Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
藁科 友朗*; 佐藤 朝子*; 比内 浩; Shaikhutdinov, N.*; Shagimardanova, E.*; 森 宙史*; 玉木 聡志*; 斎藤 元文*; 眞田 幸尚; 佐々木 祥人; et al.
Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 90(4), p.e02113-23_1 - e02113-23_23, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Biotechnology & Applied Microbiology)A major incident occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station following the tsunami triggered by the Tohoku-Pacific Ocean Earthquake in March 2011, whereby seawater entered the torus room in the basement of the reactor building. Here, we identify and analyze the bacterial communities in the torus room water and several environmental samples. Samples of the torus room water (1  10
10 Bq
Bq Cs/L) were collected by the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings from two sampling points between 30 cm and 1 m from the bottom of the room (TW1) and the bottom layer (TW2). A structural analysis of the bacterial communities based on 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing revealed that the predominant bacterial genera in TW1 and TW2 were similar. TW1 primarily contained the genus Limnobacter, a thiosulfate-oxidizing bacterium.
Cs/L) were collected by the Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings from two sampling points between 30 cm and 1 m from the bottom of the room (TW1) and the bottom layer (TW2). A structural analysis of the bacterial communities based on 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing revealed that the predominant bacterial genera in TW1 and TW2 were similar. TW1 primarily contained the genus Limnobacter, a thiosulfate-oxidizing bacterium.  -Irradiation tests on Limnobacter thiooxidans, the most closely related phylogenetically found in TW1, indicated that its radiation resistance was similar to ordinary bacteria. TW2 predominantly contained the genus Brevirhabdus, a manganese- oxidizing bacterium. Although bacterial diversity in the torus room water was lower than seawater near Fukushima,
-Irradiation tests on Limnobacter thiooxidans, the most closely related phylogenetically found in TW1, indicated that its radiation resistance was similar to ordinary bacteria. TW2 predominantly contained the genus Brevirhabdus, a manganese- oxidizing bacterium. Although bacterial diversity in the torus room water was lower than seawater near Fukushima,  70% of identified genera were associated with metal corrosion. Latent environment allocation - an analytical technique that estimates habitat distributions and co-detection analyses - revealed that the microbial communities in the torus room water originated from a distinct blend of natural marine microbial and artificial bacterial communities typical of biofilms, sludge, and wastewater. Understanding the specific bacteria linked to metal corrosion in damaged plants is important for advancing decommissioning efforts.
70% of identified genera were associated with metal corrosion. Latent environment allocation - an analytical technique that estimates habitat distributions and co-detection analyses - revealed that the microbial communities in the torus room water originated from a distinct blend of natural marine microbial and artificial bacterial communities typical of biofilms, sludge, and wastewater. Understanding the specific bacteria linked to metal corrosion in damaged plants is important for advancing decommissioning efforts.
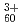 impacts
impacts北山 巧*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 354, p.183 - 186, 2015/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:16.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)According to an inelastic-thermal-spike (i-TS) model, which is regarded as the most promising among several models proposed to explain the formation of an ion track, a part of the energy deposited to electrons in a solid by a swift heavy ion is gradually transferred to target atoms via electron-phonon coupling. The temperature of target atoms rises along the ion path and consequently an ion track is formed when the temperature exceeds the melting point. Therefore, the temperature of target atoms along the ion path is regarded as a key parameter for the i-TS model; however, such a spatiotemporally-localized temperature is difficult to measure because the processes involved occur in a very short period ( 10
10 s) and in a very localized area. In this study, the temperature of target atoms along the ion path is estimated experimentally with transmission-electron-microscope (TEM) observation of desorption of Au nanoclusters (the melting point
s) and in a very localized area. In this study, the temperature of target atoms along the ion path is estimated experimentally with transmission-electron-microscope (TEM) observation of desorption of Au nanoclusters (the melting point  1300 K) on an amorphous Si
1300 K) on an amorphous Si N
N thin film under 1.1-MeV C
thin film under 1.1-MeV C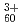 -ion irradiation to the fluence of
-ion irradiation to the fluence of  5
5 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . TEM images show that Au nanoclusters, deposited at the areal density of 1.16
. TEM images show that Au nanoclusters, deposited at the areal density of 1.16 10
10 particles/cm
particles/cm , disappear in a surface area with a diameter of
, disappear in a surface area with a diameter of  20 nm around each ion track, whose diameter is
20 nm around each ion track, whose diameter is  4 nm, after irradiation. This indicates that the temperature at the film surface rises locally to at least 1300 K by the ion bombardment.
4 nm, after irradiation. This indicates that the temperature at the film surface rises locally to at least 1300 K by the ion bombardment.

 ions observed using high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy
ions observed using high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy中嶋 薫*; 森田 陽亮*; 北山 巧*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; 藤居 義和*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 332, p.117 - 121, 2014/08
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:45.19(Instruments & Instrumentation)Our previous observation that an impact of sub-MeV C ion makes an ion track in a thin amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN) film suggests emission of thousands of atoms from the cylindrical region. Sputtering yields of a-SiN films by C
ion makes an ion track in a thin amorphous silicon nitride (a-SiN) film suggests emission of thousands of atoms from the cylindrical region. Sputtering yields of a-SiN films by C ions were evaluated in order to confirm this observation. A-SiN films deposited on Si(001) were irradiated with 540-keV C
ions were evaluated in order to confirm this observation. A-SiN films deposited on Si(001) were irradiated with 540-keV C
 ions at fluences from 2.5
ions at fluences from 2.5 10
10 to 1
to 1 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm . The compositional depth profiles of the irradiated samples were measured with high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy, and the sputtering yields were estimated at 3900
. The compositional depth profiles of the irradiated samples were measured with high-resolution Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy, and the sputtering yields were estimated at 3900  500 N atoms/ion and 1500
500 N atoms/ion and 1500  1000 Si atoms/ion. The sputtering yield of N was two orders of magnitude larger than the elastic sputtering yield by the SRIM code or than the measured electronic sputtering yield of a-SiN by 50-MeV Cu ions previously reported. Such a large sputtering yield cannot be explained either by the elastic sputtering or by the electronic sputtering. However, an estimation of the synergistic effect based on the inelastic thermal spike model roughly explains the observed large sputtering yield, indicating that the synergistic effect of the nuclear and electronic stopping powers plays an important role.
1000 Si atoms/ion. The sputtering yield of N was two orders of magnitude larger than the elastic sputtering yield by the SRIM code or than the measured electronic sputtering yield of a-SiN by 50-MeV Cu ions previously reported. Such a large sputtering yield cannot be explained either by the elastic sputtering or by the electronic sputtering. However, an estimation of the synergistic effect based on the inelastic thermal spike model roughly explains the observed large sputtering yield, indicating that the synergistic effect of the nuclear and electronic stopping powers plays an important role.

 ions
ions中嶋 薫*; 永野 賢悟*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 平田 浩一*; 木村 健二*
Applied Physics Letters, 104(11), p.114103_1 - 114103_4, 2014/03
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:28.98(Physics, Applied)In the secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS), use of cluster ions has an advantage of having a high sensitivity of intact large molecular ions over monatomic ions. This paper presents further yield enhancement of the intact biomolecular ions with measuring the secondary ions emitted from a self-supporting thin film in the forward direction, which is the same direction as primary beams. Phenylalanine amino-acid films deposited on self-supporting thin Si N
N films were bombarded with 5-MeV C
films were bombarded with 5-MeV C
 ions. Secondary ions emitted in the forward and backward directions were measured under the bombardments of the SiN and phenylalanine sides, respectively. The yield of intact phenylalanine molecular ions emitted in the forward direction is about one order of magnitude larger than the backward direction, while fragment ions of phenylalanine molecules are suppressed. This suggests a large potential of transmission cluster-ion SIMS for the analysis of biological materials.
ions. Secondary ions emitted in the forward and backward directions were measured under the bombardments of the SiN and phenylalanine sides, respectively. The yield of intact phenylalanine molecular ions emitted in the forward direction is about one order of magnitude larger than the backward direction, while fragment ions of phenylalanine molecules are suppressed. This suggests a large potential of transmission cluster-ion SIMS for the analysis of biological materials.
 N
N films
films森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 石川 法人; 北條 喜一; 辻本 将彦*; 磯田 正二*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 315, p.142 - 145, 2013/11
被引用回数:13 パーセンタイル:67.08(Instruments & Instrumentation)Thin films of amorphous Si N
N (thickness 5-30 nm) were irradiated with 360-720 keV C
(thickness 5-30 nm) were irradiated with 360-720 keV C
 ions in order to investigate ion track formation. Ion tracks were observed with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). The length and the radial density profile of the track were measured for various combinations of the film thickness and the energy of C
ions in order to investigate ion track formation. Ion tracks were observed with transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM). The length and the radial density profile of the track were measured for various combinations of the film thickness and the energy of C
 ions. The length of the ion track produced in a 30-nm film was found shorter than that in a 20-nm film for the same projectile energy, which indicates that there is surface effect on track formation. This can be qualitatively understood in terms of the energy dissipation process. The observed radial density profile also depends on the film thickness: The apparent density reduction increases with decreasing film thickness. The result can be explained by surface cratering.
ions. The length of the ion track produced in a 30-nm film was found shorter than that in a 20-nm film for the same projectile energy, which indicates that there is surface effect on track formation. This can be qualitatively understood in terms of the energy dissipation process. The observed radial density profile also depends on the film thickness: The apparent density reduction increases with decreasing film thickness. The result can be explained by surface cratering.

 in silicon
in silicon森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 木村 健二*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 167, 2013/01
本研究では、これまで飛程に対するクラスター効果がそれほど大きくないと考えられてきた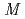


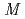
 の場合について、それを実験的に明らかにする。ここで
の場合について、それを実験的に明らかにする。ここで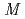
 ,
, 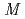
 はそれぞれ入射イオン及び標的を構成する元素の質量数である。あらかじめ表面に非晶質層を作製したSiウェファーに、30keV C
はそれぞれ入射イオン及び標的を構成する元素の質量数である。あらかじめ表面に非晶質層を作製したSiウェファーに、30keV C
 と0.5keV C
と0.5keV C を室温で2
を室温で2 10
10 atoms/cm
atoms/cm 注入し、注入した炭素の深さ分布を、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱法を用いて測定した。C
注入し、注入した炭素の深さ分布を、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱法を用いて測定した。C 注入に対するCの平均深さが6.1nmである一方、C
注入に対するCの平均深さが6.1nmである一方、C 注入の場合は4.0nmとなり、投影飛程に対する顕著なクラスター効果を観測した。
注入の場合は4.0nmとなり、投影飛程に対する顕著なクラスター効果を観測した。
 N
N by TEM
by TEM中嶋 薫*; 森田 陽亮*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 石川 法人; 北條 喜一; 辻本 政彦*; 磯田 正二*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 291, p.12 - 16, 2012/11
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:70.87(Instruments & Instrumentation)非晶質Si N
N 薄膜(厚さ20nm)に120-720keV C
薄膜(厚さ20nm)に120-720keV C
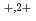 イオンを照射し、透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)で観察した。その結果、結晶性材料と違って像にコントラストがつきにくい非晶質材料中に形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観測できた。さらに、定量的な解析のため、高角散乱環状暗視野走査透過型顕微鏡法(HAADF-STEM)を用いてイオントラックを観察した。その結果、イオントラックの構造は低密度コア(半径約2.5nm)と高密度シェル(幅約2.5nm)からなり、高エネルギー重イオン照射によって非晶質SiO
イオンを照射し、透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)で観察した。その結果、結晶性材料と違って像にコントラストがつきにくい非晶質材料中に形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観測できた。さらに、定量的な解析のため、高角散乱環状暗視野走査透過型顕微鏡法(HAADF-STEM)を用いてイオントラックを観察した。その結果、イオントラックの構造は低密度コア(半径約2.5nm)と高密度シェル(幅約2.5nm)からなり、高エネルギー重イオン照射によって非晶質SiO 中に形成されたイオントラックを小角X線散乱法(SAXS)で観察した結果とよく似ていることがわかった。観測されたイオントラックは表面効果の影響を受けている可能性があるものの、今回の結果は、TEMとHAADF-STEMが非晶質材料中のイオントラックの微細構造を直接観察できることを示すものである。
中に形成されたイオントラックを小角X線散乱法(SAXS)で観察した結果とよく似ていることがわかった。観測されたイオントラックは表面効果の影響を受けている可能性があるものの、今回の結果は、TEMとHAADF-STEMが非晶質材料中のイオントラックの微細構造を直接観察できることを示すものである。

 in silicon
in silicon森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; Vandervorst, W.*; 木村 健二*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 269(19), p.2080 - 2083, 2011/10
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:46.65(Instruments & Instrumentation)あらかじめ表面に非晶質層を作製したSiウェファーに、30keV C
 と0.5keV C
と0.5keV C を室温で2
を室温で2 10
10 atoms/cm
atoms/cm 注入し、注入した炭素の深さ分布を、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱法を用いて測定した。C
注入し、注入した炭素の深さ分布を、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱法を用いて測定した。C
 注入に対するCの平均深さは6.1nmであり、一方、C
注入に対するCの平均深さは6.1nmであり、一方、C 注入の場合は4.0nmとなり、投影飛程に対する顕著なクラスター効果を観測した。
注入の場合は4.0nmとなり、投影飛程に対する顕著なクラスター効果を観測した。
藤枝 信次*; 寺井 真之*; 西藤 哲史*; 戸田 昭夫*; 三浦 喜直*; Liu, Z.*; 寺岡 有殿; 吉越 章隆; Wilde, M.*; 福谷 克之*
ECS Transactions, 6(3), p.185 - 202, 2007/00
先端CMOSのバイアス温度不安定性に関する著者らの研究成果を招待講演で紹介する。25-nm SiO から1.8-nmプラズマ窒化SiON, 1.6-nm HfSiON high-k, 1.5-nm Ni-full-silicide/HfSiONまでというようにゲートスタックがスケーリングされるにつれ、負/正バイアス温度不安定性の原因として不純物,界面ストイキオメトリ,応力等の新しい化学的・物理的要因が現れてきたことを指摘する。
から1.8-nmプラズマ窒化SiON, 1.6-nm HfSiON high-k, 1.5-nm Ni-full-silicide/HfSiONまでというようにゲートスタックがスケーリングされるにつれ、負/正バイアス温度不安定性の原因として不純物,界面ストイキオメトリ,応力等の新しい化学的・物理的要因が現れてきたことを指摘する。
 100
100 systems
systems藤枝 信次*; 三浦 喜直*; 西藤 哲史*; 寺岡 有殿; 吉越 章隆
Microelectronics Reliability, 45(1), p.57 - 64, 2005/01
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:50.73(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)界面準位測定・電子スピン共鳴・シンクロトロン放射光XPSを行って、プラズマ窒化酸化膜の負バイアス温度不安定性(NBTI)が主として界面Siダングリングボンド(P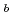 センター)からの水素脱離で起こることを明らかにした。NBTIでは非P
センター)からの水素脱離で起こることを明らかにした。NBTIでは非P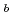 欠陥も生成されるが、窒素ダングリングボンドは含まれない。プラズマ窒化はSiO
欠陥も生成されるが、窒素ダングリングボンドは含まれない。プラズマ窒化はSiO /Si界面のストイキオメトリを劣化・界面準位を増加させるとともに、新たなP
/Si界面のストイキオメトリを劣化・界面準位を増加させるとともに、新たなP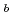 欠陥を生成する。窒化起因NBTIはこの界面欠陥の量的・質的変化に起因すると考えられる。
欠陥を生成する。窒化起因NBTIはこの界面欠陥の量的・質的変化に起因すると考えられる。
 N
N 薄膜中のイオントラックのHAADF-STEM観察
薄膜中のイオントラックのHAADF-STEM観察森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 辻本 政彦*; 磯田 正二*
no journal, ,
物質中に形成されたイオントラックに関する研究は数多くなされているが、非晶質中に形成されたイオントラックの透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)による直接観察は、結晶中のイオントラックとは異なり像にコントラストの差がつきにくいことから、ほとんど報告例がない。しかし、われわれのこれまでの研究で、非晶質中に形成されたイオントラックであってもTEMや高角散乱環状暗視野走査透過型顕微鏡法(HAADF-STEM)を用いて直接観察することが可能であることが明らかになった。実際、試料を傾斜させて観察したTEM像からは形成されたイオントラックの長さを求めることができ、また、HAADF-STEM像からはイオントラック内の原子密度分布を知ることができる。本研究では、さまざまな厚さの非晶質Si N
N 薄膜に種々のエネルギーのC
薄膜に種々のエネルギーのC イオンを照射し、イオントラックの長さやイオントラック内部の原子密度分布がどのように変化するのかを調べたので、その結果を報告する。
イオンを照射し、イオントラックの長さやイオントラック内部の原子密度分布がどのように変化するのかを調べたので、その結果を報告する。
中嶋 薫*; 森田 陽亮*; 北山 巧*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 石川 法人; 北條 喜一; 辻本 将彦*; et al.
no journal, ,
物質にイオンを照射すると、イオンの経路やその周囲の領域で物質の密度変化や構造変化が生じることがあり、物質中に形成されたこのような痕跡をイオントラックと呼ぶ。イオントラックに関する研究では、その形状や大きさ、トラック内の原子密度の分布などを知ることが課題となるため、透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)や高角度暗視野走査型透過電子顕微鏡(HAADF-STEM)などの空間的な分解能をもつ手法で観察することが望まれる。しかし、結晶性の物質中に形成されるイオントラックは結晶性の変化として捉えることができ、TEMによる直接観察が容易であるのに対して、非晶質物質中に形成されるイオントラックはTEM像にコントラストの差がつきにくいことなどから、TEMによる直接観察はほとんど試みられなかった。我々は、非晶質中に形成されるイオントラックの構造等を明らかにするために、厚さ20nmの非晶質SiN薄膜、非晶質SiO 薄膜に120-720keVのC
薄膜に120-720keVのC
 , C
, C
 イオンを照射した試料に対してTEMによる直接観察を行った。その結果、非晶質絶縁体中に形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観察することに初めて成功した。さらに、トラック内の密度分布を定量的に評価するためにHAADF-STEMによる観察を行い、イオントラックの中心部は密度が約20%低下し、それに対して周辺部は約1
イオンを照射した試料に対してTEMによる直接観察を行った。その結果、非晶質絶縁体中に形成されたイオントラックをTEMで直接観察することに初めて成功した。さらに、トラック内の密度分布を定量的に評価するためにHAADF-STEMによる観察を行い、イオントラックの中心部は密度が約20%低下し、それに対して周辺部は約1 2%密度が上昇していることを明らかにした。
2%密度が上昇していることを明らかにした。

 イオン透過によるSiN薄膜上のアミノ酸の前方二次イオン放出
イオン透過によるSiN薄膜上のアミノ酸の前方二次イオン放出永野 賢悟*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一
no journal, ,
近年、医学や生命科学の分野での利用が進んでいる二次イオン質量分析法(SIMS)による生体分子の分析において、多種類のフラグメントイオンが大量に発生すること(フラグメンテーション)が、分子の同定を困難にしている。これまでの研究から、クラスターイオンを一次イオンに用いればフラグメンテーションが避けられ、無傷の分子イオンの収量向上に有効であることがわかっている。本研究では、SIMSにおける無傷の分子イオンのさらなる収量向上を目的として、生体試料の基板に薄膜を使用して、フラグメンテーションが少ないことが期待できるクラスターイオンを背面から照射することで前方の分子イオン収量の向上に関わる有効性を調べた。窒化ケイ素薄膜に生体分子(フェニルアラニン)を蒸着した試料に、薄膜側あるいは生体分子側から5MeVのC
 イオンを照射し、それぞれ前方あるいは後方に放出された二次イオンの質量分析を行った。得られた質量スペクトルを比較した結果、薄膜側から照射して前方に放出された二次イオンはフラグメンテーションが少なく、この手法が無傷の分子イオンの収量向上に有効であることが確かめられた。
イオンを照射し、それぞれ前方あるいは後方に放出された二次イオンの質量分析を行った。得られた質量スペクトルを比較した結果、薄膜側から照射して前方に放出された二次イオンはフラグメンテーションが少なく、この手法が無傷の分子イオンの収量向上に有効であることが確かめられた。

 照射による非晶質SiNのスパッタリング
照射による非晶質SiNのスパッタリング北山 巧*; 森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 松田 誠; 左高 正雄*; 辻本 将彦*; et al.
no journal, ,
サブMeV C イオン照射によって非晶質SiN膜中に形成されるイオントラックの微細構造を調べる研究の過程で、C
イオン照射によって非晶質SiN膜中に形成されるイオントラックの微細構造を調べる研究の過程で、C イオン1個で数千個の標的原子がスパッタリングされることを示唆する実験結果を得た。そこで、この現象を詳細に調べるために、Si基板上の非晶質SiN膜(厚さ30nm)に540keV C
イオン1個で数千個の標的原子がスパッタリングされることを示唆する実験結果を得た。そこで、この現象を詳細に調べるために、Si基板上の非晶質SiN膜(厚さ30nm)に540keV C
 イオンを照射し、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱(RBS)法によってそのスパッタリング収量を評価した結果、およそ5000atoms/ionであった。一方、弾性衝突によるスパッタリングを模擬するSRIMコードで計算すると約80atoms/ionである。このことは、本研究で考えるスパッタリングが単純な弾性衝突によるスパッタリングでは説明できないことを示している。また、SiNの電子的阻止能が540keV C
イオンを照射し、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱(RBS)法によってそのスパッタリング収量を評価した結果、およそ5000atoms/ionであった。一方、弾性衝突によるスパッタリングを模擬するSRIMコードで計算すると約80atoms/ionである。このことは、本研究で考えるスパッタリングが単純な弾性衝突によるスパッタリングでは説明できないことを示している。また、SiNの電子的阻止能が540keV C
 イオンに対する値(8keV/nm)よりも大きい19keV/nmの100MeV Xe
イオンに対する値(8keV/nm)よりも大きい19keV/nmの100MeV Xe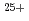 によるスパッタリング収量を同様の方法で測定すると、C
によるスパッタリング収量を同様の方法で測定すると、C 照射に比べて非常に小さくなり、電子的阻止能のみによる単純な電子的スパッタリングでも、540keV C
照射に比べて非常に小さくなり、電子的阻止能のみによる単純な電子的スパッタリングでも、540keV C
 によるスパッタリング収量は説明できない。そこで、本発表では電子的阻止能と核的阻止能の相乗効果により説明が可能であることを議論する。
によるスパッタリング収量は説明できない。そこで、本発表では電子的阻止能と核的阻止能の相乗効果により説明が可能であることを議論する。
 イオンを用いたアミノ酸の透過二次イオン質量分析
イオンを用いたアミノ酸の透過二次イオン質量分析中嶋 薫*; 永野 賢悟*; 鈴木 基史*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 平田 浩一*; 木村 健二*
no journal, ,
高分子/生体分子の二次イオン質量分析(SIMS)において高感度の測定を行うためには、目的の分子を壊さずに効率よくイオン化して放出させることが重要である。そこで分子イオンの収量が多い透過SIMSに、分子の断片化抑制効果が高いクラスターイオンを一次イオンとして用いる方式の有効性について調べた。非晶質SiN自立薄膜にアミノ酸(フェニルアラニン)薄膜を真空蒸着した試料に、SiN側から5MeV C
 イオンを照射し、透過したイオンによって試料より前方に放出される二次イオンを質量分析し、フェニルアラニン側から照射して後方に二次イオンが放出される場合と比べた。その結果、分子イオンの収量向上及び分子イオンの断片化抑制の効果が高いことが認められた。これは、フェニルアラニン薄膜表面において60個の炭素イオン/原子が十分に近接している状態(後方放出の場合)か適度に離れている状態(前方放出の場合)かで、入射イオンによるエネルギー付与密度が異なっていることを考慮すると定性的に説明できる。これによりMeV領域の高速C
イオンを照射し、透過したイオンによって試料より前方に放出される二次イオンを質量分析し、フェニルアラニン側から照射して後方に二次イオンが放出される場合と比べた。その結果、分子イオンの収量向上及び分子イオンの断片化抑制の効果が高いことが認められた。これは、フェニルアラニン薄膜表面において60個の炭素イオン/原子が十分に近接している状態(後方放出の場合)か適度に離れている状態(前方放出の場合)かで、入射イオンによるエネルギー付与密度が異なっていることを考慮すると定性的に説明できる。これによりMeV領域の高速C イオンを用いて二次イオンを前方に放出させる透過SIMSが高分子/生体分子の分析に対して有望な手法であることを示した。
イオンを用いて二次イオンを前方に放出させる透過SIMSが高分子/生体分子の分析に対して有望な手法であることを示した。
 イオン照射によって形成された非晶質Si
イオン照射によって形成された非晶質Si N
N 薄膜中のイオントラックのTEM観察
薄膜中のイオントラックのTEM観察森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 辻本 政彦*; 磯田 正二*
no journal, ,
非晶質Si N
N 薄膜に120-720keV C
薄膜に120-720keV C
 , C
, C
 イオンを照射し、透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)で観察した。その結果、非晶質材料中に形成されたイオントラックを初めてTEMで直接観察した。さらに、定量的な解析のため、高角散乱環状暗視野走査透過型電子顕微鏡法(HAADF-STEM)を用いてイオントラックを観測した。観測されたイオントラックは低密度コア(半径
イオンを照射し、透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)で観察した。その結果、非晶質材料中に形成されたイオントラックを初めてTEMで直接観察した。さらに、定量的な解析のため、高角散乱環状暗視野走査透過型電子顕微鏡法(HAADF-STEM)を用いてイオントラックを観測した。観測されたイオントラックは低密度コア(半径 4nm)と高密度シェル(幅
4nm)と高密度シェル(幅 4nm)からなり、高エネルギー重イオン照射によって非晶質SiO
4nm)からなり、高エネルギー重イオン照射によって非晶質SiO 中に形成されたイオントラックを小角X線散乱法(XAXS)で観測した結果とよく似ている。このことは、材料・照射イオン種によらず、コア-シェル構造が非晶質材料中に形成されるイオントラックの普遍的な特徴であることを示唆する。観測されたイオントラックの半径は、今回のエネルギー領域(電子的阻止能は急激に増大するが、核的阻止能は減少する)では入射イオンのエネルギーにほとんど依存しなかった。このことは、核的阻止能もまたイオントラック形成にかかわり、電子的阻止能よりもその効果が高いことを示す。
中に形成されたイオントラックを小角X線散乱法(XAXS)で観測した結果とよく似ている。このことは、材料・照射イオン種によらず、コア-シェル構造が非晶質材料中に形成されるイオントラックの普遍的な特徴であることを示唆する。観測されたイオントラックの半径は、今回のエネルギー領域(電子的阻止能は急激に増大するが、核的阻止能は減少する)では入射イオンのエネルギーにほとんど依存しなかった。このことは、核的阻止能もまたイオントラック形成にかかわり、電子的阻止能よりもその効果が高いことを示す。

 イオン透過によるSiN薄膜上のアミノ酸の前方二次イオン放出
イオン透過によるSiN薄膜上のアミノ酸の前方二次イオン放出永野 賢悟*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一
no journal, ,
近年、医学や生命科学の分野での利用が進んでいる二次イオン質量分析法(SIMS)による生体分子の分析において、多種類のフラグメントイオンが大量に発生すること(フラグメンテーション)が、分子の同定を困難にしている。これまでの研究から、クラスターイオンを一次イオンに用いればフラグメンテーションが避けられ、無傷の分子イオン収量の向上に有効であることが分かっている。その一方で、炭素薄膜上に生体分子を塗布し、炭素薄膜側から一次イオンを照射した時に前方に放出される二次イオンと、生体分子側から一次イオンを照射した時に後方に放出される二次イオンとでは、前者で収量が高いことが報告されている。そこで本研究では、これらの手法を組み合わせ、無傷の分子イオン収量のさらなる向上を目的とした。窒化ケイ素薄膜上に生体分子のフェニルアラニンを蒸着した試料に、薄膜側及び生体分子側から5MeVのC
 を照射し、前方及び後方に放出された二次イオンの質量分析を行った。得られた質量スペクトルを比較した結果、薄膜側から照射して前方に放出された二次イオンの方がフラグメンテーションが少なく、無傷の分子イオン収量の向上に有効であることが確かめられた。
を照射し、前方及び後方に放出された二次イオンの質量分析を行った。得られた質量スペクトルを比較した結果、薄膜側から照射して前方に放出された二次イオンの方がフラグメンテーションが少なく、無傷の分子イオン収量の向上に有効であることが確かめられた。
藁科 友朗*; 佐藤 朝子*; Shagimardanova, E.*; 丸山 茂徳*; 森 宙史*; 鳴海 一成*; Gusev, O.*; 斎藤 元文*; 眞田 幸尚; 佐々木 祥人; et al.
no journal, ,
原子炉内の大量の放射性物質は、福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の廃止措置を妨げている。この研究の目的は、(1)1F周囲の環境を分析して原子炉内の滞留水に存在する可能性のある微生物を調査すること、(2)微生物腐食の原因となる細菌を特定することの2つである。環境サンプルは、1Fに関連する3つの場所、敷地境界南の土壌、海岸から3km離れた表層海水、および福海底土壌から得られた。16S rRNAアンプリコンシーケンシングの結果、土壌サンプルから少なくとも17の門が確認された。最も豊富な門はアシドバクテリアとプロテオバクテリアであり、門レベルでの群集構造は、福島の低放射能の土壌からのものと類似していた。海水には、少なくとも9つの門が確認された。プロテオバクテリアとシアノバクテリアが最も豊富である。門レベルでの群構造も日立港沖の結果と類比していた。さらに、シュードモナスなどの腐食誘起細菌とディノコッカスなどの耐放射線性細菌が、土壌と海水の両方で発見された。ただし、腐食誘起細菌の相対的存在量は、全体量の1%未満である。原子炉内は還元雰囲気,嫌気性,暗所であるため、微生物群の分布も変化することが予想される。
 イオンの投影飛程に対するクラスター効果
イオンの投影飛程に対するクラスター効果森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一
no journal, ,
本研究では、これまで飛程に対するクラスター効果がそれほど大きくないと考えられてきた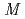


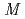
 の場合について、それを実験的に明らかにする。ここで
の場合について、それを実験的に明らかにする。ここで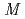
 ,
, 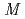
 はそれぞれ入射イオン及び標的を構成する元素の質量数である。あらかじめ表面に非晶質層を作製したSiウェファーに、30keV C
はそれぞれ入射イオン及び標的を構成する元素の質量数である。あらかじめ表面に非晶質層を作製したSiウェファーに、30keV C
 と0.5keV C
と0.5keV C を室温で2
を室温で2 10
10 atoms/cm
atoms/cm 注入し、注入した炭素の深さ分布を、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱法を用いて測定した。C
注入し、注入した炭素の深さ分布を、高分解能ラザフォード後方散乱法を用いて測定した。C 注入に対するCの平均深さが6.1nmである一方、C
注入に対するCの平均深さが6.1nmである一方、C 注入の場合は4.0nmとなり、投影飛程に対する顕著なクラスター効果を観測した。
注入の場合は4.0nmとなり、投影飛程に対する顕著なクラスター効果を観測した。
森田 陽亮*; 中嶋 薫*; 鈴木 基史*; 木村 健二*; 鳴海 一雅; 齋藤 勇一; 石川 法人; 北條 喜一; 辻本 政彦*; 磯田 正二*
no journal, ,
非晶質Si N
N 薄膜に120-720keV C
薄膜に120-720keV C
 , C
, C
 イオンを照射し、非晶質材料中に形成されたイオントラックを透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)で直接観測した。さらに、定量的な解析のため、高角散乱環状暗視野走査透過型顕微鏡法(HAADF-STEM)を用いてイオントラックを観測した。その結果、イオントラックの構造は低密度コア(半径約2.5nm)と高密度シェル(幅約2.5nm)からなり、高エネルギー重イオン照射によって非晶質SiO
イオンを照射し、非晶質材料中に形成されたイオントラックを透過型電子顕微鏡(TEM)で直接観測した。さらに、定量的な解析のため、高角散乱環状暗視野走査透過型顕微鏡法(HAADF-STEM)を用いてイオントラックを観測した。その結果、イオントラックの構造は低密度コア(半径約2.5nm)と高密度シェル(幅約2.5nm)からなり、高エネルギー重イオン照射によって非晶質SiO 中に形成されたイオントラックを小角X線散乱法(SAXS)で観測した結果とよく似ていることがわかった。このことは、材料と照射イオン種によらず、コア-シェル構造が非晶質材料中に形成されるイオントラックの普遍的な特徴であることを示唆する。また、イオントラック半径の観測から、今回のエネルギー領域では、核的阻止能もまたトラック形成にかかわり、電子的阻止能よりも効果が高いことが見いだされた。
中に形成されたイオントラックを小角X線散乱法(SAXS)で観測した結果とよく似ていることがわかった。このことは、材料と照射イオン種によらず、コア-シェル構造が非晶質材料中に形成されるイオントラックの普遍的な特徴であることを示唆する。また、イオントラック半径の観測から、今回のエネルギー領域では、核的阻止能もまたトラック形成にかかわり、電子的阻止能よりも効果が高いことが見いだされた。