Radiation hardening and -embrittlement due to He production in F82H steel irradiated at 250  C in JMTR
C in JMTR
JMTR炉にて250 Cで照射したF82H鋼の照射硬化と脆化に及ぼすHe生成効果
Cで照射したF82H鋼の照射硬化と脆化に及ぼすHe生成効果
若井 栄一 
 ; 實川 資朗; 富田 英樹*; 古谷 一幸; 佐藤 通隆*; 岡 桂一朗*; 田中 典幸*; 高田 文樹; 山本 敏雄*; 加藤 佳明; 田山 義伸; 芝 清之; 大貫 惣明*
; 實川 資朗; 富田 英樹*; 古谷 一幸; 佐藤 通隆*; 岡 桂一朗*; 田中 典幸*; 高田 文樹; 山本 敏雄*; 加藤 佳明; 田山 義伸; 芝 清之; 大貫 惣明*
Wakai, Eiichi; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Tomita, Hideki*; Furuya, Kazuyuki; Sato, Michitaka*; Oka, Keiichiro*; Tanaka, Teruyuki*; Takada, Fumiki; Yamamoto, Toshio*; Kato, Yoshiaki; Tayama, Yoshinobu; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Onuki, Somei*
低放射化マルテンサイト鋼F82Hの照射硬化と脆化に及ぼすHe生成効果とその生成量依存性を引張試験片(SS-3)と破壊靭性試験片(0.18DCT)を用いて評価した。中性子照射はJMTR炉にて250 Cで約2.2dpaまで行った。本研究ではHeを材料中に生成させるためにボロン10を添加した。He生成量を変数にするため、ボロン10とボロン11の配合比(0:1, 1:1, 1:0)を変えて、ボロン添加総量を60mass ppmに揃えた3種類の添加材を作製し、照射前後の特性を比較してボロンの化学的な効果を最小限に抑えた。また、これらの試料での生成He量は約5, 150, 300appmである。一方、ボロンの効果を完全に排除した50MeVのサイクロトロン照射実験も行った。この方法ではボロンを添加しないF82H鋼を用い、直径3mm,厚さ0.3mmのTEM片に約120
Cで約2.2dpaまで行った。本研究ではHeを材料中に生成させるためにボロン10を添加した。He生成量を変数にするため、ボロン10とボロン11の配合比(0:1, 1:1, 1:0)を変えて、ボロン添加総量を60mass ppmに揃えた3種類の添加材を作製し、照射前後の特性を比較してボロンの化学的な効果を最小限に抑えた。また、これらの試料での生成He量は約5, 150, 300appmである。一方、ボロンの効果を完全に排除した50MeVのサイクロトロン照射実験も行った。この方法ではボロンを添加しないF82H鋼を用い、直径3mm,厚さ0.3mmのTEM片に約120 Cで約85appmのHeを均一に注入した後、スモールパンチ試験によって強度特性を評価した。この弾き出し損傷量は約0.03dpaであった。これらの試験結果から中性子照射後の降伏応力と最大引張応力はHe生成量の増加に伴ってやや増大した。また、中性子照射後の延性脆性遷移温度(DBTT)は40
Cで約85appmのHeを均一に注入した後、スモールパンチ試験によって強度特性を評価した。この弾き出し損傷量は約0.03dpaであった。これらの試験結果から中性子照射後の降伏応力と最大引張応力はHe生成量の増加に伴ってやや増大した。また、中性子照射後の延性脆性遷移温度(DBTT)は40 Cから150
Cから150 Cの範囲にあり、He生成量の増加に伴って高温にシフトした。また、サイクロトロンHe照射法によっても同様のHeによるDBTTシフト効果が確認できた。
Cの範囲にあり、He生成量の増加に伴って高温にシフトした。また、サイクロトロンHe照射法によっても同様のHeによるDBTTシフト効果が確認できた。
The dependence of helium production on radiation-hardening and -embrittlement has been examined in a reduced-activation martensitic F82H steel doped with  B,
B,  B and
B and  B+
B+ B irradiated at 250
B irradiated at 250 C to 2.2 dpa. The total amounts of doping boron were about 60 massppm. The range of He concentration produced in the specimens was from about 5 to about 300 appm. Tensile and fracture toughness tests were performed after neutron irradiation. 50 MeV-He
C to 2.2 dpa. The total amounts of doping boron were about 60 massppm. The range of He concentration produced in the specimens was from about 5 to about 300 appm. Tensile and fracture toughness tests were performed after neutron irradiation. 50 MeV-He irradiation was also performed to implant about 85 appm He atoms at 120
irradiation was also performed to implant about 85 appm He atoms at 120 C by AVF cyclotron to 0.03 dpa, and small punch testing was performed to obtain DBTT. Radiation-hardening of the neutron-irradiated specimens increased slightly with increasing He production. The 100 MPam
C by AVF cyclotron to 0.03 dpa, and small punch testing was performed to obtain DBTT. Radiation-hardening of the neutron-irradiated specimens increased slightly with increasing He production. The 100 MPam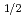 DBTT for the F82H+
DBTT for the F82H+ B, F82H+
B, F82H+ B+
B+ B, and F82H+
B, and F82H+ B were 40, 110, and 155
B were 40, 110, and 155 C, respectively. The shifts of DBTT due to He production were evaluated as about 70
C, respectively. The shifts of DBTT due to He production were evaluated as about 70 C by 150 appmHe and 115
C by 150 appmHe and 115 C by 300 appmHe. The DBTT shift in the small punch testing was evaluated as 50
C by 300 appmHe. The DBTT shift in the small punch testing was evaluated as 50 C.
C.