Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maeda, Seiichiro; Oki, Shigeo; Otsuka, Satoshi; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Ozawa, Takayuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/06
The next generation fast reactor is being investigated in Japan, aiming at several targets such as "safety", "reduction of environmental burden" and "economic competitiveness". As for the safety aspect, FAIDUS concept is adopted to avoid re-criticality in core destructive accidents. The uranium-plutonium mixed oxide fuel, in which minor actinide elements are included, will be applied to reduce the amount and potential radio-toxicity of radioactive wastes. The high burn-up fuel is pursued to reduce fuel cycle cost. The candidate concept of the core and fuel design, which could satisfy various design criteria by design devisals, has been established. In addition, JAEA is investigating material properties and irradiation behavior of MA-MOX fuel. JAEA is developing the fuel design code especially for the fuel pin with annular pellets of MA-bearing MOX. Furthermore, JAEA is developing oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) ferritic steel cladding for the high burnup fuel.
Morita, Kenji; Morimoto, Makoto; Hisada, Masaki; Fukui, Yasutaka
JAEA-Technology 2015-038, 30 Pages, 2016/02
The Old Waste Treatment Facility for JOYO (Old JWTF) has been operated to treat radioactive liquid waste from the experimental fast reactor JOYO and post irradiation examination facilities. Operation of Old JWTF stopped in 1995, and dismantling & decontamination method has discussed. As a response to discussion results of remote and dismantling method in high dose environment on 2013, its concept examination was discussed on 2014. Results are follows. As a cutting tool for Old JWTF equipment, wire saw is selected from cutting ability (speed and thickness of objects). Discussed the component technology of wire saw remote operation system (handling, monitoring, collection method of secondary waste, else).
Morita, Kenji; Morimoto, Makoto; Hisada, Masaki; Fukui, Yasutaka
JAEA-Technology 2015-037, 28 Pages, 2016/01
Deuterium Critical Assembly (DCA) achieved first critically in 1969 and used for research and development program of Advanced Thermal Reactor. To achieved the aim of facility, DCA decommissioning work started in 2002. Decommissioning schedule consists of 4 stages. The third stage, which is the main work (To dismantle and remove reactor vessel and main equipment), was started in 2008 and will be finished at 2023. This report describes DCA decommissioning work and data (Ability of cutting tools and Man-hours) in 2013.
 at high temperatures up to 2190 K
at high temperatures up to 2190 KMorimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 443(1-3), p.286 - 290, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.62(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In this study, measurement was conducted for the sliced MOX pellets containing 30% of Pu prepared by a conventional powder metallurgy technology. Oxygen-to-metal (O/M) ratios of the samples were adjusted in the range from 1.92 to 2.00. The thermal diffusivities of these samples were measured at temperature up to 2150 K with the laser flash method. Thermal diffusivities of the near-stoichiometric samples obtained in the cooling process were greatly lower than those in the heating process unlike measurement below 1770 K. On the other hand, they were almost identical for the sample of 1.946 in O/M. It was also shown that thermal diffusivity decreased with the temperature but increased with the O/M.
Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Ogasawara, Masahiro*
Proceedings of Plutonium Futures; The Science 2010 (CD-ROM), p.339 - 340, 2010/09
Nuclear fuel pellets are stored before loading into a reactor. In some cases, the fuel pellets are left for several years. When uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel pellets are stored for a long time, lattice defects induced by self-irradiation ( decay) accumulate and these defects affect physical properties of the pellets, i.e. lattice parameter, electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of fuel pellets is one of the most important properties for fuel design and performance analyses; it is known to decrease due to the defects induced by self-irradiation, but it can be recovered by heating the pellets. In this study, the recovery behavior of thermal conductivity of a MOX fuel pellet stored for long time was investigated as a function of time and temperature, in order to make it easy to analyze the thermal performance of fuel pellets.
decay) accumulate and these defects affect physical properties of the pellets, i.e. lattice parameter, electrical resistivity and thermal conductivity. The thermal conductivity of fuel pellets is one of the most important properties for fuel design and performance analyses; it is known to decrease due to the defects induced by self-irradiation, but it can be recovered by heating the pellets. In this study, the recovery behavior of thermal conductivity of a MOX fuel pellet stored for long time was investigated as a function of time and temperature, in order to make it easy to analyze the thermal performance of fuel pellets.
 solid solutions
solid solutionsMorimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 452(1), p.54 - 60, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:77.85(Chemistry, Physical)Plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel with high Pu content have been developed as a fuel of fast reactor (FR). As the storage time of Pu raw material between reprocessing and fabrication increases, americium content of the fabricated MOX fuel increases up to a few percent. In this work, the thermal conductivity of MOX fuel containing Am was investigated as a part of clarifying the effect of Am content on thermal physical properties. The pellets of (Am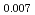 Pu
Pu U)O
U)O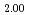 , (Am
, (Am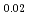 Pu
Pu U)O
U)O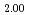 and (Am
and (Am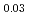 Pu
Pu U)O
U)O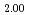 were prepared. The oxygen to metal ratio (O/M ratio) of sintered pellet was adjusted to 2.00. The thermal diffusivity measurement was carried out in the range of temperature from 900 K to 1700 K by the laser flash method, and thermal conductivity of these pellets was evaluated. The heat capacity for evaluating thermal conductivity was derived from heat capacity of UO
were prepared. The oxygen to metal ratio (O/M ratio) of sintered pellet was adjusted to 2.00. The thermal diffusivity measurement was carried out in the range of temperature from 900 K to 1700 K by the laser flash method, and thermal conductivity of these pellets was evaluated. The heat capacity for evaluating thermal conductivity was derived from heat capacity of UO , PuO
, PuO and AmO
and AmO by using the Kopp-Neumann rule.
by using the Kopp-Neumann rule.
 oxide
oxideMorimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Kashimura, Motoaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 374(3), p.378 - 385, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:89.2(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of (U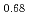 Pu
Pu Am
Am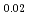 )O
)O solid solutions (x = 0.0 - 0.1) were studied at temperatures from 900 to 1773 K. Thermal conductivities were obtained from the thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method. The thermal conductivities obtained experimentally up to about 1400K could be expressed by a classical phonon transport model,
solid solutions (x = 0.0 - 0.1) were studied at temperatures from 900 to 1773 K. Thermal conductivities were obtained from the thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method. The thermal conductivities obtained experimentally up to about 1400K could be expressed by a classical phonon transport model,  = (A+BT)
= (A+BT) , A(x) = 2.89
, A(x) = 2.89 x + 2.24
x + 2.24 10
10 (m K/W) and B(x) = (- 6.70
(m K/W) and B(x) = (- 6.70 x + 2.48)
x + 2.48)  10
10 (m/W). The experimental values of A showed a good agreement with theoretical predictions. The experimental values of B could be fairly expressed by the theoretical prediction in the region x
(m/W). The experimental values of A showed a good agreement with theoretical predictions. The experimental values of B could be fairly expressed by the theoretical prediction in the region x  0.04, but not deviated from the ones in the region x
0.04, but not deviated from the ones in the region x  0.04. Although this reason could not be understood well, it is most likely that the uncertainty in the measurement of melting temperature cause this difference.
0.04. Although this reason could not be understood well, it is most likely that the uncertainty in the measurement of melting temperature cause this difference.
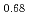 Pu
Pu Am
Am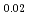 )O
)O in high temperature region
in high temperature regionKomeno, Akira; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kato, Masato; Kashimura, Motoaki; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 97(1), p.616 - 617, 2007/11
no abstracts in English
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Komeno, Akira; Nakamichi, Shinya; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Sugata, Hiromasa*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2006-049, 32 Pages, 2006/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has developed a fast breeder reactor(FBR), and plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) having low density and 20-30%Pu content has used as a fuel of the FBR, Monju. In plutonium, Americium has been accumulated during long-term storage, and Am content will be increasing up to 2-3% in the MOX. It is essential to evaluate the influence of Am content on physical properties of MOX on the development of FBR in the future. In this study melting points and thermal conductivities which are important data on the fuel design were measured systematically in wide range of composition, and the effects of Am accumulated were evaluated. The solidus temperatures of MOX were measured as a function of Pu content, oxygen to metal ratio(O/M) and Am content using thermal arrest technique. The sample was sealed in a tungsten capsule in vacuum for measuring solidus temperature. In the measurements of MOX with Pu content of more than 30%, a rhenium inner capsule was used to prevent the reaction between MOX and tungsten. In the results, it was confirmed that the melting points of MOX decrease with as an increase of Pu content and increase slightly with a decrease of O/M ratio. The effect of Am content on the fuel design was negligible small in the range of Am content up to 3%. Thermal conductivities of MOX were evaluated from thermal diffusivity measured by laser flash method and heat capacity calculated by Nuemann- Kopp's law. The thermal conductivity of MOX decreased slightly in the temperature of less than 1173K with increasing Am content. The effect of Am accumulated in long-term storage fuel was evaluated from melting points and thermal conductivities measured in this study. It is concluded that the increase of Am in the fuel barely affect the fuel design in the range of less than 3%Am content.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Kihara, Yoshiyuki; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Uno, Hiroki*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
JNC TN8400 2004-022, 44 Pages, 2005/03
Japan Nuclear Development Institute has developed homogeneous mixed oxide fuel containing minor actinide as a fuel of an advanced fast reactor. Study on the sintering behavior of the fuel was carried out and the heat treatment technique for preparing homogeneous low O/M fuel had been developed. In this report, oxygen potential was measured and phase relation was evaluated, which are needed essentially for developing the new type fuel.Oxygen potential of (Npsub0.02Amsub0.02Pusub0.3Usub0.66)Osub2-X was measured by gas equilibrium method as a function of temperature and O/M ratio. The MOX with MA has slightly higher oxygen potential as compared with that of MOX without MA. And the model of oxygen potential was derived from the measurement results based on lattice defect theory.In samples with low O/M ratio, two fcc phases were observed at room temperature. The temperature of the phase separation was measured and it is observed that the addition of MA have the effect to be decreased the phase separation temperature. In the MOX containing MA and Nd simulated a low decontaminated fuel, the Pu-Am-Nd oxides were precipitated by decreasing O/M ratio in less than 1.96.
Kimura, Hiromi*; Sasaki, Masayoshi*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Takeda, Tsuyoshi*; Kodama, Hiroshi*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Imai, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 337-339, p.614 - 618, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.9(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Terakado, Tsuguo; Morimoto, Makoto; Izawa, Osamu; Ishida, Koichi; Hoshino, Katsuaki; Suzuki, Shinya; Ito, Hideaki; Aoki, Hiroshi; Odo, Toshihiro
JNC TN9430 2004-003, 87 Pages, 2004/03
This paper describes the results of Secondary Cooling System main pumps test ,which were done as a part of JOYO MK-3 function test. The function tests were cexcuted to get the operating characteristics of secondary cooling system, after the Intermediate Heat Exchangers, Dump Heat Exchangers, secondary main pump motors, pump speed control board and rheostat were replaced in the MK-3 conversion. These tests are composed of six items. These tests purpose are confirmed in the function of the Main pumps, sodium purification system and argon cover gas pressure control system in Secondary Cooling System. (1) SKS-205-1: flow control test, (2) SKS-205-2: flow coast down characteristics test, (3) SKS-205-3: running operation test, (4) SKS-205-4: pump vibration measurement test, (5) SKS-212: secondary sodium purification system electromagnetic-pump flow control test, (6) SKS-213: argon cover gas pressure in secondary cooling system pressure control test function tests are satisfied the design criteria. We have confirmed the system performance of the main pump, secondary sodium purification system and argon cover gas pressure control system in the Secondary Cooling System after the MK-3 conversion.
Morimoto, Makoto; Suto, Masayoshi; Ito, Yoshio; Ito, Hideaki; Aoki, Hiroshi; Odo, Toshihiro
JNC TN9430 2004-002, 60 Pages, 2004/03
This paper describes the result of the sodium purity measurement test on MK-III function tests. This test meant cold traps caught impurity which was carried into the primary and the secondary cooling system by MK-III modification work of the heat transport system, and the amount of impurity was evaluated by plugging temperature before and after the primary and secondary purification operation. Then the following two tests were practiced. Test number and name was shown. (1)SKS-122 Measurement test of purity on primary sodium purification system (2)SKS-211 Measurement test of purity on secondary sodium purification system As the cold traps could catch impurity which made with MK-III modificatlon work, impurity concentrations of sodium in the both of systems were generally within the reference limits of JOY0, while the function tests took in practice for Mk-III. As a result, the amount of impurity Oxygen caught by cold traps calculated approximately 400g in the primary sodium cooling system and approximately 1100g in the secondary one.
Oya, Yasuhisa*; Morimoto, Yasutomi*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Yagyu, Junichi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Goto, Yoshitaka*; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Okuno, Kenji*; Miya, Naoyuki; et al.
Physica Scripta, T108, p.57 - 62, 2004/00
no abstracts in English
; ; ; ; Yasu, Tetsunori; Morimoto, Makoto;
PNC TN9410 95-243, 48 Pages, 1995/09
The Register on Machinery and Tools is used for recording, summarizing, and accumulating the career of operation and maintenance, the operation experiences, and the results of research and development. It has been provided in order to secure equipment maintenance, safety control, and stable plant operation. Arrange and improvement of the Register on Machinery and tools is indispensable for preparing the technical reports (ex. "JOYO" Operation and Maintenance Experience Compile (JOMEC)), and for Job transfer from the person who was in charged of the system. This report summarizes the register from 1992 to 1994, related to the primary sodium purification system, the primary sodium sampling system, the gas chromatography monitor of primary cover gas, the primary argon gas sampling system, the sodium fill and drain system, the primary argon gas system, and the compressed air supply system. The conspicuous contents are as follows; (1)The electromagnetic pump (EMP) in the primary sodium purification system has been impossible to be started several times, because the purification line was blockaded. The EMP was coming back into operation successfully by changing over of the lines, etc. The blockade line was melted by temperature increasing of the flowing sodium at restored EMP. (2)The outlet valve of the primary sodium sampling system did not operate because of broken stem pin. It was repaired. (3)There were movement inferiority of the fore side valve of the dehumidified tower in the compressed air supply system, and damage of control air piping, etc. We successfully kept continuous operation by replacing the damage parts. After that, the fore side valve control unit was renewed in order to cope with superannuating of dehumidified control system. (4)The other systems had been favorably operated without particular trouble.
Tamaoki, Tetsuo*; Yamamoto, Hiroki*; Sato, Masuo*; Yoshida, Megumi*; Kaneko, Tomoko*; Terunuma, Seiichi; Takatsuto, Hiroshi; Morimoto, Makoto
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 34(7), p.665 - 677, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Morimoto, Makoto; Okubo, Toshiyuki; ; ; ; ;
PNC TN9410 91-334, 64 Pages, 1991/10
An failed fuel detection and location system (FFDL) using a sipping method is adopted as the FFDL of Joyo. FFDL has not operated since the first falled fuel simulated (FFDL-I) test in April, 1985 because Joyo has not yet experienced any operation with breached fuels. Therefore, the operational test (II) of FFDL was carried out on July 12 19, 1991 for a preparation of the FFDL-II test which is scheduled in 1992. Main results from the test are as follows ; (1)The adequacy of the functions and operating procedure of FFDL was reaffirmed and the operating experience was gained. (2)Radioactivity measurement was conducted by FFDL for six subassemblies and their integrity was confirmed.
19, 1991 for a preparation of the FFDL-II test which is scheduled in 1992. Main results from the test are as follows ; (1)The adequacy of the functions and operating procedure of FFDL was reaffirmed and the operating experience was gained. (2)Radioactivity measurement was conducted by FFDL for six subassemblies and their integrity was confirmed.