 250m, 350m調査坑道)および覆工コンクリート(東立坑深度374m 380m)の原位置施工試験を実施した。HFSCの周辺岩盤および地下水への影響を評価するため、原位置施工試験の実施箇所から定期的にコンクリートおよび岩石のコアを採取し、各種分析を実施した。また、140m調査坑道においては、普通ポルトランドセメント(OPC)の施工区間を設け、HFSCと同様の分析を行い、OPCとHFSCの影響の違いについて比較した。本データ集は、平成21年から平成30年にかけて、各深度からのコア試料に対して実施した分析結果について取りまとめたものである。
380m)の原位置施工試験を実施した。HFSCの周辺岩盤および地下水への影響を評価するため、原位置施工試験の実施箇所から定期的にコンクリートおよび岩石のコアを採取し、各種分析を実施した。また、140m調査坑道においては、普通ポルトランドセメント(OPC)の施工区間を設け、HFSCと同様の分析を行い、OPCとHFSCの影響の違いについて比較した。本データ集は、平成21年から平成30年にかけて、各深度からのコア試料に対して実施した分析結果について取りまとめたものである。
Rizaal, M.; 中島 邦久; 斉藤 拓巳*; 逢坂 正彦; 岡本 孝司*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(9), p.1062 - 1073, 2020/09
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:65.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)福島第一原子力発電所2号機においてペデスタル内よりもペデスタル外で線量が高くなっている現象が見つかっている。この線量の上昇については、原子炉格納容器内の配管に使用されている保温材(ケイ酸カルシウム)がガス状あるいは粒子状となって沈着したセシウム(Cs)と化学反応を起こして固着するとともに破損してペデスタル外に堆積することで線量が上昇した可能性があると考えている。そこで、本研究では、化学反応の有無を調べるため、反応温度等を調べることのできる熱重量示差熱分析装置(TG-DTA)を用いて、水素-水蒸気含有雰囲気下、最高1100 Cまで温度を上昇させて、主なセシウム化合物の一つである水酸化セシウムと保温材との混合物に対して分析を行った。その結果、575-730
Cまで温度を上昇させて、主なセシウム化合物の一つである水酸化セシウムと保温材との混合物に対して分析を行った。その結果、575-730 Cの範囲で反応が起こり、試験後試料のX線回折パターンや元素分析機能付き走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM/EDS)による試料表面の元素分布の結果から、保温材の構成物質であるケイ素(Si)に加え、不純物として含まれるアルミニウム(Al)と安定な化合物(CsAlSiO
Cの範囲で反応が起こり、試験後試料のX線回折パターンや元素分析機能付き走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM/EDS)による試料表面の元素分布の結果から、保温材の構成物質であるケイ素(Si)に加え、不純物として含まれるアルミニウム(Al)と安定な化合物(CsAlSiO )を形成することが分かった。したがって、ペデスタル外で見つかった高線量の原因として、保温材が関係する可能性があることが分かった。
)を形成することが分かった。したがって、ペデスタル外で見つかった高線量の原因として、保温材が関係する可能性があることが分かった。
Herranz, L. E.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Nitheanandan, T.*; Sandberg, N.*; Barr , F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; 中村 秀夫
, F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; 中村 秀夫
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 127, p.103432_1 - 103432_14, 2020/09
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:21.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)WGAMA started on Dec. 31st 1999 to assess and strengthen the technical basis needed for the prevention, mitigation and management of potential accidents in NPP and to facilitate international convergence on safety issues and AM analyses and strategies. WGAMA addresses reactor thermal-hydraulics (Thys), in-vessel behavior of degraded cores, containment behavior and protection, and FP release, transport, deposition and retention, for both current and advanced reactors. This paper summarizes such WGAMA contributions in Thys, CFD and severe accidents, which include the Fukushima-Daiichi accident impacts on the WGAMA activities and their substantial outcomes. Around 50 technical reports have become reference in the related fields, which appear in References. Recommendations in these reports include further research, some of which have given rise to the joint projects conducted or underway within the OECD framework. Ongoing WGAMA activities are numerous and a number of them are to be launched in the near future, which are shortly mentioned too.
Wan, T.; 大林 寛生; 佐々 敏信
Nuclear Technology, 205(1-2), p.188 - 199, 2019/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To perform basic research and development to realize future accelerator-driven systems, a lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) alloy spallation target will be installed within the framework of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project, Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The target will be bombarded by high-power pulsed proton beams (250 kW, 400 MeV, 25 Hz, and 0.5 ms in pulse duration). The Beam Window (BW) of the spallation target is critical because it should survive under severe conditions that occur, i.e., high temperature, high irradiation, intense stress, and various kinds of damage. Therefore, the target vessel should be carefully designed to obtain an adequate safety margin. Our previous research indicates that there is a stagnant flow region in the LBE at the BW tip due to the symmetric configuration of the target, which causes high temperature and concentration of stress on the BW. On the basis of our previous work, three types of upgraded target head designs are studied in the current research to reduce/move the stagnant flow region from the BW tip and to increase the target safety margin. Thermal-hydraulic analyses and structural analyses for the target head designs are carried out numerically under a steady-state condition. Results illustrate that the designs can almost eliminate the stagnant flow region in the LBE. As a consequence, the concentration of thermal stress on the BW is released and greatly decreased. The safety margin of the target is improved through this study.
中村 秀夫
Proceedings of ANS International Conference on Best Estimate Plus Uncertainties Methods (BEPU 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2018/00
軽水炉の安全評価にて、システム解析コードを用いて不確かさを考慮した最適評価解析(BEPU)を行うとき、本来目標である高温高圧で多様な形状を有する実機での伝熱流動条件下に生じる事故現象の精確な予測には依然として残されている課題がある。その中で、主に流路サイズと圧力(流体物性)に依存した現象のスケーリングが関与する課題の例を挙げ、Keynote講演での議論に資する。
Wan, T.; 大林 寛生; 佐々 敏信
Proceedings of 17th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-17) (USB Flash Drive), 13 Pages, 2017/09
To realize the future Accelerator-driven systems (ADSs), an ADS Target Test Facility (TEF-T) will be constructed within the framework of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project to carry out basic R&Ds. A LBE spallation target will be installed in the TEF-T facility and be bombarded by high power pulsed proton beams (250 kW, 400 MeV, 25 Hz, 0.5 ms in pulse duration). The beam window (BW) of the spallation target is critical because it should survive under severe conditions, i.e., high temperature, high irradiation, intense stress and various occurred damage. Therefore, the target vessel should be carefully designed to obtain enough safety margin. Our previous research indicated that there are stagnant flow region in LBE at the BW tip due to the symmetric configuration of target, which causes high temperature and stress concentration on the BW. To reduce/move the stagnant flow region from BW tip and to increase the target safety margin, on the basis of our previous work, three types of upgraded target head designs were performed steadily in the present study. The thermal-hydraulic analyses and structural analyses for the target head designs have been carried out numerically under a steady-state condition. Results illustrated that the designs can almost eliminate the stagnant flow region in LBE. As a consequence, the thermal stress concentration on BW has been released and greatly decreased. The safety margin of target has been improved through this study.
秋本 肇; 菅原 隆徳
JAEA-Data/Code 2016-008, 87 Pages, 2016/09
鉛ビスマス冷却加速器駆動システム(ADS)の基本設計に資するため、定格運転時の熱流動解析を行った。概念設計で得られた機器の性能諸元と寸法を整理し、ADS設計解析コード用入力データを作成した。急峻な半径方向出力分布を有するADSの炉心部分を詳細にモデル化し、炉心内の3次元的な流体混合が炉心冷却に与える影響を評価した。定格運転時の熱流動解析の結果から、(1)定格運転時の最高被覆管表面温度と最高燃料中心温度は設計制限値を下回る。(2)燃料集合体間の冷却材流量配分に対する半径方向出力分布の影響は小さい。急峻な半径方向出力分布がある場合でも炉心加熱区間入口における冷却材流量分布はほぼ平坦である。(3)燃料棒表面における熱伝達率に対する半径方向出力分布の影響は小さい。出力の違いに伴う被覆管表面温度の差異は、主に燃料棒に隣接する冷却材温度の違いにより決定される。(4)蒸気発生器4基における熱水力学的挙動は対称である。また、主循環ポンプ2基における熱水力学的挙動も対称である。ことがわかった。詳細な計算で明らかとなって熱水力学的挙動を踏まえて入力データを簡素化した簡易モデルを作成した。
栃尾 大輔; 藤本 望
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.425 - 431, 2016/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:9.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEAでは、将来型高温ガス炉の設計を行っている。この原子炉には異なる温度のヘリウムガスの合流点が多くある。構造物健全性又は温度制御の観点から高温ガス炉の配管内におけるヘリウムガスの混合特性を明らかにする必要がある。過去にHTTRで、ヘリウムガスの混合が十分でないことにより、原子炉入口温度が目標値より低くなるよう制御されていた。現在、この制御系は原子炉入口ヘリウムガスの混合平均温度を使った制御方法へと改良されている。本論文は、HTTRの1次系におけるヘリウムガスの混合挙動を明らかにするために、熱流動解析を行った。その結果、1次系におけるヘリウムガスの混合挙動は主に環状部流路のアスペクト比に影響を受け、高温ガス炉の配管設計では混合特性を考慮する必要があることが分かった。
渡辺 収*; 大山 一弘*; 遠藤 淳二*; 堂田 哲広; 小野 綾子; 上出 英樹; 村上 貴裕*; 江口 譲*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(9), p.1102 - 1121, 2015/09
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:72.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)自然循環崩壊熱除去系を採用した1500MW出力ナトリウム冷却高速炉(SFR)の安全性を確保するための自然循環評価手法を開発した。この評価手法は、炉心温度平坦化を考慮して炉心最高温度を評価できる1次元安全解析、1次系と崩壊熱除去系の局所的な流れや温度成層化を評価できる3次元流動解析、統計的安全評価手法から構成される。1次元及び3次元解析手法の妥当性をSFR1次冷却系の1/10スケール水試験と1次系及び崩壊熱除去系の1/7スケールナトリウム試験の結果を用いて確認し、1次元安全解析手法のSFR実機評価への適用性を乱流モデルが組込まれた3次元解析の結果との比較によって確認した。最後に、1次元安全解析手法を用いてSFR実機を対象とした統計的安全評価を実施した。
秋本 肇
JAEA-Data/Code 2014-031, 75 Pages, 2015/03
鉛ビスマス冷却加速器駆動核変換システム(ADS)の熱設計解析に資するため、軽水炉過渡解析コードJ-TRACをコードの骨組みとして、ADS用熱設計解析コードを整備した。軽水炉, ナトリウム冷却高速炉に対する安全解析及びこれまで行われたADSに対する熱流動解析を対象としてADS用熱設計解析コードに必要な解析機能を摘出した。J-TRACコードに不足する解析機能を追加するため、鉛ビスマス共晶合金(LBE), アルゴンガス, 窒化物燃料の物性値ルーチン並びに液体金属に対する強制対流領域における壁面熱伝達率相関式をJ-TRACコードに組み込んだ。LBE単相流の圧力損失解析、窒化物燃料集合体の熱伝達解析、及び蒸気発生器熱伝達解析を行い、追加した解析機能が所期の通りにJ-TRACコードに組み込めていることを確認した。
西原 哲夫; 稲垣 嘉之
Nuclear Technology, 153(1), p.100 - 106, 2006/01
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:52.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)日本原子力研究所では高温ガス炉HTTRを利用した水素製造の研究開発を進めている。本システムの主要課題の1つとして、安定な運転を行うための制御技術の開発がある。化学反応器の下流に設置する蒸気発生器を用いてヘリウム温度の変動を緩和し、熱負荷変動を吸収することを提案した。起動運転と化学反応器の負荷喪失事象を対象として熱流動解析を行った。原料ガスの流量変化に伴う化学反応器出口の大きなヘリウム温度の変動は蒸気発生器出口で緩和されることを示した。この結果、HTTRは原料ガスの流量によらず、通常運転を継続することができる。
高瀬 和之; 吉田 啓之; 小瀬 裕男*; 秋本 肇
Computational Fluid Dynamics 2004, p.649 - 654, 2006/00
日本原子力研究開発機構が研究を進めている革新的水冷却炉は減速材の割合を減らして中性子の減速を抑制することで高い転換比が期待できる原子炉であり、炉心には直径13mm程の燃料棒が1mm程度の燃料棒間ギャップ幅で三角ピッチ状に稠密に配置される。このような狭隘流路内の二相流挙動を高温高圧の原子炉条件下で詳細に計測することは困難であることから、著者らは実験データを必要としないシミュレーションだけによる評価法の開発を行っている。本論文では、革新的水冷却炉の炉心燃料集合体1カラム内二相流を対象にして、超高性能計算機による大規模シミュレーションの結果を示す。本研究によって、燃料集合体内の狭隘流路に設置されるスペーサまわりの気相と液相の挙動や燃料棒外表面を薄膜状に流れる液膜挙動などが定量的に明らかになるとともに、シミュレーションを主体とした炉心熱設計手法の実現に対して高い見通しが得られた。