Measurement of total neutron cross section of Niobium-93 at J-PARC MLF ANNRI
J-PARC MLF ANNRIでのニオブ-93中性子全断面積の測定
遠藤 駿典 

 ; 木村 敦
; 木村 敦 

 ; 中村 詔司
; 中村 詔司 
 ; 岩本 修
; 岩本 修 
 ; 岩本 信之
; 岩本 信之 
 ; 藤 暢輔
; 藤 暢輔 

 ; 瀬川 麻里子
; 瀬川 麻里子 

 ; 前田 亮
; 前田 亮 
 ; 常山 正幸*
; 常山 正幸*
Endo, Shunsuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Toh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Tsuneyama, Masayuki*
ニオブ-93はモノアイソトープでステンレスの強化元素の一つであり、原子炉の構造体として利用されてる。またNbは超伝導磁石にも用いられており、核融合炉や加速器のでも利用されている。したがって原子力工学の観点からニオブの高精度な中性子全断面積の決定が重要となる。Nbの断面積はT. WangやN. J. Drindakらによって既に求められてはいる。しかし求められた共鳴パラメータは最大で10%程度の乖離が見られるため、より高精度な共鳴パラメータの決定を目指して、2019年6月にJ-PARC MLF ANNRIにて中性子透過率測定による全断面積の測定実験を行なった。ANNRIは核データ測定用に作られたビームラインで、ゲルマニウム 線検出器とリチウムガラス中性子検出器が設置されている。ターゲットは必要な統計量から見積もり、25mm
線検出器とリチウムガラス中性子検出器が設置されている。ターゲットは必要な統計量から見積もり、25mm  25mm
25mm  10mm
10mm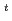 のNb板を用いた。ターゲットサイズが大きく、吸収断面積が熱中性子で1.1bと小さいため、測定結果の低エネルギー側において回折の影響が見られた。核データのような1つの原子に対する反応を見る場合、結晶構造によって生じる回折の効果は不要な情報である。したがって回折の影響を評価し取り除くことで、1原子あたりの全断面積の導出を行う。本発表では現状での断面積の結果と、回折の影響評価に関して報告する。本研究は科研費(JP17H01076)の助成を受けたものである。
のNb板を用いた。ターゲットサイズが大きく、吸収断面積が熱中性子で1.1bと小さいため、測定結果の低エネルギー側において回折の影響が見られた。核データのような1つの原子に対する反応を見る場合、結晶構造によって生じる回折の効果は不要な情報である。したがって回折の影響を評価し取り除くことで、1原子あたりの全断面積の導出を行う。本発表では現状での断面積の結果と、回折の影響評価に関して報告する。本研究は科研費(JP17H01076)の助成を受けたものである。
Niobium (Nb)-93, which is mono isotope, is one of the material elements to strengthen stainless steel and is used for structural materials of nuclear reactors. Since Nb is also used as an element of superconductor alloys, it has been used in fields such as fusion reactor and accelerator development. Determination of neutron total cross section with high accuracy is therefore required in the field of nuclear technology. The cross sections of Nb were measured by T. Wang (2011), N. J. Drindak (2006) and so on. However, the resonance parameters determined by them have discrepancies up to about 10% each other. In order to determine the more precise values of resonance parameters, transmission measurements were performed to evaluate total cross section of Nb-93 at the ANNRI of MLF in J-PARC in June of 2019. The ANNRI is one of beamlines in MLF, and Germanium gamma-ray detectors and the Liglass neutron detectors are installed to measure nuclear reactions. A target was natural Nb plate of 25 mm  25 mm
25 mm  10 mm
10 mm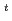 whose size was determined from necessary statistic. Since the target size was big and the thermal-neutron capture cross-section is small (about 1.1 barns), the effect of neutron diffraction was observed in low neutron energy region. When discussing reactions to a single nucleus, the effect of diffraction resulting from crystal structure is unnecessary information. Thus, this effect must be estimated and removed to determine the total cross section as nuclear data for a single nucleus. In this poster, I will present preliminary results of the experiment and the estimated effects of neutron diffraction. This work has been supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (JP17H01076).
whose size was determined from necessary statistic. Since the target size was big and the thermal-neutron capture cross-section is small (about 1.1 barns), the effect of neutron diffraction was observed in low neutron energy region. When discussing reactions to a single nucleus, the effect of diffraction resulting from crystal structure is unnecessary information. Thus, this effect must be estimated and removed to determine the total cross section as nuclear data for a single nucleus. In this poster, I will present preliminary results of the experiment and the estimated effects of neutron diffraction. This work has been supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (JP17H01076).