Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-001, 94 Pages, 2025/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2023, along with the verification of each system, a three-dimensional reconstruction model was generated using images acquired from a moving camera on the monitoring platform in a simulated environment, and an integrated experiment was conducted to demonstrate that it is possible to present images from the optimal viewpoint for the visualization target, with the cooperation of each research theme.
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
 Bi
Bi
Park, P.*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Spargue, M.*; Sakuya, A. P.*; Chen, S. A.*; Frontzek, M. D.*; Tian, W.*; Sibille, R.*; Mazzone, D. G.*; Tabata, Chihiro; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.4384_1 - 4384_9, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Takahatake, Yoko; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.195 - 198, 2025/05
Extraction chromatgraphy technology for trivalent minor actinide (MA(III) ; Am(III) and Cm(III)) recovery from the solution generated by an extraction process in reprocessing of spent nuclear fuel has been developed. A fine particle is generated in the solution. The fine particle must be removed before MA recovery operation, because that leads clogging of the extraction chlomatography column. In order to prevent clogging the column, filtration system utilizing porous silica beads packed column has been designed. In this study, a fine particle trapping system was developed and particle removal performance of the system was experimentally evaluated using alumina particles as simulated fine particle. Column experiments revealed that the fine particle with the particle size from 0.12 to 15  m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
m is cause of clogging of the filtration column. Since simulated fine particles were trapped on filtration experiments, a filtration system using the porous silica beads column is practical,
Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Matsumoto, Saori*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Hayashi, Kiichiro*; Endo, Rie*; Bell , M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Volkova, O.*
, M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Volkova, O.*
Steel Research International, 96(5), p.2300766_1 - 2300766_6, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:70.74(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The density of Ni-based superalloys is measured using the maximum bubble pressure (MBP) method. The viscosity is evaluated using the oscillating crucible method. The surface tension is simultaneously measured using the MBP method.
Neubert, L.*; Bell , M. R.*; Yamamoto, Taisei*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ahrenhold, F.*; Volkova, O.*
, M. R.*; Yamamoto, Taisei*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Ahrenhold, F.*; Volkova, O.*
Steel Research International, 96(5), p.202400237_1 - 202400237_8, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.18(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) C alloy measured in the electrostatic levitation furnace onboard the international space station
C alloy measured in the electrostatic levitation furnace onboard the international space stationIshikawa, Takehiko*; Oda, Hirohisa*; Koyama, Chihiro*; Shimonishi, Rina*; Ikeuchi, Rumiko*; Paradis, P.-F.*; Okada, Jumpei*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Yamano, Hidemasa
International Journal of Microgravity Science and Application, 42(2), p.420202_1 - 420202_10, 2025/04
Koarashi, Jun; Takeuchi, Erina; Kokubu, Yoko; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko
Radiocarbon, 67(2), p.307 - 317, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Radiocarbon ( C) dating of soil samples by accelerator mass spectrometry has been proven useful for studying carbon (C) cycling in terrestrial ecosystems. There are, however, two main difficulties in sample preparation for this application: contamination of samples with modern C and inhibition of graphite formation due to sulfur (S)-containing impurities. Here we evaluated these effects from three different sample preparation methods, by conducting
C) dating of soil samples by accelerator mass spectrometry has been proven useful for studying carbon (C) cycling in terrestrial ecosystems. There are, however, two main difficulties in sample preparation for this application: contamination of samples with modern C and inhibition of graphite formation due to sulfur (S)-containing impurities. Here we evaluated these effects from three different sample preparation methods, by conducting  C measurements of
C measurements of  C-dead sample and S-rich soil samples. The preparation methods were all successful in graphite formation and
C-dead sample and S-rich soil samples. The preparation methods were all successful in graphite formation and  C measurement for soil samples with an organic S content
C measurement for soil samples with an organic S content  6.9%. The different methods showed different percent Modern Carbon (pMC) values ranging from 0.19% to 0.64% for
6.9%. The different methods showed different percent Modern Carbon (pMC) values ranging from 0.19% to 0.64% for  C-dead sample. However, the three methods had little influence on the determination of
C-dead sample. However, the three methods had little influence on the determination of  C age for samples at least younger than 12,000 yr BP. The methods examined in the present study can be used for
C age for samples at least younger than 12,000 yr BP. The methods examined in the present study can be used for  C dating with sufficient accuracy in the application to C cycle studies.
C dating with sufficient accuracy in the application to C cycle studies.
 Co gamma irradiation test results with calculated results
Co gamma irradiation test results with calculated resultsTakeda, Ryoma; Shibata, Hiroshi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Seki, Misaki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Testing 2024-007, 33 Pages, 2025/03
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) in Oarai Research and Development Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing various reactor materials, irradiation techniques and instruments for more than 30 years. Among them, the development of self-powered neutron detectors (SPNDs) and gamma detectors (SPGDs) has been carried out, and several research results have been reported. In this report, we compare and verify these test results with the theoretical output results obtained by the calculation code created in the JAEA report (JAEA-Data/Code 2021-018). The comparison was made with the irradiation test results of SPGD, a cobalt-60 gamma irradiation facility. As a result, it was found that the calculation results reproduced the test results well when the emitter diameter was relatively small compared to the range of Compton scattered electrons by the gamma rays. On the other hand, when the emitter diameter is relatively large, the output current in the test results is only about half of the calculated output current. The self-shielding effect of the emitter may be one of the reasons for the difference in the emitter diameter, and a new formulation, such as incorporating the effect of self-shielding caused by a larger emitter diameter or a non-isotropic  -ray field as a change in the mean electron range or mean minimum energy in the calculation code, is necessary. The new formulation is necessary.
-ray field as a change in the mean electron range or mean minimum energy in the calculation code, is necessary. The new formulation is necessary.
Kokubu, Yoko; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Nishio, Kazuhisa*; Ikeda, Koki
JAEA-Review 2024-066, 67 Pages, 2025/03
The Tono Geoscience Center of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has undertaken backfilling and restoration activities at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) site since fiscal year 2020. These activities are being conducted in accordance with "The MIU Project from FY2020 Onwards," outlining the procedures for backfilling, restoration, and environmental monitoring at the MIU site. The backfilling activity was completed in January 2022, and thereafter, the observation of the backfilled shafts was commenced. On November 6, 2023, the settlement of the backfilled surface was observed in the Main Shaft and the Ventilation Shaft. By December 5, 2023, the depth of the settlement reached 12.9 m in the Main Shaft and 27.7 m in the Ventilation Shaft. After an evaluation by the MIU safety confirmation committee, which assessed the settlement condition and recommended countermeasures, the affected areas were backfilled for safety reasons. This report summarizes the observed settlement of the backfilled surface, the subsequent rebackfilling efforts, and the condition of the surface settlement areas. The condition of the backfilled sections has been confirmed up to June 2024.
Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Takeuchi, Akihisa*
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 109, p.1421 - 1436, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:93.94(Chemistry, Physical)Our preceding investigation revealed that multiple hydrogen traps at coherent interfaces of MgZn precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn
precipitates initiated spontaneous interface decohesion, causing hydrogen-induced quasicleavage cracking in Al-Zn-Mg alloys. Herein, we performed a quantitative and systematic investigation to discern the mechanisms by which hydrogen trapped at coherent/semi-coherent interfaces of precipitates could influence macroscopic hydrogen embrittlement by modulating the coherent interface of MgZn through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn
through aging. To explore this hydrogen embrittlement phenomenon based on hydrogen trapping at the precipitate interface, we determined the hydrogen trapping energy of the semi-coherent MgZn interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn
interface via first-principles calculations (0.56 eV/atom). Hydrogen partitioning of all hydrogen trapping sites, including vacancies, grain boundaries, and coherent and semi-coherent MgZn interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn
interfaces, revealed that in overaged alloys, over 90% of the hydrogen was sequestered at semi-coherent interfaces. Owing to the inherent characteristics of the MgZn interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
interface, the hydrogen sequestered at the semi-coherent interface decreased the interfacial cohesive energy, causing semispontaneous decohesion of the interface and quasicleavage fracture in the Al-Zn-Mg alloys. These results implied that intergranular fracture was not directly induced by hydrogen trapped at grain boundaries but rather by the decohesion of precipitate interfaces along grain boundaries.
 Sb
Sb with a honeycomb network
with a honeycomb networkAdachi, Tadashi*; Ogawa, Taiki*; Komiyama, Yota*; Sumura, Takuya*; Saito-Tsuboi, Yuki*; Takeuchi, Takaaki*; Mano, Kohei*; Manabe, Kaoru*; Kawabata, Koki*; Imazu, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.L100508_1 - L100508_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Takeuchi, Ryuji; Kokubu, Yoko; Nishio, Kazuhisa*
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-015, 68 Pages, 2025/02
The Tono Geoscience Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting the environmental monitoring investigation to confirm the environmental impacts associated with the backfilling of shafts and tunnels at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). This report summarizes the results of the environmental impact investigations conducted as part of the environmental monitoring investigation around the MIU Site in FY2023, which include groundwater level measurement in wells, river flow rate measurement, water analysis of Hazama river, noise and vibration surveys, and soil survey.
Yoon, J.-Y.*; Takeuchi, Yutaro*; Takechi, Ryota*; Han, J.*; Uchiyama, Tomohiro*; Yamane, Yuta*; Kanai, Shun*; Ieda, Junichi; Ohno, Hideo*; Fukami, Shunsuke*
Nature Communications (Internet), 16, p.1171_1 - 1171_8, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)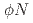 correlation function
correlation functionAbreu, L. M.*; Gubler, P.; Khemchandani, K. P.*; Mart nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physics Letters B, 860, p.139175_1 - 139175_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:52.60(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Bell , M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Sherstneva, A.*; Yamamoto, Taisei*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Weinberg, M.*; Volkova, O.*
, M. R.*; Neubert, L.*; Sherstneva, A.*; Yamamoto, Taisei*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Weinberg, M.*; Volkova, O.*
Steel Research International, p.2400252_1 - 2400252_10, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In this study, the thermophysical properties of low-sulfur manganese-boron steel with varying boron and sulfur contents at different temperatures are investigated.
Takeuchi, Ryuji; Kokubu, Yoko; Nishio, Kazuhisa*
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-011, 120 Pages, 2024/12
The Tono Geoscience Center of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting the groundwater pressure and hydrochemical monitoring to confirm the restoration process of the surrounding geological environment associated with the backfilling of shafts and tunnels of Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU). This report summarizes the data of the groundwater pressure and hydrochemical monitoring from boreholes and so forth at and around the MIU conducted in FY2023.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2024-021, 126 Pages, 2024/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on water stopping, repair and stabilization of lower PCV by geopolymer, etc" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to propose a construction method to stop jet deflectors by improved geopolymer and ultra-heavy muddy water, and to repair the lower part of the dry well. In addition, in order to increase the options for on-site construction in unknown situations such as deposition conditions, we will examine a wide range of construction outside the pedestal, and evaluate the feasibility of the construction method by the latest thermal flow simulation method.
Pla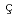 ais, A.*; Bouly, F.*; Froidefond, E.*; Lagniel, J.-M.*; Normand, G.*; Orduz, A. K.*; Yee-Rendon, B.; De Keukeleere, L.*; Van De Walle, J.*
ais, A.*; Bouly, F.*; Froidefond, E.*; Lagniel, J.-M.*; Normand, G.*; Orduz, A. K.*; Yee-Rendon, B.; De Keukeleere, L.*; Van De Walle, J.*
Proceedings of 32nd Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2024) (Internet), p.563 - 568, 2024/10
Reliability is an important feature for high power particle accelerators. This is particularly true for Accelerator-Driven Systems (ADS), for that every beam interruption can strongly affect the availability of the nuclear reactor. Many of these outages come from the loss of accelerating cavities or of their associated systems. Cavity failures can be compensated for by retuning other cavities of the linac. Finding the ideal compensation settings is however a difficult challenge that involves beam dynamics and multi-objective optimisation, and which raises very different issues according to the linac under study. For instance in the SPIRAL2 linac, a lot of cavities are mobilized for the compensation and the search space has a very high number of dimensions. Plus, it has quite low margins on the longitudinal acceptance. Linacs for ADS (such as the Japan Atomic Energy Agency ADS or MYRRHA) have a specific fault-tolerance design which facilitate the optimisation, but cavities have to be retuned in a few seconds. Hence we developed LightWin, a tool to automatically and systematically find compensation settings for every cavity failure of any given linac. In this study, we will present LightWin latest developments as well as the compensation strategies that we developed for SPIRAL2 and ADS linacs, both from a beam dynamics and a mathematical point of view.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2024-011, 121 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Quantitative evaluation of long-term state changes of contaminated reinforced concrete considering the actual environments for rational disposal" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. Estimating waste volume and concentration is essential for decommissioning concrete structures at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station.