Generation of  He
He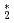 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
松下 琢*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; 林田 洋寿*; 廣井 孝介 
 ; 広田 克也*; 井口 哲夫*; 伊藤 大介*; 北口 雅暁*; 鬼柳 善明*; 國立 將真*; 久保 渉*; 齊藤 泰司*; 清水 裕彦*; 篠原 武尚
; 広田 克也*; 井口 哲夫*; 伊藤 大介*; 北口 雅暁*; 鬼柳 善明*; 國立 將真*; 久保 渉*; 齊藤 泰司*; 清水 裕彦*; 篠原 武尚 

 ; 鈴木 颯*; 富田 英生*; 辻 義之*; 和田 信雄*
; 鈴木 颯*; 富田 英生*; 辻 義之*; 和田 信雄*
Matsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Saito, Yasushi*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Wada, Nobuo*
For flow visualization study of quantum turbulence in superfluid  He,
He,  He
He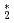 excimers are unique tracers which follow only normal-fluid component flow above 1 K. To generate detectable small
excimers are unique tracers which follow only normal-fluid component flow above 1 K. To generate detectable small  He
He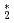 clouds (clusters) required for full-space velocity field measurements, we have adopted a new method based on neutron absorption reaction of
clouds (clusters) required for full-space velocity field measurements, we have adopted a new method based on neutron absorption reaction of  He impurities in
He impurities in  He and conducted proof-of-principle experiments. Generation of the
He and conducted proof-of-principle experiments. Generation of the  He
He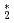 excimers was detected by laser-induced fluorescence using photomultiplier tubes. The fluorescence was observed to increase proportionally to the neutron flux, suggesting that a sufficient amount of
excimers was detected by laser-induced fluorescence using photomultiplier tubes. The fluorescence was observed to increase proportionally to the neutron flux, suggesting that a sufficient amount of  He
He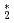 excimers were generated by neutrons. We also estimated the number of
excimers were generated by neutrons. We also estimated the number of  He
He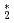 excimers possibly generated by
excimers possibly generated by  -rays and found that the relevant contribution was less than 40%. Thus, the majority of the
-rays and found that the relevant contribution was less than 40%. Thus, the majority of the  He
He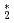 excimers was confirmed to be generated via n-
excimers was confirmed to be generated via n- He absorption reactions.
He absorption reactions.