水ファントムに対する290MeV/u炭素ビーム入射中性子収量の測定
Measurement of neutron yields from a water phantom induced by 290 MeV/u carbon beam
執行 信寛*; 魚住 祐介*; 上原 春彦*; 西澤 知也*; 平林 慶一*; 佐藤 大樹 

 ; 佐波 俊哉*; 古場 裕介*; 高田 真志*; 松藤 成弘*
; 佐波 俊哉*; 古場 裕介*; 高田 真志*; 松藤 成弘*
Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Uozumi, Yusuke*; Uehara, Haruhiko*; Nishizawa, Tomoya*; Hirabayashi, Keiichi*; Satoh, Daiki; Sanami, Toshiya*; Koba, Yusuke*; Takada, Masashi*; Matsufuji, Naruhiro*
粒子線がん治療において照射時に患者体内で生成される中性子や 線などの二次放射線の放出エネルギーや角度分布を把握することは、施設の安全設計とそれによる運転員や公衆の放射線防護にとって重要である。本研究では、重粒子線がん治療に利用される290MeV/u炭素ビームを人体を模擬した水ファントムに入射し、生成される中性子の二重微分収量を測定した。実験は、放射線医学総合研究所HIMAC施設にて行った。ファントムは、奥行き20cm,高さ32cm,厚さ1cmのアクリル容器からなり、内部を純水で満たした。中性子検出器には、直径と長さがともに12.7cm及び5.08cmである2種類の液体有機シンチレータを採用した。中性子エネルギーは飛行時間法に基づき導出した。測定角度は15
線などの二次放射線の放出エネルギーや角度分布を把握することは、施設の安全設計とそれによる運転員や公衆の放射線防護にとって重要である。本研究では、重粒子線がん治療に利用される290MeV/u炭素ビームを人体を模擬した水ファントムに入射し、生成される中性子の二重微分収量を測定した。実験は、放射線医学総合研究所HIMAC施設にて行った。ファントムは、奥行き20cm,高さ32cm,厚さ1cmのアクリル容器からなり、内部を純水で満たした。中性子検出器には、直径と長さがともに12.7cm及び5.08cmである2種類の液体有機シンチレータを採用した。中性子エネルギーは飛行時間法に基づき導出した。測定角度は15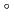 から90
から90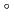 までの6点である。実験値と粒子・重イオン輸送コードシステムPHITSの計算値との比較において、PHITSは実験値をおおむね再現した。しかし、高エネルギー側で実験値を過小評価、低エネルギー側で過大評価することが明らかになった。
までの6点である。実験値と粒子・重イオン輸送コードシステムPHITSの計算値との比較において、PHITSは実験値をおおむね再現した。しかし、高エネルギー側で実験値を過小評価、低エネルギー側で過大評価することが明らかになった。
Heavy ion cancer therapy has been increased by reason of its clinical advantages. During the treatment, the secondary particles such as neutron and  -ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of the secondary neutrons yields data is essential for assessment of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities. Neutron energy spectra from a water phantom simulating the patient body were obtained at GSI only for forward directions. We measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incident on a water phantom in wide angular range from 15
-ray are produced by nuclear reactions of a heavy ion incidence on a nucleus in a patient body. Estimation of the secondary neutrons yields data is essential for assessment of radiation safety on both of workers and public in treatment facilities. Neutron energy spectra from a water phantom simulating the patient body were obtained at GSI only for forward directions. We measured the neutron yields from carbon ion incident on a water phantom in wide angular range from 15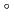 to 90
to 90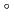 with the therapeutic ion energy.
with the therapeutic ion energy.