高速炉用ウラン・プルトニウム混合酸化物燃料の融点に及ぼす酸素・金属比の影響
Effect of oxygen-to-metal ratio on melting temperature of uranium and plutonium mixed oxide fuel for fast reactor
加藤 正人 

 ; 森本 恭一
; 森本 恭一  ; 中道 晋哉
; 中道 晋哉 
 ; 菅田 博正*; 小無 健司*; 鹿志村 元明; 安部 智之
; 菅田 博正*; 小無 健司*; 鹿志村 元明; 安部 智之
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Nakamichi, Shinya; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
高速炉用MOX燃料の融点について、Pu, Am, O/Mをパラメータとしてサーマルアレスト法により測定を行った。測定には、試料とカプセル材との反応を抑えるためにReを用いた。測定された固相線温度は、PuとAmが増加するほどまたO/Mが低下するほど上昇した。U-Pu-O系において、融点の最大値は、ハイポストイキオメトリの領域にあると考えられる。また、UO -PuO
-PuO -AmO
-AmO -PuO
-PuO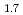 系について理想溶液モデルを用いて固相線温度及び液相線温度の評価を行い、実験値を
系について理想溶液モデルを用いて固相線温度及び液相線温度の評価を行い、実験値を 25Kで再現することを確認した。
25Kで再現することを確認した。
The melting temperatures of MOX for fast reactor fuel were investigated as functions of Pu content, Am content and oxygen-to-metal (O/M) ratio using thermal arrest technique. Rhenium inner was used for the measurement to prevent the reaction between the sample and capsule materials. The solidus temperatures decreased with increasing Pu and Am content and increased with decreasing O/M ratio. It is considered that the maximum temperature in U-Pu-O system varies in hypostoichiometric composition region. The melting temperatures were evaluated by ideal solid solution model in UO -PuO
-PuO -AmO
-AmO -PuO
-PuO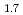 system, and the model was derived for calculating solidus and liquidus temperature. The derived model reproduced the experimental data with
system, and the model was derived for calculating solidus and liquidus temperature. The derived model reproduced the experimental data with  25 K.
25 K.