土壌有機物分解CO 炭素同位体比の経時変化
炭素同位体比の経時変化
The Change of the carbon isotopic ratio in the CO derived from soil organic matter decomposition over the incubation time
derived from soil organic matter decomposition over the incubation time
守屋 耕一*; 森泉 純*; 山澤 弘実*; 小嵐 淳 

 ; 安藤 麻里子
; 安藤 麻里子 

Moriya, Koichi*; Moriizumi, Jun*; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Koarashi, Jun; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko
森林生態系における炭素循環評価には、主要な炭素貯蔵庫でCO 放出源である土壌有機物の評価が不可欠である。本研究では、土壌有機物を長期間培養してCO
放出源である土壌有機物の評価が不可欠である。本研究では、土壌有機物を長期間培養してCO 放出速度の変化を測定し、有機物無機化モデルにフィッティングすることで、土壌有機物を易・中・難分解性の3つに分けて評価した。結果より、土壌に存在する有機物のほとんどは1年以上残留する難分解性であり、表層に中分解性炭素がわずかに存在することが明らかとなった。分解により放出されるCO
放出速度の変化を測定し、有機物無機化モデルにフィッティングすることで、土壌有機物を易・中・難分解性の3つに分けて評価した。結果より、土壌に存在する有機物のほとんどは1年以上残留する難分解性であり、表層に中分解性炭素がわずかに存在することが明らかとなった。分解により放出されるCO の安定同位体比(
の安定同位体比(
 C)は、培養開始後1週間で急激に減少する易分解性炭素が有機物自体よりも高い
C)は、培養開始後1週間で急激に減少する易分解性炭素が有機物自体よりも高い
 C値を持ち、その後緩やかに分解される中分解性炭素は逆に有機物自体よりも低い
C値を持ち、その後緩やかに分解される中分解性炭素は逆に有機物自体よりも低い
 C値を持つ経時変化を示した。これらの結果は、分解の基質である化合物が培養の経過に伴い変化していることを示唆しており、今後有機物分解過程の解明に炭素同位体を利用できる可能性を示すものである。
C値を持つ経時変化を示した。これらの結果は、分解の基質である化合物が培養の経過に伴い変化していることを示唆しており、今後有機物分解過程の解明に炭素同位体を利用できる可能性を示すものである。
To understand the decomposition mechanism in the soil, we researched the relationship between compositions of SOM and CO derived from SOM decomposition (SOMD-CO
derived from SOM decomposition (SOMD-CO ) by using
) by using  C and
C and  C. With the soil incubation, we measured CO
C. With the soil incubation, we measured CO production rates of soil and carbon isotopic ratios in SOMD-CO
production rates of soil and carbon isotopic ratios in SOMD-CO . The CO
. The CO production rates decreased rapidly at the beginning of incubation, and then decreased slowly. On the other hand,
production rates decreased rapidly at the beginning of incubation, and then decreased slowly. On the other hand, 
 C
C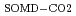 before incubation was larger than
before incubation was larger than 
 C
C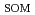 . After 40-70 days of incubation,
. After 40-70 days of incubation, 
 C
C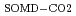 became smaller than
became smaller than 
 C
C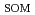 , and then
, and then 
 C
C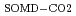 after 120-170 days approached
after 120-170 days approached 
 C
C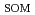 . We consider these results as follows. SOM is composed of three components, rapidly decomposable SOM that has large
. We consider these results as follows. SOM is composed of three components, rapidly decomposable SOM that has large 
 C, slowly decomposable SOM that has small
C, slowly decomposable SOM that has small 
 C and passive SOM that has the same value as
C and passive SOM that has the same value as 
 C
C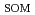 . With the progress of soil decomposition, the dominant component in SOMD-CO
. With the progress of soil decomposition, the dominant component in SOMD-CO changed. Therefore,
changed. Therefore, 
 C
C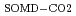 changed too.
changed too.