Assessing the role of RecA protein in the radioresistant bacterium 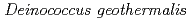
放射線抵抗性細菌デイノコッカス・ジオサーマリスにおけるRecAタンパク質の役割の評価
Sghaier, H.*; 佐藤 勝也; 大庭 寛史*; 鳴海 一成
Sghaier, H.*; Sato, Katsuya; Oba, Hirofumi*; Narumi, Issei
The moderately thermophilic bacterium 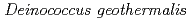 exhibits extraordinary resistance to ionizing radiation. RecA protein is considered to be one of the most important participants in radioresistance. To assess the role of the RecA protein in
exhibits extraordinary resistance to ionizing radiation. RecA protein is considered to be one of the most important participants in radioresistance. To assess the role of the RecA protein in  , the
, the  gene was isolated from
gene was isolated from  and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. After the
and overexpressed in Escherichia coli. After the  RecA protein (GeoRecA) was purified, the recombination activity was investigated
RecA protein (GeoRecA) was purified, the recombination activity was investigated  . GeoRecA most efficiently promoted the strand exchange reaction between homologous linear double-stranded DNA and circular single-stranded DNA substrates at 50
. GeoRecA most efficiently promoted the strand exchange reaction between homologous linear double-stranded DNA and circular single-stranded DNA substrates at 50 C. Like
C. Like  RecA protein (DraRecA), GeoRecA could promote DNA strand exchange reaction
RecA protein (DraRecA), GeoRecA could promote DNA strand exchange reaction 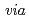 normal and inverse pathways. Furthermore, GeoRecA complemented the RecA deficiency of
normal and inverse pathways. Furthermore, GeoRecA complemented the RecA deficiency of  . These results indicate that GeoRecA is a functional homologue of DraRecA and plays an important role in radioresistance. However, unlike DraRecA, GeoRecA could not complement the RecA deficiency of
. These results indicate that GeoRecA is a functional homologue of DraRecA and plays an important role in radioresistance. However, unlike DraRecA, GeoRecA could not complement the RecA deficiency of  , suggesting that GeoRecA require more strict intracellular conditions than DraRecA does to fulfill its function.
, suggesting that GeoRecA require more strict intracellular conditions than DraRecA does to fulfill its function.