Assessment of  Re chelate-conjugated bisphosphonate for the development of new radiopharmaceuticals for bones
Re chelate-conjugated bisphosphonate for the development of new radiopharmaceuticals for bones
骨への新規放射性医薬品の開発に関する Reビスホネート錯体の評価
Reビスホネート錯体の評価
上原 知也*; Jin, Z. L.*; 小川 数馬*; 秋澤 宏行*; 橋本 和幸; 中山 守雄*; 荒野 泰*
Uehara, Tomoya*; Jin, Z. L.*; Ogawa, Kazuma*; Akizawa, Hiromichi*; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Nakayama, Morio*; Arano, Yasushi*
 Reとビスホスホネートの一つであるHEDPとが形成する
Reとビスホスホネートの一つであるHEDPとが形成する Re-HEDP多核錯体は、癌性骨転移の疼痛緩和剤として、その臨床応用が期待されている。しかしながら、血液からの消失速度が遅いため、骨髄被曝が危惧されている。そのため、速やかな血液クリアランスを示す
Re-HEDP多核錯体は、癌性骨転移の疼痛緩和剤として、その臨床応用が期待されている。しかしながら、血液からの消失速度が遅いため、骨髄被曝が危惧されている。そのため、速やかな血液クリアランスを示す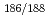 Re標識薬剤の開発が望まれている。そこで、ビスホスホネート部位(APD)に安定な放射性レニウム錯体([
Re標識薬剤の開発が望まれている。そこで、ビスホスホネート部位(APD)に安定な放射性レニウム錯体([ Re]CpTR-Gly)を結合させた薬剤として、[
Re]CpTR-Gly)を結合させた薬剤として、[ Re]CpTR-Gly-APDを設計・合成し、そのマウス体内動態を
Re]CpTR-Gly-APDを設計・合成し、そのマウス体内動態を Re-HEDPと比較検討し、その有用性を評価した。まず、生体内で非常に安定であることが確認された。また、マウス体内動態の実験から、[
Re-HEDPと比較検討し、その有用性を評価した。まず、生体内で非常に安定であることが確認された。また、マウス体内動態の実験から、[ Re]CpTR-Gly-APDは
Re]CpTR-Gly-APDは Re-HEDPに比べて骨への有意に高い集積を示す一方で、血液から速やかな放射能消失を示した。さらに、
Re-HEDPに比べて骨への有意に高い集積を示す一方で、血液から速やかな放射能消失を示した。さらに、 Re-HEDPで観察された胃への放射能集積は観察されなかった。以上の結果は[
Re-HEDPで観察された胃への放射能集積は観察されなかった。以上の結果は[ Re]CpTR-Gly-APDの設計の有用性を示すものであり、生体内で安定かつ血漿タンパク質との結合が少なく、さらに低濃度の配位子による標識が可能な二官能性キレート構造をビスホスホネートと結合させることにより、より有用な薬剤の開発が可能となると考えられる。
Re]CpTR-Gly-APDの設計の有用性を示すものであり、生体内で安定かつ血漿タンパク質との結合が少なく、さらに低濃度の配位子による標識が可能な二官能性キレート構造をビスホスホネートと結合させることにより、より有用な薬剤の開発が可能となると考えられる。
In this study, a key factor affecting the pharmacokinetics of a chelate-conjugated BP was investigated to estimate the validity and the applicability of molecular design. Chemically inert and well-characterized [ Re]CpTR-Gly was conjugated with 3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate and purified by HPLC to prepare [
Re]CpTR-Gly was conjugated with 3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate and purified by HPLC to prepare [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD. Plasma stability, plasma protein binding, hydroxyapatite (HA) binding and the pharmacokinetics of [
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD. Plasma stability, plasma protein binding, hydroxyapatite (HA) binding and the pharmacokinetics of [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD were compared with those of
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD were compared with those of  Re 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonate (HEDP). The HPLC-purified [
Re 1-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonate (HEDP). The HPLC-purified [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD showed higher plasma stability, higher HA binding, higher bone accumulation and lower plasma protein binding than did
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD showed higher plasma stability, higher HA binding, higher bone accumulation and lower plasma protein binding than did  Re -HEDP. Although
Re -HEDP. Although  Re -HEDP possessed HA binding and bone accumulation similar to those of [
Re -HEDP possessed HA binding and bone accumulation similar to those of [ Re]CpTR-Gly-APD, the specific activity of
Re]CpTR-Gly-APD, the specific activity of  Re -labeled BPs was found to play a crucial role in bone accumulation and blood clearance. Thus, the molecular design of chelate-conjugated BP would be useful for the development of bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals with a variety of radionuclides by selecting chelating molecules that provide high specific activities.
Re -labeled BPs was found to play a crucial role in bone accumulation and blood clearance. Thus, the molecular design of chelate-conjugated BP would be useful for the development of bone-seeking radiopharmaceuticals with a variety of radionuclides by selecting chelating molecules that provide high specific activities.