Measurement of the isomer production ratio for the 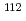 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARC
Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARC
J-PARCの中性子ビームを用いた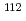 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd反応におけるアイソマー生成比の測定
Cd反応におけるアイソマー生成比の測定
早川 岳人*; 藤 暢輔 

 ; Huang, M.; 静間 俊行*; 木村 敦
; Huang, M.; 静間 俊行*; 木村 敦 

 ; 中村 詔司
; 中村 詔司 
 ; 原田 秀郎
; 原田 秀郎 

 ; 岩本 信之
; 岩本 信之 
 ; 千葉 敏*; 梶野 敏貴*
; 千葉 敏*; 梶野 敏貴*
Hayakawa, Takehito*; Toh, Yosuke; Huang, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Chiba, Satoshi*; Kajino, Toshitaka*
The astrophysical origin of a rare isotope  Sn has remained still an open question. An isomer (
Sn has remained still an open question. An isomer (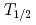 =14.1 y) in
=14.1 y) in  Cd is an s-process branching point from which a nucleosynthesis flow reaches to
Cd is an s-process branching point from which a nucleosynthesis flow reaches to  Sn. The
Sn. The  -process abundance of
-process abundance of  Sn depends on the isomer production ratio in the
Sn depends on the isomer production ratio in the 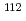 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction. However, the ratio has not been measured in an energy region higher than the thermal energy. We have measured
Cd reaction. However, the ratio has not been measured in an energy region higher than the thermal energy. We have measured  rays following neutron capture reactions on
rays following neutron capture reactions on 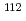 Cd using two cluster HPGe detectors in conjunction with a time-of-flight method at J-PARC. We have obtained the result that the relative
Cd using two cluster HPGe detectors in conjunction with a time-of-flight method at J-PARC. We have obtained the result that the relative  -ray intensity ratio of the isomer is almost constant in an energy region of up to 5 keV. This result suggests that the
-ray intensity ratio of the isomer is almost constant in an energy region of up to 5 keV. This result suggests that the  -process contribution to the solar abundance of
-process contribution to the solar abundance of  Sn is negligibly small. We have found that the ratio of a resonance at 737 eV shows about 1.5 times higher than other ratios. This enhancement can be explained by a
Sn is negligibly small. We have found that the ratio of a resonance at 737 eV shows about 1.5 times higher than other ratios. This enhancement can be explained by a  -wave neutron capture. This result suggests measurements of decay
-wave neutron capture. This result suggests measurements of decay  rays to isomers are effective to assign the spin and parity for neutron capture resonances.
rays to isomers are effective to assign the spin and parity for neutron capture resonances.