 線照射下における希釈海水を含むゼオライト中ステンレス鋼の局部腐食挙動
線照射下における希釈海水を含むゼオライト中ステンレス鋼の局部腐食挙動
Localized corrosion behavior of stainless steel in the diluted artificial sea-water contacted with zeolite under  -ray irradiation
-ray irradiation
加藤 千明 

 ; 佐藤 智徳
; 佐藤 智徳 
 ; 中野 純一; 上野 文義
; 中野 純一; 上野 文義 
 ; 山岸 功
; 山岸 功  ; 山本 正弘
; 山本 正弘 
Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Nakano, Junichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao; Yamamoto, Masahiro
福島第一原子力発電所事故の汚染水処理に用いた使用済み吸着塔の局部腐食発生条件に関する基礎的検討として、 線照射下における人工海水を含んだゼオライト中のステンレス鋼(SUS316L)の電気化学試験を行った。ステンレス鋼の自然浸漬電位は
線照射下における人工海水を含んだゼオライト中のステンレス鋼(SUS316L)の電気化学試験を行った。ステンレス鋼の自然浸漬電位は 線照射により貴化し、吸収線量率の増加に従いその定常自然浸漬電位が上昇した。一方、ゼオライト共存系では
線照射により貴化し、吸収線量率の増加に従いその定常自然浸漬電位が上昇した。一方、ゼオライト共存系では 線照射下の電位上昇が抑制された。この電位上昇は、主に放射線分解で生じるH
線照射下の電位上昇が抑制された。この電位上昇は、主に放射線分解で生じるH O
O 濃度の増加によるものであることを明らにした。ゼオライトは
濃度の増加によるものであることを明らにした。ゼオライトは 線照射により生成するH
線照射により生成するH O
O を分解し、その電位上昇が抑制されることを明らかにした。ステンレス鋼の局部腐食発生電位は、照射の有無、ゼオライトの種類や接触により大きく変化しないことから、ゼオライト共存は
を分解し、その電位上昇が抑制されることを明らかにした。ステンレス鋼の局部腐食発生電位は、照射の有無、ゼオライトの種類や接触により大きく変化しないことから、ゼオライト共存は 線照射下において定常自然浸漬電位を低下させ、局部腐食発生リスクを低減できることが期待できることを明らかにした。
線照射下において定常自然浸漬電位を低下させ、局部腐食発生リスクを低減できることが期待できることを明らかにした。
In relation to the consideration for long-term storage of spent Cs adsorption vessels containing zeolites in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, corrosion of the vessel material in the spent Cs adsorption vessel is one of important issues. We performed electrochemical tests of stainless steel (SUS 316L) in the zeolites containing artificial seawater under  -ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential (
-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential ( ) and critical pitting potential (
) and critical pitting potential (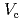 ), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after
), of SUS 316L were measured to understand the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel in this study. The rest potential of the stainless steel increased with increasing time after  -ray irradiation. The
-ray irradiation. The  , defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing
, defined as the steady rest potential, increased with increasing dose rate, while increasing  was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H
was suppressed by contact with the zeolites. Concentration of H O
O in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H
in bulk water increased with increasing dose rate. The concentration increasing was suppressed by contact with the zeolites due to decomposition of H O
O . There was good relationship between
. There was good relationship between  and the concentration of H
and the concentration of H O
O . The
. The 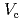 of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl
of SUS 316L contacted with the zeolites decreased with increasing Cl ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the
ion concentration and is slightly smaller than the 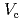 in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing
in the bulk water. The contact with the zeolites causes the suppressant of increasing  under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.
under the irradiation. The contact with the zeolite can reduce probability in the localized corrosion for SUS 316L.