Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
丸山 結; 杉山 智之*; 島田 亜佐子; Lind, T.*; Bentaib, A.*; Sogalla, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Albright, L.*; Clayton, D.*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.4782 - 4795, 2023/08
The Analysis of Information from Reactor Buildings and Containment Vessels of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS) (ARC-F) project was initiated in January 2019 for three years with 22 signatories from 12 countries. Three main tasks were implemented in the ARC-F project, which were relevant to 1) refinement of analysis for accident scenarios and associated fission product (FP) transport and dispersion, 2) compilation and management of data and information, and 3) discussion for the next-phase project. Various activities were performed in Task 1, covering improvement of analysis for accident scenarios, and in-depth analyses for specific phenomena such as in-vessel melt progression, molten core/concrete interaction, FP transport and source term, hydrogen combustion and atmospheric dispersion of FPs. Through these studies, analyses for accident scenarios with severe accident codes were refined and important phenomena with large uncertainties were clarified. In order to share well selected and organized information from the FDNPS with the project partners, two databases, information source database and sample database, were built under Task 2. The analysis techniques including the separation of iodine species were developed also in Task 2 and applied to the analysis of FPs in several samples taken from the FDNPS. The next-phase project was discussed in Task 3, resulting in launching the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Information Collection and Evaluation (FACE) project. The FACE project officially started in July 2022 with the participation of 23 organizations from 12 countries and the European Commission.
Lind, T.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; 丸山 結
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2022/03
The accident progression and fission product release from the three damaged units of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant were systematically investigated in the OECD/NEA BSAF project phases 1 and 2. As a result of those investigations, a good progress was achieved in establishing defendable accident scenarios and the corresponding fission product releases to the environment. Nonetheless, there are some areas requiring further work, particularly concerning fission product behavior. They are addressed in the OECD/NEA project "Analysis of Information from Reactor Buildings and Containment Vessels of Fukushima Daiichi NPS" (ARC-F). Based on the outcome of the BSAF project, several focus areas were selected for further investigations in the ARC-F project, one of them being the behavior of fission products and source term. In this paper, five topics which were ranked with a high significance as open issues based on the BSAF project regarding fission product behavior are discussed: i) fission product speciation, ii) iodine chemistry, iii) pool scrubbing, iv) fission product transport and behavior in the buildings, and v) uncertainty analysis and variant calculations. Significant progress has been made in these five topics in the ARC-F project. In this paper, background is given for choosing these topics for specific investigations based on the outcome of the BSAF project. The topics are described and the approach to study them in the ARC-F given along with some exemplary, preliminary results. Finally, the readers' attention is drawn to open issues which are not included in the ARC-F work scope and could need further attention.
Gupta, S.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Lebel, L. S.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Marchetto, C.*; 丸山 結; Dehbi, A.*; Suckow, D.*; K rkel
rkel , T.*
, T.*
Proceedings of 19th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-19) (Internet), 16 Pages, 2022/03
Pool scrubbing is a major topic in water cooled nuclear reactor technology as it is one of the means for mitigating the source-term to the environment during a severe accident. Pool scrubbing phenomena include coupled interactions between bubble hydrodynamics, aerosols and gaseous radionuclides retention mechanisms under a broad range of thermal-hydraulic conditions as per accident scenarios. Modeling pool scrubbing in some relevant accident scenarios has shown to be affected by substantial uncertainties. In this context, IPRESCA (Integration of Pool scrubbing Research to Enhance Source-term CAlculations) project aims to promote a better integration of international research activities related to pool scrubbing by providing support in experimental research to broaden the current knowledge and database, and by supporting analytical research to facilitate systematic validation and model enhancement of the existing pool scrubbing codes. The project consortium includes more than 30 organisations from 15 countries involving research institutes, universities, TSOs, and industry. For IPRESCA activities, partners join the project with in-kind contributions. IPRESCA operates under NUGENIA Technical Area 2/SARNET (Severe Accident) - Sub Technical Area 2.4 (Source-term). The present paper provides an introduction and overview of the IPRESCA project, including its objectives, organizational structure and the main outcomes of completed activities. Furthermore, key activities currently ongoing or planned in the project framework are also discussed.
丸山 智幸*; Baha Balantekin, A.*; Cheoun, M.-K.*; 梶野 敏貴*; 日下部 元彦*; Mathews, G. J.*
Physics Letters B, 824, p.136813_1 - 136813_8, 2022/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:52.69(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We study neutrino and antineutrino emission from the direct Urca process in neutron-star matter in the presence of strong magnetic fields. We calculate the neutrino emissivity of the direct Urca process, whereby a neutron converts to a proton, an electron and an antineutrino, or a proton-electron pair converts to a neutron-neutrino pair. We solve exact wave functions for protons and electrons in the states described with Landau levels. We find that the direct Urca process can satisfy the kinematic constraints even in density regions where this process could not normally occur in the absence of a magnetic field.
Khatib-Rahbar, M.*; Barrachin, M.*; Denning, R.*; Gabor, J.*; Gauntt, R.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Hobbins, R.*; Jacquemain, D.*; 丸山 結; Metcalf, J.*; et al.
NUREG/CR-7282, ERI/NRC 21-204 (Internet), 160 Pages, 2021/04
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) is preparing to accept anticipated licensing applications for the commercial use of accident tolerant fuel (ATF) in commercial nuclear power plants in the United States. It is the objective of the NRC to evaluate the effects of ATF designs on severe accident behavior, and to determine potential changes to the NRC severe accident analysis computer codes that would simulate plant conditions using ATFs commensurate with the accuracy in accident analyses involving conventional fuels. This report documents the development of Phenomena Identification and Ranking Tables (PIRTs) for near-term ATFs under severe accident conditions in light water reactors (LWRs). The PIRTs were developed by a panel of experts for various near-term ATF design concepts (i.e., FeCrAl cladding, zirconium alloy cladding coated with chromium, and Cr O
O dopants in uranium dioxide fuels) in addition to the impacts from fuel enrichment and burnup. Panel members also considered the severe accident implications of the longer-term ATF concepts. The main figures-of-merit considered in this ranking process are the amount of fission products released into the containment and the quantity of combustible gases generated during an accident. Special focus is given to whether existing severe accident codes and models would be sufficient as applied to LWRs employing these fuels, and whether additional experimental studies or model development would be warranted.
dopants in uranium dioxide fuels) in addition to the impacts from fuel enrichment and burnup. Panel members also considered the severe accident implications of the longer-term ATF concepts. The main figures-of-merit considered in this ranking process are the amount of fission products released into the containment and the quantity of combustible gases generated during an accident. Special focus is given to whether existing severe accident codes and models would be sufficient as applied to LWRs employing these fuels, and whether additional experimental studies or model development would be warranted.
Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Lind, T.*; 丸山 結; Gauntt, R.*; Bixler, N.*; Morreale, A.*; Dolganov, K.*; Sevon, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 206(9), p.1449 - 1463, 2020/09
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:98.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)The OECD/NEA Benchmark Study at the Accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (BSAF) project, which started in 2012 and continued until 2018, was one of the earliest responses to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi. The project, divided into two phases addressed the investigation of the accident at Unit 1, 2 and 3 by Severe Accident (SA) codes until 500 h focusing on thermal-hydraulics, core relocation, Molten Corium Concrete Interaction (MCCI) and fission products release and transport. The objectives of BSAF were to make up plausible scenarios based primarily on SA forensic analysis, support the decommissioning and inform SA codes modeling. The analysis and comparison among the institutes have brought up vital insights regarding the accident progression identifying periods of core meltdown and relocation, Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV) and Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) leakage/failure through the comparison of pressure, water level and CAMS signatures. The combination of code results and inspections (muon radiography, PCV inspection) has provided a picture of the current status of the debris distribution and plant status. All units present a large relocation of core materials and all of them present ex-vessel debris with Unit 1 and Unit 3 showing evidences of undergoing MCCI. Uncertainties have been identified in particular on the time and magnitude of events such as corium relocation in RPV and into cavity floor, RPV and PCV rupture events. Main uncertainties resulting from the project are the large and continuous MCCI progression predicted by basically all the SA codes and the leak pathways from RPV to PCV and PCV to reactor building and environment. The BSAF project represents a pioneering exercise which has set the basis and provided lessons learned not only for code improvement but also for the development of new related projects to investigate in detail further aspects of the Fukushima Daiichi accident.
Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Lind, T.*; 丸山 結; Gauntt, R.*; Bixler, N.*; Morreale, A.*; Dolganov, K.*; Sevon, T.*; et al.
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.1147 - 1162, 2019/08
The OECD/NEA Benchmark Study at the Accident of the Fukushima Daiichi NPS project (BSAF) has started in 2012 until 2018 as one of the earliest responses to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi NPS. The project addressed the investigation of the accident at Units 1, 2 and 3 by severe accident (SA) codes focusing on thermal-hydraulics, core relocation, molten core/concrete interaction (MCCI) and fission products release and transport. The objectives of BSAF were to make up plausible scenarios based primarily on SA forensic analysis, support the decommissioning and inform SA codes modeling. The analysis and comparison among the institutes have brought up vital insights regarding the accident progression identifying periods of core meltdown and relocation, reactor vessel (RV) and primary containment vessel (PCV) leakage/failure through the comparison of pressure, water level and CAMS measurement. The combination of code results and inspections has provided a picture of the current state of the debris distribution and plant state. All units present a large relocation of core materials and all of them present ex-vessel debris with units 1 and 3 showing evidences of undergoing MCCI. Uncertainties have been identified in particular on the time and magnitude of events such as corium relocation in RV and into cavity floor, RV and PCV rupture events. Main uncertainties resulting from the project are the large and continuous MCCI progression predicted by basically all the SA codes and the leak pathways from RV to PCV and PCV to reactor building and environment. The BSAF project represents a pioneering exercise which has set the basis and provided lessons learned not only for code improvement but also for the development of new related projects to investigate in details further aspects of the Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident.
Bentaib, A.*; Chaumeix, N.*; Grosseuvres, R.*; Bleyer, A.*; Gastaldo, L.*; Maas, L.*; Jallais, S.*; Vyazmina, E.*; Kudriakov, S.*; Studer, E.*; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2018/10
In the framework of the French MITHYGENE project, the new highly instrumented ENACCEF2 facility was built at the Institut de Combustion Aerothermique Reactivite et Environnement (ICARE) of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) in Orleans (France) to address the flame propagation in hydrogen combustion during a severe accident. The ENACCEF2 facility is a vertical tube of 7.65 m height and 0.23 m inner diameter. In the lower part of the tube, annular obstacles are installed to promote turbulent flame propagation. At the initiative of the MITHYGENE project consortium and the European Technical Safety Organisation Network (ETSON), a benchmark on hydrogen combustion was organised with the goal to identify the current level of the computational tools in the area of hydrogen combustion simulation under conditions typical for safety considerations for NPP. In the proposed paper, the simulation results obtained by participating organizations, using both Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and lumped-parameter computer codes, are compared to experimental results and analysed.
市丸 智*; 竹中 久貴*; 並河 一道*; Gullikson, E. M.*; 圓山 桃子; 奥 哲*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 86(9), p.093106_1 - 093106_7, 2015/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:14.95(Instruments & Instrumentation)EUV分光のための広帯域Mo/Siグレーディッド多層膜ミラーを製作した。このミラーは、波長15nm 17nm、有効エリア1100
17nm、有効エリア1100 1500mm
1500mm において平均16%という、直径1インチの標準的なMo/Si多層鏡より約4倍大きい反射率を有しており、この波長領域でのEUV蛍光計測に使用可能であることを示している。
において平均16%という、直径1インチの標準的なMo/Si多層鏡より約4倍大きい反射率を有しており、この波長領域でのEUV蛍光計測に使用可能であることを示している。
有田 廉*; 中里 智治*; 清水 俊彦*; 山ノ井 航平*; Empizo, M.*; 堀 達広*; 福田 一仁*; 南 佑輝*; 猿倉 信彦*; 圓山 桃子; et al.
Optical Materials, 36(12), p.2012 - 2015, 2014/10
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:45.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)EUV励起によるZnO結晶の発光パターンのシングルショットイメージを計測した。EUVビームの集光点にZnOを置いたときの発光パターンのサイズは横5.0 m、縦4.7
m、縦4.7 mであり、これはEUVレーザーのスポットサイズ1
mであり、これはEUVレーザーのスポットサイズ1 m、発光観測用拡大光学系(シュワルツシルトミラーとレンズ)の分解能4
m、発光観測用拡大光学系(シュワルツシルトミラーとレンズ)の分解能4 mよりも大きい。我々はZnOの実効的な発光寿命からエキシトンの拡散長を見積もった。発光寿命は励起密度に依存してエキシトンーエキシトン衝突による消光により短くなっている。我々の結果からは、空間分解能を改善するためにより短寿命のZnOが望ましいことが示唆された。
mよりも大きい。我々はZnOの実効的な発光寿命からエキシトンの拡散長を見積もった。発光寿命は励起密度に依存してエキシトンーエキシトン衝突による消光により短くなっている。我々の結果からは、空間分解能を改善するためにより短寿命のZnOが望ましいことが示唆された。
伊尾木 公裕*; 秋場 真人; Barabaschi, P.*; Barabash, V.*; Chiocchio, S.*; Daenner, W.*; Elio, F.*; 榎枝 幹男; 江里 幸一郎; Federici, G.*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 329-333(1), p.31 - 38, 2004/08
被引用回数:14 パーセンタイル:66.09(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ITER主要コンポーネントの発注仕様書の準備が現在進行中である。製造方法や非破壊検査法などを考慮しつつ炉構造機器(真空容器や容器内機器)の詳細設計を現在行っている。R&D開発については、20度あるいは30度の入射角の超音波試験,2チャンネルモデルによる流量配分の試験,第一壁のモックアップやパネルの製造及び試験,ハウジングを含めた全システムとしてのフレキシブル支持構造の試験,リーク試験のための予備真空領域を設けた同軸冷却管接続の試験,ダイバータの垂直ターゲットのプロトタイプの製造と試験などが行われた。こうした結果により、設計の成立性について確信を与えるとともに、低コストの代替え製造法の可能性を示すものである。
大野 富生*; Subekti, M.*; 丸山 裕太*; 鍋島 邦彦; 工藤 和彦*
第13回インテリジェント・システム・シンポジウム講演論文集, p.212 - 217, 2003/12
本研究では、ニューラルネットワークモデルの一つである多層パーセプトロンを用いて原子力プラントのシミュレーション方法について述べる。ニューラルネットワークの主な特徴は学習による高速な処理でモデルを得ることが可能である。さらに、入力に「時間同期信号」と「進展同期信号」を加えることにより、いろいろな大きさや進展速度を持つ異常事象にも対応することができる。PWRシミュレータで作成した幾つかのサンプルデータを学習させることによって、学習以外の進展速度を持つ異常、特に外挿にも適用できることが明らかになった。
 by means of X-ray lasers
by means of X-ray lasersTai, R.; 並河 一道*; 岸本 牧; 田中 桃子; 助川 鋼太*; 長谷川 登; 河内 哲哉; 加道 雅孝; Lu, P.; 永島 圭介; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 89(25), p.257602_1 - 267602_4, 2002/12
被引用回数:40 パーセンタイル:81.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)温度に対する無秩序表面ドメイン構造の振舞を調べるためにピコ秒X線レーザースペックル計測が初めて行われた。フェロエレクトリックドメインによって引き起こされた過渡的な表面構造はキューリー温度へ向かっての温度増加に伴い減少し、キューリー温度以上で完全に消滅する。c/aドメインの空間的な配置の急激な変化は、キューリー温度より2度以下から始まることが観測された。そしてそこでは、平気的なドメインの大きさは(Tc-T)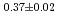 により減少することがわかった。キューリー温度近くのパラ状態において存在すると考えられていながら、従来の手法では不可能であった分極クラスターの観察を遂行できる見通しが得られた。
により減少することがわかった。キューリー温度近くのパラ状態において存在すると考えられていながら、従来の手法では不可能であった分極クラスターの観察を遂行できる見通しが得られた。
丸山 敏毅; Bonasera, A.*; Papa, M.*; 千葉 敏
European Physical Journal A, 14(2), p.191 - 197, 2002/07
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:77.67(Physics, Nuclear)フェルミ多体系の分子動力学手法である「拘束条件分子動力学」(CoMD)を用いて非常に重い原子核同士の比較的低エネルギーでの衝突をシミュレートする。そこで形成された巨大な複合系は古典的な崩壊障壁が存在しないにもかかわらず非常に長い時間(約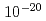 秒)存在するという結果が得られた。これは「静的なQED過程による自発的な電子陽電子放出」を起こすと言われている強い静電場を作り出すメカニズムの候補になり得ると言う意味でも重要である。また、この巨大複合系が非対称分裂を起こした場合に超重核を作り出す可能性についても議論をした。
秒)存在するという結果が得られた。これは「静的なQED過程による自発的な電子陽電子放出」を起こすと言われている強い静電場を作り出すメカニズムの候補になり得ると言う意味でも重要である。また、この巨大複合系が非対称分裂を起こした場合に超重核を作り出す可能性についても議論をした。
 solutions
solutions羽場 宏光; 塚田 和明; 浅井 雅人; 後藤 真一*; 豊嶋 厚史; 西中 一朗; 秋山 和彦; 平田 勝; 市川 進一; 永目 諭一郎; et al.
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 3(1), p.143 - 146, 2002/06
われわれの研究グループでは、超アクチノイド元素である104番元素ラザホージウム(Rf)の溶液化学実験を進めている。まず、Rfの同族元素Zr並びにHfに加え擬4族元素Thの放射性トレーサーを製造し、バッチ法により1.1-13.1M HNO 並びに1.0-11.5M HCl系における陰イオン交換分配係数を系統的に測定した。また、Rfの単一原子の化学実験を行うために、繰り返し実験が可能な迅速イオン交換分離装置(AIDA)を開発した。原研タンデム加速器を用いて、
並びに1.0-11.5M HCl系における陰イオン交換分配係数を系統的に測定した。また、Rfの単一原子の化学実験を行うために、繰り返し実験が可能な迅速イオン交換分離装置(AIDA)を開発した。原研タンデム加速器を用いて、 Ge(
Ge( O,xn),
O,xn), Gd(
Gd( O,xn)並びに
O,xn)並びに Cm(
Cm( O,5n)反応によってそれぞれ
O,5n)反応によってそれぞれ  Zr,
Zr,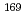 Hf並びに
Hf並びに Rfを製造し、4.0-11.5M HCl並びに8.0M HNO
Rfを製造し、4.0-11.5M HCl並びに8.0M HNO 系における陰イオン交換実験を行った。塩酸系では、7.0-11.5Mの範囲でRfの分配係数は塩酸濃度の増加とともに急激に増加し、陰イオン塩化物錯体([Rf(OH)Cl
系における陰イオン交換実験を行った。塩酸系では、7.0-11.5Mの範囲でRfの分配係数は塩酸濃度の増加とともに急激に増加し、陰イオン塩化物錯体([Rf(OH)Cl ]
] ,[RfCl
,[RfCl ]
] )の形成を示唆した。また、樹脂への吸着性の強さは、Rf
)の形成を示唆した。また、樹脂への吸着性の強さは、Rf Zr
Zr Hfの順であることがわかった。一方、8.0M HNO
Hfの順であることがわかった。一方、8.0M HNO 系では、Rfは同族元素ZrとHfと同様に陰イオン交換樹脂に対して低い吸着性を示し、ThやPuと全く異なることがわかった。
系では、Rfは同族元素ZrとHfと同様に陰イオン交換樹脂に対して低い吸着性を示し、ThやPuと全く異なることがわかった。
Papa, M.*; 丸山 敏毅; Bonasera, A.*
Physical Review C, 64(2), p.024612_1 - 024612_6, 2001/08
被引用回数:217 パーセンタイル:98.91(Physics, Nuclear)フェルミオン多体系の微視的シミュレーション手法として、高速かつフェルミオン多体系の性質を記述可能な分子動力学を開発した。これは計算時間のかかる反対称化や、これを近似するパウリポテンシャルの使用の代わりに、Thomas-Fermi的な運動量分布を各時刻で確率的、強制的に与えるものである。これを原子核衝突における破砕反応計算に適用したところ、拘束条件が期待通りに作用しフェルミオン多体系に特徴的な核子の位相空間分布が実現できた。また破砕片質量数分布の実験値との非常に良い一致を得た。
千葉 敏; Chadwick, M. B.*; 仁井田 浩二*; 丸山 敏毅; 丸山 智幸*; 岩本 昭
Physical Review C, 53(4), p.1824 - 1832, 1996/04
被引用回数:39 パーセンタイル:85.82(Physics, Nuclear)QMD理論を用いて、90~200MeV領域における Al、
Al、 Niと
Niと Zrの核子入射・核子放出反応における前平衡過程の角度分布の解析を行った。QMDはパラメータ調整なしに測定された(p,xp')及び(p,xn)反応の微分断面積を再現できることが分かった。次いで、前平衡過程のより詳しい研究を行った。さらに、多重前平衡過程の検討を1GeVまで行った。
Zrの核子入射・核子放出反応における前平衡過程の角度分布の解析を行った。QMDはパラメータ調整なしに測定された(p,xp')及び(p,xn)反応の微分断面積を再現できることが分かった。次いで、前平衡過程のより詳しい研究を行った。さらに、多重前平衡過程の検討を1GeVまで行った。
Chadwick, M. B.*; 千葉 敏; 仁井田 浩二*; 丸山 敏毅; 岩本 昭
Physical Review C, 52(5), p.2800 - 2803, 1995/11
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:68.53(Physics, Nuclear)中間エネルギー核子入射核反応における前平衡過程からの多重粒子放出反応の研究を、量子論的分子動力学(QMD)と多段階直接反応模型(Feshback-kerman-koonin)理論によって行った。2粒子放出までは両理論による予測値は一致しているが、QMDはさらに3, 4, ...粒子放出まで含めて計算が可能であり、これによって入射粒子のエネルギーとしての多重前平衡過程の重要性を定量的に推定することが可能となった。その結果、50MeV以上では2粒子、180MeV以上では3粒子、約400MeV以上では4粒子放出を前平衡過程に含める必要があることが分かった。
神谷 富裕; 水橋 清; 峰原 英介; 宇都宮 伸宏*; 田中 隆一; 丸山 倫夫*; M.Koh*; 則武 克誌*; 松川 貴*; 杉森 正章*; et al.
JAERI-M 94-033, 108 Pages, 1994/03
早稲田大学と原研は、MeV領域のマイクロビーム技術の開発を目的として、マイクロビーム形成装置を共同で設計・製作し、同大学理工学研究所の1.7MVタンデム加速器のビームラインに設置した。同加速器から引出された3MeV、He のビームを用いてビーム集束化の実験を行い、ターゲットにおいて1.7
のビームを用いてビーム集束化の実験を行い、ターゲットにおいて1.7 1.9
1.9 m
m のサイズのビームスポットを得た。また、ビーム集束研究の基盤技術として、加速器、特にイオン源の電流安定化の検討・精密二連四重極電磁石レンズ(Qレンズ)の磁場解析、振動測定等を行うとともに、マイクロビーム技術開発研究に必要な実験の基礎となるデータを得た。本報告は本装置の概要及び共同研究の成果について述べる。
のサイズのビームスポットを得た。また、ビーム集束研究の基盤技術として、加速器、特にイオン源の電流安定化の検討・精密二連四重極電磁石レンズ(Qレンズ)の磁場解析、振動測定等を行うとともに、マイクロビーム技術開発研究に必要な実験の基礎となるデータを得た。本報告は本装置の概要及び共同研究の成果について述べる。
奥村 進; 上松 敬; 横田 渉; 神谷 富裕; 福田 光宏; 中村 義輝; 奈良 孝幸; 石堀 郁夫; 荒川 和夫; 丸山 正壽*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Cyclotrons and Their Applications, p.648 - 651, 1993/00
JAERI AVFサイクロトロンの制御システムについて説明する。本制御システムは3階層の機能分散型コンピュータシステムである。システム全体の制御やタッチパネルなどのマンマシンインターフェースは VA
VA 3500で管理される。機器のグループごとの制御は、
3500で管理される。機器のグループごとの制御は、 tVAX1000で行われる。各機器は、UDCと呼ぶワンボードマイコンを用いて制御される。サイクロトロンの運転はタッチパネルやロータリーエンコーダを用いて行う。UDCと上位計算機との通信には、Message Treeと呼ぶ多重化方式を採用している。また、未熟練運転員の運転操作を支援するためにエキスパートシステムを開発した。
tVAX1000で行われる。各機器は、UDCと呼ぶワンボードマイコンを用いて制御される。サイクロトロンの運転はタッチパネルやロータリーエンコーダを用いて行う。UDCと上位計算機との通信には、Message Treeと呼ぶ多重化方式を採用している。また、未熟練運転員の運転操作を支援するためにエキスパートシステムを開発した。