Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanai, Kenji; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; Seki, Yoshitaka*
JAEA-Research 2007-057, 71 Pages, 2007/07
In underground repositories for radioactive waste, significant quantities of gases may be generated as a result of metal corrosion. These gases may migrate through the engineered barrier system and the geological barrier. The potential impact of gas generation, accumulation and migration on the performances of the various barriers such as drainage of contaminated water from the repository and/or damaging of the engineered barriers due to a gas over-pressure should be assessed. The sensitivity analysis was carried out using the modified TOUGH2 model in order to clarify the impact of any input parameters. The following facts became clear as a result of this study. For the cementitious material (waste/cementitious filler), an impact of the absolute permeability and residual pore-water saturation was large. For the buffer material, absolute permeability of gas, capillary exclusion pressure and residual pore-water saturation was large.
Ando, Kenichi*; Mihara, Morihiro; Noda, Masaru*; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*
Proceedings of 11th International High-Level Radioactive Waste Management Conference (IHLRWM) (CD-ROM), p.655 - 662, 2006/00
This study focus on gas generation associated with metal corrosion, bio-degradation of organic materials and radiolysis and gas migration through the engineered barrier system (EBS) into the surrounding host rock. Two Phase Flow analysis was performed and evaluated in terms of the development of gas pressure and discharged water from the EBS. In addition radioactive gas transport from the repository and across the reference land surface, and resaturation behavior were examined.
Ando, Kenichi*; Noda, Masaru*; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; Mihara, Morihiro
JNC TN8400 2005-026, 131 Pages, 2005/09
In TRU waste disposal system, significant quantities of gases may be generated due to metal corrosion, radiolysis effect and microorganism activities. It is therefore recommended that the potential impact of gas generation and migration on TRU waste repository should be evaluated. In this study, gas generation rates were calculated in the repository and gas migration analyses in the disposal system were carried out using two phase flow model with results of gas generation rates. First, the time dependencies of gas generation rate in each TRU waste repositories were evaluated based on amounts of metal, organic matter and radioactivity. Next, the accumulation pressure of gases and expelled pore water volume contained nuclides in the repository were calculated by TOUGH2 code. After that, the results showed that the increase of gas pressure was the range of 1.3 to 1.4MPa. In the repository with and without buffer, the rate of expelled pore water was 0.006 - 0. 009m /y and 0.018 - 0. 024m
/y and 0.018 - 0. 024m /y, respectively. In addition, the radioactive gas migration through the repository and geosphare are evaluated. And re-saturation analysis is also performed to evaluate the initial condition of the system.
/y, respectively. In addition, the radioactive gas migration through the repository and geosphare are evaluated. And re-saturation analysis is also performed to evaluate the initial condition of the system.
Tanai, Kenji; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*
JNC TN8400 2003-051, 107 Pages, 2004/02
Suitable modelling of gas production and migration behaviour is strongly required for performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal in a geological repository. Especially for gas migration in buffer materials, it is very important to examine their ability to reproduce in herent gas migration behaviour which is caused by creation of discrete pathways in clay materials. JNC has examined the limitation of reproducibility of conventional two-phase flow model and anhanced TOUGH2 which has newly developed module implemented expanded Kozeny-Carman relationship and pathway dilation/resealing model. JNC also surveyed the state of the art of model development of gas migration in multi-barriers. In FY 2003, the surverillance of gas migration modelling was continued and handled migration mechanisms, basic mathematical models, strength and weakness of each developed gas migration models were extracted and tabulated. Based on these outcomes, thebasic correspondence of models to barrier materials, which should apply to performance assessment for a near-field system, was examined. In consequence, conventional two-phase flow models of gas migration are generally applicable for cementitious materials and rocks without mudrocks. But if it is required to understand more precisely the distribution of gas release at the surface, then more detailed uderstanding of flow in fractures would be required. For clay and mudrocks, it is necessary that comparison of applicability with three types of models, which include GAMBIT-GWS model, conventional two-phase flow models coupled with effect of stress field and expanded Kozeny-Carman relationship with pathway dilation/resealing model.
Tanai, Kenji; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*
JNC TN8400 2003-024, 23 Pages, 2003/11
The knowledge obtained from previous studies are as follows, i) The gas permeabilities are 10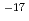 m
m for the 30wt% sand mixtures at a dry density of 1.6 Mg m
for the 30wt% sand mixtures at a dry density of 1.6 Mg m and 10
and 10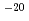 to 10
to 10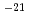 m
m for the bentonite (100%) at a dry density of 1.8 Mg m
for the bentonite (100%) at a dry density of 1.8 Mg m , ii) The breakthrough pressure seems to be almost the same as the swelling pressure at constant volume condition, iii) Gas pathways created during the first gas injection period are closed due to bentonite swelling during the resaturation period. For the recent experiment, it is obtained two peak of gas flow rate. In particular, maximum flow rate at secondary peak is obtained apploximately 1667cc min
, ii) The breakthrough pressure seems to be almost the same as the swelling pressure at constant volume condition, iii) Gas pathways created during the first gas injection period are closed due to bentonite swelling during the resaturation period. For the recent experiment, it is obtained two peak of gas flow rate. In particular, maximum flow rate at secondary peak is obtained apploximately 1667cc min . This peak is probably indicative of generation of cracks in the specimen by particle displacement. Breakthrough pressure (2.5 MPa) is larger than the swelling pressure of the bentonite (swelling pressure is approximately 1.0 MPa at a dry density of 1.6 Mg m
. This peak is probably indicative of generation of cracks in the specimen by particle displacement. Breakthrough pressure (2.5 MPa) is larger than the swelling pressure of the bentonite (swelling pressure is approximately 1.0 MPa at a dry density of 1.6 Mg m ). It may be that there is a time lag between the gas pressure change in the clay and expansion of cracks due to large pumping rate (0.05 cc min-1). The gas migration pathways are unstable due to stress condition in bentonite specimen and/or heterogeneity of specimen. The distribution of bulk density in the specimen was measured to demonstrate that X-ray CT was reliable new technique for the non-distructive measurement of gas migration through bentonite specimen. The degree of X-ray attenuation depends on the bulk density of the bentonite specimen. The change in bulk density in this test specimen is not cleared from this test case. These experimental results are probably indicative of migration along preferential pathways rather than uniform flow in the matrix of bentonite specimen.
). It may be that there is a time lag between the gas pressure change in the clay and expansion of cracks due to large pumping rate (0.05 cc min-1). The gas migration pathways are unstable due to stress condition in bentonite specimen and/or heterogeneity of specimen. The distribution of bulk density in the specimen was measured to demonstrate that X-ray CT was reliable new technique for the non-distructive measurement of gas migration through bentonite specimen. The degree of X-ray attenuation depends on the bulk density of the bentonite specimen. The change in bulk density in this test specimen is not cleared from this test case. These experimental results are probably indicative of migration along preferential pathways rather than uniform flow in the matrix of bentonite specimen.
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *
JNC TJ8440 2003-004, 90 Pages, 2003/02
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; Ito, Takao*; Oba, Toshiyuki*
JNC TJ8400 2003-061, 25 Pages, 2003/02
Gas production resulting from some mechanisms, including metal corrosion and microbial degradation in a geological repository, enables to lead overpressurization of pore pressure and enhanced release of pore water with dissolved radionuclides. In this study, gas injection experiments under three-dimensional confinement pressure, a gas-water capillary pressure test using high speed centrifuge method and high pressure mercury injection test were performed on tuff core samples to clarify flow parameters of gas and water. Results of the gas injection tests under the condition of constant injection pressure and axial flow were described. The water permeability of saturated samples were existing between 8.4  10
10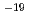 and 8.9
and 8.9  10
10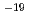 m
m although the gas permeability of dried sample were varied between 2.3
although the gas permeability of dried sample were varied between 2.3  10
10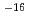 and 2.5
and 2.5  10
10 m
m depending on gas injection pressure. Gas breakthrough phenomenon after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was indicated rather slow increase of gas outflow than that observed on clay materials. Obtained excess pressure when the breakthrough phenomena occurred were 700 and 1,700 kPa. Grater the gas injection pressure, higher the excess pressure at breakthrough. Threshold pressure obtained from the capillary pressure test was order of 10
depending on gas injection pressure. Gas breakthrough phenomenon after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was indicated rather slow increase of gas outflow than that observed on clay materials. Obtained excess pressure when the breakthrough phenomena occurred were 700 and 1,700 kPa. Grater the gas injection pressure, higher the excess pressure at breakthrough. Threshold pressure obtained from the capillary pressure test was order of 10 kPa which was two order of magnitude lower than the value of clay materials. Based on these experimental results, the gas migration process and the retention curve of the tuff sample indicated typical properties observed on porous media. Thus it is expected that the conventional continuum two-phase flow model will be applied reasonably for the tuff sample.
kPa which was two order of magnitude lower than the value of clay materials. Based on these experimental results, the gas migration process and the retention curve of the tuff sample indicated typical properties observed on porous media. Thus it is expected that the conventional continuum two-phase flow model will be applied reasonably for the tuff sample.
Mihara, Morihiro; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; Ito, Takao*; Oba, Toshiyuki*
JNC TJ8400 2003-060, 81 Pages, 2003/02
Gas migration phnomena in potential components of near-field barrier system was investigated.
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2002-047, 44 Pages, 2002/02
Gas production resulting from mechanisms which includes metal corrosion and microbial degradation in a geological repository are able to lead an overpressurisation and enhanced release of radionuclides. An improved method of gas injection test of clay materials regarding test conditions and methods of gas flow rate measurement were examined and some key issues are recommended. Gas injection experiments of saturated mortar and cement paste and quantitative evaluation of gas and water flow properties in these materials were carried out. Water permeability of saturated mortar and cement paste are 10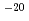 m
m and 10
and 10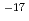 m
m respectively, although their gas permeability of dried sample were 10
respectively, although their gas permeability of dried sample were 10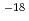 m
m and 10
and 10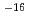 m
m respectively. Under the condition of constant injection pressure and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then the injection pressure rose a peak value range from 0.5 MPa to 8.2 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10
respectively. Under the condition of constant injection pressure and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then the injection pressure rose a peak value range from 0.5 MPa to 8.2 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10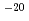 - 10
- 10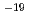 m
m . Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough phenomenon. A conventional continuum two-phase flow model was applied for simulation of the gas injection experiments. The simulation results of gas injection test were compared with measured test's data. The results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data.
. Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough phenomenon. A conventional continuum two-phase flow model was applied for simulation of the gas injection experiments. The simulation results of gas injection test were compared with measured test's data. The results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data.
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2002-046, 167 Pages, 2002/02
Gas production resulting from mechanisms which includes metal corrosion and microbial degradation in a geological repository are able to lead an overpressurisation and enhanced release of radionuclides. An improved method of gas injection test of clay materials regarding test conditions and methods of gas flow rate measurement were examined and some key issues are recommended. Gas injection experiments of saturated mortar and cement paste and quantitative evaluation of gas and water flow properties in these materials were carried out. Water permeability of saturated mortar and cement paste are 10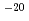 m
m and 10
and 10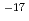 m
m respectively, although their gas permeability of dried sample were 10
respectively, although their gas permeability of dried sample were 10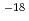 m
m and 10
and 10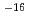 m
m respectively. Under the condition of constant injection pressure and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then the injection pressure rose a peak value range from 0.5 MPa to 8.2 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10
respectively. Under the condition of constant injection pressure and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then the injection pressure rose a peak value range from 0.5 MPa to 8.2 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10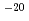 - 10
- 10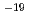 m
m . Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough phenomenon. A conventional continuum two-phase flow model was applied for simulation of the gas injection experiments. The simulation results of gas injection test were compared with measured test's data. The results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data.
. Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough phenomenon. A conventional continuum two-phase flow model was applied for simulation of the gas injection experiments. The simulation results of gas injection test were compared with measured test's data. The results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data.
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-032, 153 Pages, 2000/02
Gas production resulting from mechanisms, which include metal corrosion and microbial degradation in TRU (TransUranic nuclide bearing) waste repository, can lead to overpressurisation and enhanced release of radionuclides. In this study, gas injection experiment and quantitative evaluation of gas flow properties in bentonite/sand mixture (70 weight percent of bentonite and 30 weight percent of quartz sand, 1.6 Mg/m of dry density) were carried out. Under the condition of cylindrical, constant volume geometry and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then an injection pressure rises to a peak value range from 2 MPa to 7 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10
of dry density) were carried out. Under the condition of cylindrical, constant volume geometry and axial flow, gas breakthrough phenomenon at which sharp increase of gas outflow rate after rapid rise in outflow rate of water was observed. Then an injection pressure rises to a peak value range from 2 MPa to 7 MPa higher than backpressure. Afterward, outflow rate of gas increased to a steady state value in the permeability range 10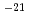 - 10
- 10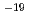 m
m . Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough. When the gas injection pressure decreased, outflow rate of water declined coincidentally. An enhanced two-phase flow modei in which bentonite/sand gas flow sub-model, based on Kozeny-Carman model, is added to conventional two-phase flow model was used for simulation. Simulation results of gas injection test were compared with the test's data. Results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data. Also, two-dimensional calculation of gas migration in a multi-barrier repository of TRU waste was implemented. Parameter values used here without reseal pressure were identified through the simulation of the test's results. Comparing these results with other simulation results obtained by conventional two-phase flow model shows that the maximum pore pressure was almost same value between two different models. But estimated value of expelled water from cavern by enhanced two-phase flow model was less than the value from conventional two-phase flow calculation. Therefor in view of the expelled water, former ...
. Outflow of water continued after gas breakthrough. When the gas injection pressure decreased, outflow rate of water declined coincidentally. An enhanced two-phase flow modei in which bentonite/sand gas flow sub-model, based on Kozeny-Carman model, is added to conventional two-phase flow model was used for simulation. Simulation results of gas injection test were compared with the test's data. Results of the simulation were in reasonably agreement with obtained experimental data. Also, two-dimensional calculation of gas migration in a multi-barrier repository of TRU waste was implemented. Parameter values used here without reseal pressure were identified through the simulation of the test's results. Comparing these results with other simulation results obtained by conventional two-phase flow model shows that the maximum pore pressure was almost same value between two different models. But estimated value of expelled water from cavern by enhanced two-phase flow model was less than the value from conventional two-phase flow calculation. Therefor in view of the expelled water, former ...
Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *; *
JNC TJ8400 2000-031, 29 Pages, 2000/02
no abstracts in English
*; Yamamoto, Mikihiko*; *; *
PNC TJ1277 93-003, 30 Pages, 1993/02
IT IS EXPECTED TO ACCUMULATE LARGE QUANTITY OF TRANSURANIC WASTES (AND LONGLIVED /
/ LOW LEVEL RADIOACTIVE WASTES). IN THE CIRCUMSTANCES,ATOMIC ENERGYCOMMITTEE RECOMMENDED THAT IT IS NECESSARY TO PRESENT APPLICABLE TECHNOLOGY FORISOLATING TRANSURANIC WASTE TILL 2000.THE LONG TERM SAFETY OF ISOLATION TECHNOLOGY MUST BE CONVINCINGLY ASSESSED PRIORTO ITS APPLICATION. THEREFORE MODELS WHICH CAN PREDICT RELEASE AND MIGRATION OFRADIONUCLIDES WITH ADEQUATE ACCURACY NEED TO BE DEVELOPED AND VALIDATED. IN THISINVESTIGATION,THE PURPOSE OF WHICH IS TO IDENTIFY PRINCIPAL PHENOMENA FORPERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT AND TO INTEGRATE SIMPLIFIED SYSTEM MODELS FOR OVERALLSAFETY ASSESSMENT.IN 1993 FOUR SUBJECTS LISTED BELOW WERE INVESTIGATED.(1)SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TRU WASTE ISOLATION.(2)INVESTIGATION OF ASSESSMENT METHODS FOR IMPORTANT PHENOMENA OF TRU WASTEISOLATION.(3)PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT FOR GAS GENERATION FROM TRU WASTES.(4)DEVELOPMENT OF TOTAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT METHDOOLO
LOW LEVEL RADIOACTIVE WASTES). IN THE CIRCUMSTANCES,ATOMIC ENERGYCOMMITTEE RECOMMENDED THAT IT IS NECESSARY TO PRESENT APPLICABLE TECHNOLOGY FORISOLATING TRANSURANIC WASTE TILL 2000.THE LONG TERM SAFETY OF ISOLATION TECHNOLOGY MUST BE CONVINCINGLY ASSESSED PRIORTO ITS APPLICATION. THEREFORE MODELS WHICH CAN PREDICT RELEASE AND MIGRATION OFRADIONUCLIDES WITH ADEQUATE ACCURACY NEED TO BE DEVELOPED AND VALIDATED. IN THISINVESTIGATION,THE PURPOSE OF WHICH IS TO IDENTIFY PRINCIPAL PHENOMENA FORPERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT AND TO INTEGRATE SIMPLIFIED SYSTEM MODELS FOR OVERALLSAFETY ASSESSMENT.IN 1993 FOUR SUBJECTS LISTED BELOW WERE INVESTIGATED.(1)SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT FOR PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF TRU WASTE ISOLATION.(2)INVESTIGATION OF ASSESSMENT METHODS FOR IMPORTANT PHENOMENA OF TRU WASTEISOLATION.(3)PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT FOR GAS GENERATION FROM TRU WASTES.(4)DEVELOPMENT OF TOTAL PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT METHDOOLO