Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakano, Hiroko; Nishikata, Kaori; Nagata, Hiroshi; Ide, Hiroshi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2022-073, 23 Pages, 2023/01
A practical training course using the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor) and other research infrastructures was held from July 24th to July 31st in 2019 for Asian young researchers and engineers. This course was adopted as Japan-Asia Youth Exchange Program in Science (SAKURA Exchange Program in Science) which is the project of the Japan Science and Technology Agency, and this course aims to enlarge the number of high-level nuclear researchers/engineers in Asian countries which are planning to introduce a nuclear power plant, and to promote the use of facilities in future. In this year, 12 young researchers and engineers joined the course from 6 countries. This course consists of lectures, which are related to irradiation test research, safety management of nuclear reactors, nuclear characteristics of the nuclear reactors, etc., practical training such as practice of research reactor operation using simulator and technical tour of nuclear facilities on nuclear energy. The content of this course in FY 2019 is reported in this paper.
Kaminaga, Masanori; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Hori, Naohiko; Naka, Michihiro
IAEA-TECDOC-1943, p.45 - 56, 2021/02
The JMTR operation was once stopped in order to have a check & review in August 2006, and the refurbishment and restart of JMTR was finally determined by the national discussion. The refurbishment was started from FY2007, and was finished in March 2011. However, at the end of the FY2010, the Great-Eastern-Japan-Earthquake occurred, and functional tests before the JMTR restart were delayed. On the other hand, based on the safety assessments considering the 2011 earthquake new regulatory requirements have established on Decmber18, 2013 by the NRA. The new regulatory requirements include the satisfaction of integrities for the updated earthquake forces, Tsunami, the consideration of natural phenomena, and the management of consideration in the Beyond Design Basis Accidents (BDBA) to protect fuel damage and to mitigate impact of the accidents. Analyses related to the new regulatory requirements have intensively been performed timely, and an application to the NRA had been submitted in March 27, 2015. After submission of application, seismic resistance assessment of JMTR reactor building was carried out by assuming the standard earthquake ground motion of 810 ga. As the results, it was found that seismic reinforcement work for reactor building and reactor pool wall were required. As a result, it became clear that at least 7 years of reinforcement work period and cost of about 40 billion yen are required for seismic reinforcement and to meet new regulatory standards. At the same time, it was made clear that high availability such as 8 operation cycles per year as originally planned cannot be expected due to aiging problem. For this reason, JAEA positioned JMTR as a decommissioning facility in the mid- and long-term plan of JAEA announced in April 2017. On the other hand, JAEA started to study the construction of a new material testing reactor. The examination results will be compiled by the end of FY2019. In this paper, outline of JMTR decommissioning plan is described.
Eguchi, Shohei; Nakano, Hiroko; Otsuka, Noriaki; Nishikata, Kaori; Nagata, Hiroshi; Ide, Hiroshi; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2019-012, 22 Pages, 2019/10
A practical training course using the JMTR and other research infrastructures was held from July 31st to August 7th in 2018 for Asian young researchers and engineers. This course was adopted as Japan-Asia Youth Exchange Program in Science (SAKURA Exchange Program in Science) which is the project of the Japan Science and Technology Agency, and this course aims to enlarge the number of high-level nuclear researchers/engineers in Asian countries which are planning to introduce a nuclear power plant, and to promote the use of facilities in future. In this year, 11 young researchers and engineers joined the course from 6 countries. This course consists of lectures, which are related to irradiation test research, safety management of nuclear reactors, nuclear characteristics of the nuclear reactors, etc., practical training such as practice of research reactor operation using simulator and technical tour of nuclear facilities on nuclear energy. The content of this course in FY 2018 is reported in this paper.
Eguchi, Shohei; Shibata, Hiroshi; Imaizumi, Tomomi; Nagata, Hiroshi; Tanimoto, Masataka; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2017-032, 26 Pages, 2018/02
A practical training course using the JMTR and other research infrastructures was held from July 24th to August 4th in 2017 for Asian young researchers and engineers. This course was adopted as Japan-Asia Youth Exchange Program in Science (SAKURA Exchange Program in Science) which is the project of the Japan Science and Technology Agency, and this course aims to enlarge the number of high-level nuclear researchers/engineers in Asian countries which are planning to introduce a nuclear power plant, and to promote the use of facilities in future. In this year, 10 young researchers and engineers joined the course from 6 countries. This course consists of lectures, which are related to irradiation test research, safety management of nuclear reactors, nuclear characteristics of the nuclear reactors, etc., practical training such as practice of research reactor operation using simulator and technical tour of nuclear facilities on nuclear energy. The content of this course in FY 2017 is reported in this paper.
Eguchi, Shohei; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Shibata, Hiroshi; Tanimoto, Masataka; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2017-007, 32 Pages, 2017/03
A practical training course using the JMTR and other research infrastructures was held from July 25th to August 5th in 2016 for domestic and foreign young researchers and engineers. This course aims to enlarge the number of high-level nuclear researchers/engineers in Japan and foreign countries which are planning to introduce a nuclear power plant, and to promote the use of facilities in future. In this year, 13 young researchers and engineers joined the course from 7 countries. This course consists of lectures, which are related to irradiation test research, safety management of nuclear reactors, nuclear characteristics of the nuclear reactors, etc., practical training and technical tour of nuclear facilities on nuclear energy. At the end of the course, the trainees discussed the energy policy and prospect of each country, each country's research reactor, and trainee's current research. The content of this course in FY 2016 is reported in this paper.
Eguchi, Shohei; Koike, Sumio; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Tanimoto, Masataka; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
UTNL-R-0492, p.9_1 - 9_8, 2016/03
no abstracts in English
Hiyama, Kazuhisa; Hanawa, Nobuhiro; Kurosawa, Akihiko; Eguchi, Shohei; Hori, Naohiko; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Ueda, Hisao; Shimada, Hiroshi; Kanda, Hiroaki*; Saito, Isamu*
JAEA-Technology 2013-045, 32 Pages, 2014/02
This report summarizes regarding to develop of real-time multifunctional access control system which is able to manage worker's access control and exposure dose at real-time in the reactor building, besides worker's location and worker might be fall down by accident.
Watahiki, Shunsuke; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Imaizumi, Tomomi; Nagata, Hiroshi; Ide, Hiroshi; Komukai, Bunsaku; Kimura, Nobuaki; Miyauchi, Masaru; Ito, Masayasu; Nishikata, Kaori; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2013-021, 43 Pages, 2013/07
The number of research reactors in the world is decreasing because of their aging. On the other hand, the necessity of research reactor, which is used for human resources development, progress of the science and technology, industrial use and safety research is increasing for the countries which are planning to introduce the nuclear power plants. From above background, the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center began to discuss a basic concept of Multipurpose Compact Research Reactor (MCRR) for education and training, etc., on 2010 to 2012. This activity is also expected to contribute to design tool improvement and human resource development in the center. In 2011, design study of reactor core, irradiation facilities with high versatility and practicality, and hot laboratory equipment for the production of Mo-99 was carried out. As the result of design study of reactor core, subcriticality and operation time of the reactor in consideration of an irradiation capsule, and about the transient response of the reactor to the reactivity disturbance during automatic control operation, it was possible to do automatic operation of MCRR, was confirmed. As the result of design study of irradiation facilities, it was confirmed that the implementation of an efficient mass production radioisotope Mo-99 can be expected. As the result of design study with hot laboratory facilities, Mo-99 production, RI export devised considered cell and facilities for exporting the specimens quickly was designed.
Ishihara, Masahiro; Kimura, Nobuaki; Takemoto, Noriyuki; Ooka, Makoto; Kaminaga, Masanori; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Komori, Yoshihiro; Suzuki, Masahide
Proceedings of 5th International Symposium on Material Testing Reactors (ISMTR-5) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2012/10
The JMTR has been utilized for fuel/material irradiation examinations of LWRs, HTGR, fusion reactor as well as for RI productions. The refurbishment of the JMTR was started from the beginning of JFY 2007, and finished in March 2011 as planned schedule. Unfortunately, at the end of the JFY 2010 on March 11, the Great-Eastern-Japan-Earthquake occurred, and functional tests before the JMTR restart were delayed by the earthquake. Moreover, a detail inspection found some damages such as small cracks in the concrete structure, ground sinking around the reactor building. Consequently, the restart will delay from June 2011. Now, the safety evaluation of the facility after the earthquake disaster is being carried out aiming at the restart of the JMTR. The renewed JMTR will be started from JFY 2012 and operated for a period of about 20 years until around JFY 2030. The usability improvement of the JMTR is also discussed with users as the preparations for re-operation.
Imaizumi, Tomomi; Miyauchi, Masaru; Ito, Masayasu; Watahiki, Shunsuke; Nagata, Hiroshi; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Naka, Michihiro; Kawamata, Kazuo; Yamaura, Takayuki; Ide, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2011-031, 123 Pages, 2012/01
The number of research reactors in the world is decreasing because of their aging. However, the planning to introduce the nuclear power plants is increasing in Asian countries. In these Asian countries, the key issue is the human resource development for operation and management of nuclear power plants after constructed them, and also the necessity of research reactor, which is used for lifetime extension of LWRs, progress of the science and technology, expansion of industry use, human resources training and so on, is increasing. From above backgrounds, the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center began to discuss basic concept of a multipurpose low-power research reactor for education and training, etc. This design study is expected to contribute not only to design tool improvement and human resources development in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center but also to maintain and upgrade the technology on research reactors in nuclear power-related companies. This report treats the activities of the working group from July 2010 to June 2011 on the multipurpose low-power research reactor in the Neutron Irradiation and Testing Reactor Center and nuclear power-related companies.
Ide, Hiroshi; Hori, Naohiko; Gorai, Shigeru; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2011-019, 24 Pages, 2011/06
Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) is a testing reactor dedicated to the irradiation tests of materials and fuels. The reactor type of the JMTR is light water moderated and cooled tank type. It achieved first criticality in 1968. Operation was started in 1970. The JMTR had been being operated for 38 years from first criticality to the JMTR No.165 cycle finished. The restart of the JMTR has been strongly requested from various users as the only irradiation testing reactor in Japan. Finally, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) decided the refurbishment and restart of the JMTR in December 2006, and the refurbishment works was started from FY 2007. This report summarized JMTR refurbishment and safety management during reactor shutdown.
Oto, Tsutomu; Kimura, Tadashi; Fukasaku, Akitomi; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2010-066, 22 Pages, 2011/01
The refurbishment of JMTR is scheduled from the beginning of FY 2007 to the end of FY 2010. An integrity investigation for concrete structures of the JMTR buildings was carried out in early phase of the refurbishment. This paper describes investigated results and repair work of the vent stack, trenches, canal building and the filter bank. Investigated items were the concrete surface deterioration, rebound number (nondestructive estimation of strength), comprehensive strength using drilled concrete core test piece, carbonation depth, reinforced bar corrosion and chloride ion content. The integrity of these concrete structures was confirmed by these investigations. Based on the investigation results, repair works such as re-painting were carried out from the viewpoint of preventive maintenance for the vent stack, trenches and canal building.
Onoue, Ryuji; Ebisawa, Hiroyuki; Fukasaku, Akitomi; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2010-059, 19 Pages, 2010/12
The JMTR is a light water moderated and cooled tank-type reactor. First criticality was achieved in March 1968. The refurbishment of JMTR is scheduled from the beginning of FY2007 to the end of FY2010. An investigation on aged components was carried out since the beginning of FY2007. In this paper, the aged-investigations for heat exchangers and tanks in the primary cooling system are presented. The integrity of three heat exchangers was confirmed by the eddy current testing for heat exchanger tubes, visual observation using endoscope, liquid penetration test of tube plates and thickness measurement of the main body. The visual inspection test and liquid penetration test were carried out to confirm the integrity of tanks in the primary cooling system. The heat exchangers and tanks in the primary cooling system will be continuously used in the future operation of the JMTR by appropriate maintenance activities based on the long-term maintenance program.
Yonekawa, Minoru; Sozawa, Shizuo; Kato, Yoshiaki; Shibata, Akira; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Review 2010-049, 18 Pages, 2010/11
The hot laboratory (JMTR-HL) was founded to examine the objects mainly irradiated in the JMTR (Japan Materials Testing Reactor), and has been operated since 1971. The JMTR has been stopped from FY2006 for the refurbishment and will be re-started from FY2011. The post irradiation examination for high burn up fuels and large specimen will be carried out in the restarted JMTR. The JMTR-HL plans to put a three dimensional X-ray Computerized Tomography (CT) inspection system in place until the restart of JMTR in order to satisfy the requirement of valuable irradiation data for safety and plant life time management of nuclear power plants in the future. The three dimensional X-ray CT inspection system is able to observe a defect geometry closely and visually compared with a two dimensional system. In this paper, system design, production, installation and performance tests of an X-ray CT inspection system in a hot cell are reported. The X-ray CT inspection system consists of a computed tomography scanner, an X-ray source, a movable sample positioned, an X-ray detector, a collimator, and so on. After installation of apparatus, performance tests using irradiated fuel rods and radioisotopes were carried out to confirm the influence of  rays and transmission X-ray property. By this development of the X-ray CT inspection system, it became possible to provide data with high technical value for post irradiation examination of high burn-up fuels and large type specimens.
rays and transmission X-ray property. By this development of the X-ray CT inspection system, it became possible to provide data with high technical value for post irradiation examination of high burn-up fuels and large type specimens.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Komeda, Masao; Arai, Masaji; Sagawa, Hisashi; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
Proceedings of 12th International Group on Research Reactors (12th IGORR) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2009/10
Yagi, Masahiro; Horiguchi, Hironori; Yokoo, Kenji; Oyama, Koji; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2008-072, 79 Pages, 2008/09
A crack had been found on the weld of one reflector element in JRR-4. A survey revealed that the cause for the crack was the expansion of graphite reflector in the reflector element. It appeared that the expansion of graphite reflector was caused by fast neutron irradiation at low temperature. The survey confirmed radiographically that graphite reflectors in the other reflector elements without the crack expanded similarly by the irradiation growth. Irradiated graphite reflectors were carefully observed and were precisely measured the three dimensions after dismantling the irradiated reflector elements in order to understand quantitatively the irradiation growth behavior of IG-110 graphite under the JRR-4 operation condition. As the results, it was confirmed that growth of graphite reflectors increased with increasing of fast neutron fluence. The maximum irradiation growth per fast neutron fluence was 7.13 10
10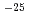 %m
%m /n, the minimum was 4.21
/n, the minimum was 4.21 10
10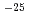 %m
%m /n, the average was 5.71
/n, the average was 5.71 10
10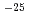 %m
%m /n in the range of fast neutron fluence below 2.5
/n in the range of fast neutron fluence below 2.5 10
10 n/m
n/m .
.
Komeda, Masao; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
Proceedings of International Conference on the Physics of Reactors, Nuclear Power; A Sustainable Resource (PHYSOR 2008) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2008/09
Research reactors use a burnable poison to suppress an excess reactivity in the beginning of reactor lifetime. The JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3) has used cadmium wires of radius 0.02cm as a burnable poison. This report describes burn-up calculations of plate fuel models and full core models with MVP-BURN, which is a burn-up calculation code using Monte Carlo method and has been developed in JAEA (Japan Atomic Energy Agency). As the results of calculations of plate models, between a model composed of one burn-up region along the radius direction and a model composed of a few burn-up regions along the radius direction, the effective absorption cross section of  Cd has had different tendency on reaching approximate 40th day (10000 MWd/t). And as results of calculations of full core model, it has been indicated that k
Cd has had different tendency on reaching approximate 40th day (10000 MWd/t). And as results of calculations of full core model, it has been indicated that k is almost same till approximate 80th day (22000 MWd/t) between a model composed of one burn-up region along the vertical direction and a model composed of a few burn-up regions along the vertical direction. However difference of
is almost same till approximate 80th day (22000 MWd/t) between a model composed of one burn-up region along the vertical direction and a model composed of a few burn-up regions along the vertical direction. However difference of  Cd burn-up becomes pronounced and each k
Cd burn-up becomes pronounced and each k makes a difference after 80th day.
makes a difference after 80th day.
Hirose, Akira; Wada, Shigeru; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-033, 87 Pages, 2007/03
Neutron-Transmutation-Doped Silicon Semiconductor (NTD-Si) has good properties for the power device. In recent years the demand of NTD-Si has increased significantly due to mass production of hybrid-cars. We have been investigated the expansion technology of the NTD-Si productivity using the research reactors JRR-3, JRR-4 and JMTR of JAEA in order to meet the demand. The conceptual design of the automated silicon irradiation device using the JRR-3 Uniformity Irradiation System was carried out as one of the effective measures. After a Si ingot is irradiated once, it is turned over manually and irradiated again in order to irradiate the ingot uniformly. With the conventional equipment, it is necessary to wait radioactivity of the ingot decrease less than the permissible level with holding the ingot in the irradiation equipment. The waiting procedure takes 48 hours or more. Because the automated NTD-Si irradiation device reduces the manual operation process and the waiting time, it is effective to shorten the waiting period. This report is concerning the conceptual design of the automated silicon irradiation device for the JRR-3 Uniformity Irradiation System.
Hirose, Akira; Wada, Shigeru; Sasajima, Fumio; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi; Kameyama, Iwao*; Aizawa, Ryoji*; Kikuchi, Naoyuki*
JAEA-Technology 2006-059, 122 Pages, 2007/01
It is expected that the demand for NTD-Si increases rapidly because of recent productive increase of hybrid-cars. In order to meet the demand, we have investigated the expansion technology of the NTD-Si productivity using the JRR3. This report describes the production of equipment for the external cooling device while proposed as one of the result of the investigation for the JRR-3 uniformity irradiation equipment. After an ingot was irradiated once, it is turned over manually and irradiated again in order irradiate the ingot uniformly. With the conventional equipment, it was necessary to wait the radioactivity of ingot decrease less than the permissible level with holding the ingot in the irradiation equipment. It was effective to shorten the waiting period by using an external cooling device for production increase of NTD-Si. It is expected that the productivity of NTD-Si will be increased by using the external cooling device.