Ultrahigh yield strength and large uniform elongation achieved in ultrafine-grained titanium containing nitrogen
窒素を含む超微細粒チタンで達成される超高強度と大きな一様伸び
Chong, Y.*; 都留 智仁 

 ; Guo, B.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; 井上 耕治*; 辻 伸泰*
; Guo, B.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; 井上 耕治*; 辻 伸泰*
Chong, Y.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Guo, B.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Inoue, Koji*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
本研究では、室温でのチタンの引張特性と変形挙動に及ぼす窒素含有量と結晶粒径の影響を体系的に調査した。巨大ひずみ加工と焼鈍により、超高降伏強度(1.04GPa)と大きな均一伸び(10%)の前例のない相乗効果を組み合わせた、完全再結晶微細構造を備えた超微細粒(UFG)Ti-0.3wt.%N合金が得られた。Ti-0.3wt.%N合金の硬化およびひずみ硬化メカニズムは、変形下部構造の観察と第一原理計算によって包括的に研究された。UFG Ti-0.3wt.%Nの優れた強度/延性バランスへの窒素の寄与は2倍であることが明らかになった。粒子内の窒素原子は、八面体から六面体のサイトへの窒素のシャッフルにより、角柱面上の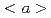 転位の運動を強く妨げ、純Tiの6倍の摩擦応力の増加を引き起こした。さらに、Ti-0.3wt.%N合金の柱面と錐面の間の積層欠陥エネルギー差が大幅に減少することで、
転位の運動を強く妨げ、純Tiの6倍の摩擦応力の増加を引き起こした。さらに、Ti-0.3wt.%N合金の柱面と錐面の間の積層欠陥エネルギー差が大幅に減少することで、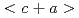 転位の活性化が容易になり、ひずみ硬化率の向上に寄与した。我々の実験的および理論的計算研究は、延性を大幅に犠牲にすることなく手頃な価格の高強度チタンの設計に関する知見を与える。
転位の活性化が容易になり、ひずみ硬化率の向上に寄与した。我々の実験的および理論的計算研究は、延性を大幅に犠牲にすることなく手頃な価格の高強度チタンの設計に関する知見を与える。
In this study, we systematically investigated the influences of nitrogen content and grain size on the tensile properties and deformation behaviors of titanium at room temperature. By high-pressure torsion and annealing, we obtained ultrafine-grained (UFG) Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy with a fully recrystallized microstructure, which combined an unprecedented synergy of ultrahigh yield strength (1.04 GPa) and large uniform elongation (10%). The hardening and strain-hardening mechanisms of Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy were comprehensively studied via deformation substructure observation and first-principles calculations. It is revealed that the contributions of nitrogen to the excellent strength/ductility balance in UFG Ti-0.3wt.%N were twofold. On one hand, nitrogen atoms inside the grains strongly impeded the motion of 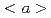 dislocations on prismatic plane due the shuffling of nitrogen from octahedral to hexahedral site, giving rise to a six-fold increase in the friction stress than pure Ti. Moreover, the greatly reduced stacking fault energy difference between prismatic and pyramidal planes in Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy facilitated an easier activation of
dislocations on prismatic plane due the shuffling of nitrogen from octahedral to hexahedral site, giving rise to a six-fold increase in the friction stress than pure Ti. Moreover, the greatly reduced stacking fault energy difference between prismatic and pyramidal planes in Ti-0.3wt.%N alloy facilitated an easier activation of 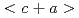 dislocations, which contributed to an enhanced strain-hardening rate. On the other hand, some nitrogen atoms segregated near the grain boundaries, a phenomenon discovered in
dislocations, which contributed to an enhanced strain-hardening rate. On the other hand, some nitrogen atoms segregated near the grain boundaries, a phenomenon discovered in  -titanium for the first time. These segregated nitrogen atoms served as an additional contributor to the yield strength of UFG Ti-0.3wt.%N, by raising the barrier against dislocation slip transfer between grains. Our experimental and theoretical calculation work provide insights for the design of affordable high strength titanium without a large sacrifice of ductility, shedding lights on a more widespread use of this high strength to weight material.
-titanium for the first time. These segregated nitrogen atoms served as an additional contributor to the yield strength of UFG Ti-0.3wt.%N, by raising the barrier against dislocation slip transfer between grains. Our experimental and theoretical calculation work provide insights for the design of affordable high strength titanium without a large sacrifice of ductility, shedding lights on a more widespread use of this high strength to weight material.