Elemental substitution effects in the electronic ferroelectric RFe O
O (R=rare earths)
(R=rare earths)
電子強誘電体RFe O
O (R:希土類)の元素置換効果
(R:希土類)の元素置換効果
吉井 賢資 
 ; 米田 安宏
; 米田 安宏 

 ; 池田 直*; 松尾 祥史*; 星山 卓也*; 堀部 陽一*; 森 茂生*
; 池田 直*; 松尾 祥史*; 星山 卓也*; 堀部 陽一*; 森 茂生*
Yoshii, Kenji; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Hoshiyama, Takuya*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
電子強誘電体RFe O
O (R:希土類)について、Feを他の元素に置換した場合の物性等について調べた。固相反応法により合成した場合、MnはFeと連続固溶し、RFe
(R:希土類)について、Feを他の元素に置換した場合の物性等について調べた。固相反応法により合成した場合、MnはFeと連続固溶し、RFe Mn
Mn O
O の化学式において、0
の化学式において、0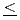 x
x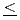 1の範囲で単相試料が得られた。一方、Cuなど他の元素を置換した場合には、限られた範囲でしか元素置換は行えなかった。たとえば、Ga置換する場合には、Feの全量に対して20パーセントほどの置換しか行えなかった。磁性・誘電性測定からは、元素置換した場合には、磁化及び誘電率は低下することがわかった。RFe
1の範囲で単相試料が得られた。一方、Cuなど他の元素を置換した場合には、限られた範囲でしか元素置換は行えなかった。たとえば、Ga置換する場合には、Feの全量に対して20パーセントほどの置換しか行えなかった。磁性・誘電性測定からは、元素置換した場合には、磁化及び誘電率は低下することがわかった。RFe O
O の誘電性の起源から推測し、これはFeイオンサイト間の電気伝導が抑えられたためと考えた。これらのほか、電子線回折や放射光実験の結果も加え、元素置換した場合のRFe
の誘電性の起源から推測し、これはFeイオンサイト間の電気伝導が抑えられたためと考えた。これらのほか、電子線回折や放射光実験の結果も加え、元素置換した場合のRFe O
O の性質についての多角的なデータを報告・議論する。
の性質についての多角的なデータを報告・議論する。
We have investigated the Fe-site substitution effects in the electronic ferroelectric RFe O
O (R=rare earths). It was found that continuous solid solutions were formed for the Mn substitution; RFe
(R=rare earths). It was found that continuous solid solutions were formed for the Mn substitution; RFe Mn
Mn O
O was synthesized for 0
was synthesized for 0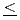 x
x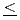 1. On the other hand, the substitution of other cations (such as Cu and Ga) was possible in limited x regions; e.g., Ga could be substituted for 0
1. On the other hand, the substitution of other cations (such as Cu and Ga) was possible in limited x regions; e.g., Ga could be substituted for 0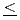 x
x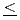 0.4-0.5 It was also found that the low-temperature magnetization and the dielectric constant were reduced by the substitution. Considering the mechanism of dielectric response in RFe
0.4-0.5 It was also found that the low-temperature magnetization and the dielectric constant were reduced by the substitution. Considering the mechanism of dielectric response in RFe O
O , the change of the physical properties likely arises from a change of electron transfer between the Fe-site ions.
, the change of the physical properties likely arises from a change of electron transfer between the Fe-site ions.