Time-of-flight elastic and inelastic neutron scattering studies on the localized 4d electron layered perovskite La Mo
Mo O
O
飛行時間法による中性子弾性散乱および非弾性散乱を用いた局在4d電子系層状ペロブスカイト化合物La Mo
Mo O
O の研究
の研究
飯田 一樹*; 梶本 亮一 
 ; 水野 雄介*; 蒲沢 和也*; 稲村 泰弘
; 水野 雄介*; 蒲沢 和也*; 稲村 泰弘 
 ; 星川 晃範*; 吉田 幸彦*; 松川 健*; 石垣 徹*; 河村 幸彦*; 井深 壮史*; 横尾 哲也*; 伊藤 晋一*; 勝藤 拓郎*
; 星川 晃範*; 吉田 幸彦*; 松川 健*; 石垣 徹*; 河村 幸彦*; 井深 壮史*; 横尾 哲也*; 伊藤 晋一*; 勝藤 拓郎*
Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Mizuno, Yusuke*; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Ibuka, Soshi*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Ito, Shinichi*; Katsufuji, Takuro*
The magnetic structure and spin wave excitations in the quasi-square-lattice layered perovskite compound La Mo
Mo O
O were studied by a combination of neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering techniques using polycrystalline sample. Neutron powder diffraction refinement revealed that the magnetic structure is ferrimagnetic in the
were studied by a combination of neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering techniques using polycrystalline sample. Neutron powder diffraction refinement revealed that the magnetic structure is ferrimagnetic in the 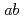 plane with antiferromagnetic stacking along the
plane with antiferromagnetic stacking along the  -axis. The inelastic neutron scattering results display strong easy-axis magnetic anisotropy along the
-axis. The inelastic neutron scattering results display strong easy-axis magnetic anisotropy along the  -axis due to the spin-orbit interaction in Mo ions. The model Hamiltonian consisting of in-plane anisotropic exchange interactions, the interlayer exchange interaction, and easy-axis single-ion anisotropy can explain our inelastic neutron scattering data well. Strong Ising-like anisotropy and weak interlayer coupling compared with the intralayer exchange interaction can explain both the high-temperature magnetoresistance and long-time magnetization decay recently observed in La
-axis due to the spin-orbit interaction in Mo ions. The model Hamiltonian consisting of in-plane anisotropic exchange interactions, the interlayer exchange interaction, and easy-axis single-ion anisotropy can explain our inelastic neutron scattering data well. Strong Ising-like anisotropy and weak interlayer coupling compared with the intralayer exchange interaction can explain both the high-temperature magnetoresistance and long-time magnetization decay recently observed in La Mo
Mo O
O .
.