Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Papadopoulos, A.*; Kyriakou, I.*; 松谷 悠佑; Cort s-Giraldo, M. A.*; Galocha-Oliva, M.*; Plante, I.*; Steward, R. D.*; Tran, N. H.*; Li, W.*; Daglis, I. A.*; et al.
s-Giraldo, M. A.*; Galocha-Oliva, M.*; Plante, I.*; Steward, R. D.*; Tran, N. H.*; Li, W.*; Daglis, I. A.*; et al.
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 64(1), p.117 - 135, 2025/03
生物学的影響を決定する放射線の線質は、一般的に微視的線量付与(特に線量平均線エネルギーy )に関連付けられる。y
)に関連付けられる。y 値の計算には、洗練されたモンテカルロ飛跡構造シミュレーション(MCTS)コードや経験的な解析モデルの使用が有効であるが、MCTSコードや解析モデルの種類により、y
値の計算には、洗練されたモンテカルロ飛跡構造シミュレーション(MCTS)コードや経験的な解析モデルの使用が有効であるが、MCTSコードや解析モデルの種類により、y 推定値は変化する。本研究では、放射線防護、宇宙応用、放射線治療などで重要とされる1MeVから1GeV陽子線を対象とし、様々なMCTSコード(PHITS, RITRACK, Geant4-DNA)や解析モデル(改良Xapsosモデル)等により計算される液相水中のy
推定値は変化する。本研究では、放射線防護、宇宙応用、放射線治療などで重要とされる1MeVから1GeV陽子線を対象とし、様々なMCTSコード(PHITS, RITRACK, Geant4-DNA)や解析モデル(改良Xapsosモデル)等により計算される液相水中のy 値と、その値により計算される放射線防護品質係数Q値を比較した。その結果、各MCTSコードや改良Xapsosモデルにより推定されたy
値と、その値により計算される放射線防護品質係数Q値を比較した。その結果、各MCTSコードや改良Xapsosモデルにより推定されたy 値は10から20%未満のレベルで良い一致を示し、改良Xapsosモデルにより推定されるQ値もMCTSに基づく予測値と良い一致を示した。これらの知見により、解析モデルは膨大な時間とCPUを必要とするMCTSの代替として使用され、実用的かつ高精度に線質係数とリスク評価を進めることができることがわかった。
値は10から20%未満のレベルで良い一致を示し、改良Xapsosモデルにより推定されるQ値もMCTSに基づく予測値と良い一致を示した。これらの知見により、解析モデルは膨大な時間とCPUを必要とするMCTSの代替として使用され、実用的かつ高精度に線質係数とリスク評価を進めることができることがわかった。
Ulanowski, A.*; 佐藤 達彦; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Balonov, M.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 64(1), p.105 - 115, 2025/03
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:87.70(Biology)Protection and operational dosimetric quantities for human external exposure have been compared for situations of outdoor exposure to natural background radiation represented by gamma radiation of primordial and cosmogenic radionuclides and by radiations produced by the galactic cosmic rays in the earth atmosphere. Calculations were performed using the data from publications of ICRU and ICRP for global geographical grid of marine and terrestrial locations. Using modelled fluence spectra of natural cosmogenic and terrestrial background radiation, the ratios of the protection to operational quantities were calculated, demonstrating the effect of high-LET neutron component on the ratios of effective dose to absorbed dose or kerma in air. The influence of the neutron component was found to be stronger for high-altitude terrestrial locations and for terrestrial and marine locations at higher geographic latitudes. The computed ratios can be used for interpretation of the measured ambient dose rate data and calculation of effective doses in radiological protection tasks or assessment of public exposure to natural and anthropogenic sources of radiation.
Muhialdin, B. J.*; Sanchez, C. F.*; 中川 洋; Ubbink, J.*
Food Biophysics, 19(1), p.172 - 181, 2024/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:19.17(Food Science & Technology)分子間相互作用が押し出しエンドウタンパク単離物(PPI)の物性に及ぼす影響について、マトリックスプレミックスに相互作用調整化合物を添加し、その結果生じる機械的および物理化学的特性の変化を調べることにより調査した。リン酸ナトリウム、尿素、ドデシル硫酸ナトリウム、 -メルカプトエタノールのいずれかを含むPPIと、4つの化合物すべてを含むPPI、脱イオン水のみを含むPPIのブレンドを、実験室規模の二軸スクリュー押出機を用いて細いストランド状に押し出した。テクスチャー・プロファイル分析から得られた硬度は、
-メルカプトエタノールのいずれかを含むPPIと、4つの化合物すべてを含むPPI、脱イオン水のみを含むPPIのブレンドを、実験室規模の二軸スクリュー押出機を用いて細いストランド状に押し出した。テクスチャー・プロファイル分析から得られた硬度は、 -メルカプトエタノールと4種類の化学物質すべてを用いて押し出したマトリックスが最も低く、コントロール・サンプルが最も高かった。マトリックスの保水性は、
-メルカプトエタノールと4種類の化学物質すべてを用いて押し出したマトリックスが最も低く、コントロール・サンプルが最も高かった。マトリックスの保水性は、 -メルカプトエタノール含有マトリックスが最も低い。この結果から、テクスチャー化PPIにおけるジスルフィド結合の重要性が確認され、疎水性および静電的相互作用が、押し出されたPPIマトリックスの特性を調節する上で補助的な役割を果たしていることが示された。
-メルカプトエタノール含有マトリックスが最も低い。この結果から、テクスチャー化PPIにおけるジスルフィド結合の重要性が確認され、疎水性および静電的相互作用が、押し出されたPPIマトリックスの特性を調節する上で補助的な役割を果たしていることが示された。
Paulbeck, C. J.*; 佐藤 達彦; 船本 幸代*; Lee, C.*; Griffin, K. T.*; Cullings, H. M.*; Egbert, S. D.*; 遠藤 章; Hertel, N. E.*; Bolch, W. E.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 62(3), p.317 - 329, 2023/08
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:37.05(Biology)胎児被ばくした原爆生存者に対する線量評価は、放射線被ばくリスクを評価する上で極めて重要となる。原子力機構、放射線影響研究所、フロリダ大学、米国がんセンターらで構成する研究チームは、これまで、1945年の日本人体型を反映した成人、小児及び胎児を含む妊婦の人体模型を作成し、前方照射や等方照射など理想的な照射条件に対してその被ばく線量を評価してきた。本研究では、原爆線量評価システムDS02に含まれる現実的な照射条件に対して、胎児及び母体の被ばく線量を評価した。その結果、現実的な照射条件においては、胎児の臓器線量は、胎児内での臓器の位置や週齢に大きく依存することが分かった。このような胎児に対する詳細被ばく線量解析結果は、将来の胎児被ばくリスク評価モデルの改訂に役立つと考えられる。
Griffin, K. T.*; 佐藤 達彦; 船本 幸代*; Chizhov, K.*; Domal, S.*; Paulbeck, C.*; Bolch, W.*; Cullings, H. M.*; Egbert, S. D.*; 遠藤 章; et al.
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 61(1), p.73 - 86, 2022/03
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:59.90(Biology)原爆生存者に対する線量評価は、放射線被ばくリスクを評価する上で極めて重要となる。原子力機構,放射線影響研究所,フロリダ大学,米国がんセンターらで構成する研究チームは、これまで、1945年の日本人体型を反映した成人,小児及び胎児を含む妊婦の人体模型を作成し、前方照射や等方照射など理想的な照射条件に対してその臓器線量を評価してきた。本研究では、原爆線量評価システムDS02に含まれる現実的な20照射条件に対して、成人及び小児の臓器線量を詳細に評価した。その結果、全線量は、造血組織,結腸,胃壁に関しては、従来手法(DS92)と比較してそれぞれ20%, 20%、及び15%の違いがあることが分かった。また中性子線量だけに着目すると、最大で2倍程度の差があることが分かった。
越智 康太郎; 舟木 泰智; 吉村 和也; 飯本 武志*; 松田 規宏; 眞田 幸尚
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 61(1), p.147 - 159, 2022/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:24.02(Biology)The ambient dose equivalent conversion coefficient (ADC) for converting from the radionuclide inventory to the ambient dose equivalent rate (ambient dose rate) is used to estimate exposure doses. We have collected actual data, ambient dose rate at 1 m above the ground level and vertical distribution of radiocesium in the soil sample, around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). The actual data during FY2011-FY2019 is used for confirming the validity of ADC. The ADC assuming the vertical distribution of radioceisum were calculated with relaxation mass depth. Good correlation was found between the calculated inventory by the ambient dose rate and ADC in this study and actual radiocesium inventory. Therefore, the ADC in this study sufficiently reflected the actual deposition status of radiocesium on the ground surface after the FDNPP accident.
山本 直樹*; 中西 真大*; Rajan, R.*; 中川 洋
Biophysics and Physicobiology (Internet), 18, p.284 - 288, 2021/12
水は生物にとって必要不可欠な溶媒である。われわれの体の6割は水で構成されており、水が不足すると多くの致命的な問題が発生する。また、タンパク質の機能は、その表面に水分子を伴って初めて発揮されることが知られている。したがって、水と生体成分がどのように相互作用しているかを、構造とダイナミクスの観点から理解することが不可欠である。凍結は水の基本的かつ単純な現象であるため、そのためのプローブとして利用することができる。さらに、細胞やタンパク質を低温下で保存することは、多くのアプリケーションにとって非常に重要であり、その結果、凍結によって無数の望ましくない結果が引き起こされることになる。
Petoussi-Henss, N.*; 佐藤 大樹; Schlattl, H.*; Zankl, M.*; Spielman, V.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 60(1), p.93 - 113, 2021/03
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:16.37(Biology)環境中の天然及び人工放射性核種に対する公衆の外部被ばく線量評価に資する線量換算係数の整備を進めている。これまでの研究で、年齢別の標準体型人を対象とした線量換算係数データベースを構築した。本研究では、新たに妊婦及び胎児を対象としたデータ整備を実施した。放射性核種は土壌深さ0.5g cm もしくは大気に一様分布していると仮定し、土壌分布に対しては原子力機構の開発する放射線輸送計算コードPHITSを用いて放射線場を解析し、大気分布に対しては既存研究におけるYURIコードの解析結果を採用した。この放射線場中に、妊婦及び胎児の解剖学的構造を精密に再現した人体数値模型を配置し、電子・光子輸送計算コードEGSを用いて臓器吸収線量を計算することで線量換算係数を導出した。本研究で整備した線量換算係数を用いることで、環境に分布した放射性核種の放射能濃度の測定値から迅速に妊婦と胎児の臓器吸収線量を評価することが可能となった。
もしくは大気に一様分布していると仮定し、土壌分布に対しては原子力機構の開発する放射線輸送計算コードPHITSを用いて放射線場を解析し、大気分布に対しては既存研究におけるYURIコードの解析結果を採用した。この放射線場中に、妊婦及び胎児の解剖学的構造を精密に再現した人体数値模型を配置し、電子・光子輸送計算コードEGSを用いて臓器吸収線量を計算することで線量換算係数を導出した。本研究で整備した線量換算係数を用いることで、環境に分布した放射性核種の放射能濃度の測定値から迅速に妊婦と胎児の臓器吸収線量を評価することが可能となった。
小橋 佑介*; 片岡 隆浩*; 神崎 訓枝; 石田 毅*; 迫田 晃弘; 田中 裕史; 石森 有; 光延 文裕*; 山岡 聖典*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 59(3), p.473 - 482, 2020/08
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:31.37(Biology)ラドン療法は古くから酸化ストレス関連疾患に用いられて、生体におけるラドン曝露の効果が研究されてきた。しかし、ラドンの同位体であるトロンの効果はまだ十分に調査されていない。本研究では酸化ストレスに注目して、マウス臓器におけるラドンやトロン吸入の生体影響を比較した。オスのBALB/cマウスを15グループに分けて(疑似吸入、ラドン吸入500Bq/m または2000Bq/m
または2000Bq/m 、トロン吸入500Bq/m
、トロン吸入500Bq/m または2000 Bq/m
または2000 Bq/m )、吸入後すぐに、生化学分析のために様々な組織を採取した。その結果、いくつかの条件下でトロン吸入によってスーパーオキシドディスムターゼや総グルタチオン量が有意に増加し、過酸化脂質量が有意に減少した。加えて、ラドンとトロンの間で異なる濃度と吸入時間で同様の効果が見られ、トロン吸入も酸化ストレスに対して抗酸化機能を高めることが示唆された。しかしながら、ラドンとトロンの性質の差を考えた慎重な解析評価が必要である
)、吸入後すぐに、生化学分析のために様々な組織を採取した。その結果、いくつかの条件下でトロン吸入によってスーパーオキシドディスムターゼや総グルタチオン量が有意に増加し、過酸化脂質量が有意に減少した。加えて、ラドンとトロンの間で異なる濃度と吸入時間で同様の効果が見られ、トロン吸入も酸化ストレスに対して抗酸化機能を高めることが示唆された。しかしながら、ラドンとトロンの性質の差を考えた慎重な解析評価が必要である
Kofler, C.*; Domal, S.*; 佐藤 大樹; Dewji, S.*; Eckerman, K.*; Bolch, W. E.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 58(4), p.477 - 492, 2019/11
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:47.51(Biology)現行の放射線防護における線量評価では、国際放射線防護委員会(ICRP)が定義する実効線量等を用いる。この実効線量は、ICRPが定義する各年齢の標準体型を模擬する人体模型により計算される臓器吸収線量から導出される。一方、標準体型から逸脱した個人を考慮した線量推定において、標準体型に基づく実効線量の適用の妥当性が議論されてきた。本研究では、標準体型以外の人体模型により、臓器線量を基本として実効線量と同様の手法で導出される損害加重線量を解析した。ここでは、土壌に沈着した放射性核種からの外部被ばく条件に対し、米国立健康統計学センターが報告する身長及び体重を網羅した351体の人体数値模型を適用した。また、ICRPが与える核種崩壊データベースから、33種類の核種を評価対象とした。その結果、環境での外部被ばくで問題となる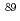 Sr,
Sr,  Sr,
Sr,  Cs及び
Cs及び Iに対して、1歳児の実効線量と損害加重線量は5%以内で一致した。一方、年齢とともに、標準体型からの逸脱による実効線量と損害加重線量の差は大きくなり、成人では+15%から-40%の偏差を持つことが明らかになった。本データは、個人の体格特性に着目する線量再構築や疫学調査における線量推定の精度を向上させるものである。
Iに対して、1歳児の実効線量と損害加重線量は5%以内で一致した。一方、年齢とともに、標準体型からの逸脱による実効線量と損害加重線量の差は大きくなり、成人では+15%から-40%の偏差を持つことが明らかになった。本データは、個人の体格特性に着目する線量再構築や疫学調査における線量推定の精度を向上させるものである。
中川 洋; 片岡 幹雄*
Biophysics and Physicobiology (Internet), 16, p.213 - 219, 2019/00
非干渉性中性子散乱はピコ~ナノ秒スケールの蛋白質ダイナミクスを調べる便利な実験手法のひとつである。この時間スケールでは、蛋白質ダイナミクスは水和と強くカップルしていて、動力学転移として観測される。非干渉性中性子散乱は水素原子の非干渉性散乱断面機が大きいため、水素原子のダイナミクスに敏感である。したがって、水和蛋白質の中性子非干渉性散乱は水和水を含めた蛋白質についての全体的なダイナミクスの情報を与える。水和水ダイナミクスを分離することは、水和に関連した蛋白質ダイナミクスを理解するために重要である。軽水・重水の交換は蛋白質と水和水のダイナミクスを分離して観測するための中性子非干渉性散乱実験において有効な方法である。中性子散乱はバンホッフ時空間相関関数と直接関係していて、分子シミュレーションによって定量的に計算できる。水和水の拡散と水素結合ダイナミクスは分子シミュレーションによって解析できる。動力学転移は水和によって生じるため、非干渉性中性子散乱データを解釈するためには、水和に関連したタンパク質ダイナミクスにおける動的なカップリングのメカニズムを解析するのに分子シミュレーションは便利である。本研究では、我々は非干渉性中性子散乱における軽水・重水の交換の手法としての利点と、蛋白質と水和水を研究するツールとして非干渉性中性子散乱と分子シミュレーションの互換性を示す。
石森 有; 田中 裕史; 迫田 晃弘; 片岡 隆浩*; 山岡 聖典*; 光延 文裕*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 56(2), p.161 - 165, 2017/05
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:40.96(Biology)吸入ラドンの体内動態を検討するため、約1MBq/m のラドンに曝露されたマウスの組織・臓器におけるラドン濃度を測定した。血液中のラドン濃度は液体シンチレーションカウンタで、組織・臓器は井戸型高純度半導体ゲルマニウム検出器で測定した。ラドン1MBq/m
のラドンに曝露されたマウスの組織・臓器におけるラドン濃度を測定した。血液中のラドン濃度は液体シンチレーションカウンタで、組織・臓器は井戸型高純度半導体ゲルマニウム検出器で測定した。ラドン1MBq/m に曝露されたとき、血液中濃度の飽和値は0.410
に曝露されたとき、血液中濃度の飽和値は0.410 0.016Bq/gであった。分配係数は、肝臓で0.74
0.016Bq/gであった。分配係数は、肝臓で0.74 0.19、筋肉で0.46
0.19、筋肉で0.46 0.13、脂肪組織で9.09
0.13、脂肪組織で9.09 0.49、その他臓器で0.22
0.49、その他臓器で0.22 0.04であった。ラドンの体内動態モデルで上記結果を再現することにより、血液-空気間の分配係数は0.414と評価した。ラドン曝露中の血液中濃度の時間変動も評価した。また、本研究と先行研究の結果を詳細に比較検討した。
0.04であった。ラドンの体内動態モデルで上記結果を再現することにより、血液-空気間の分配係数は0.414と評価した。ラドン曝露中の血液中濃度の時間変動も評価した。また、本研究と先行研究の結果を詳細に比較検討した。
松尾 龍人; 荒田 敏昭*; 小田 俊郎*; 中島 健次; 河村 聖子; 菊地 龍弥; 藤原 悟
Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports (Internet), 6, p.220 - 225, 2016/07
Hydration water is essential for a protein to perform its biological function properly. In this study, the dynamics of hydration water around F-actin and myosin subfragment-1 (S1), which are the partner proteins playing a major role in various cellular functions related to cell motility, was characterized by incoherent quasielastic neutron scattering (QENS). The QENS spectra of hydration water around F-actin and S1 provided the translational diffusion coefficient, the residence time, and the rotational correlation time. The differences in these parameters indicate a significant difference in mobility of the hydration water between S1 and F-actin: S1 has the typical hydration water, the mobility of which is reduced compared with that of bulk water, while F-actin has the unique hydration water, the mobility of which is close to that of bulk water rather than the typical hydration water around proteins.
松尾 龍人; 武田 壮一*; 小田 俊郎*; 藤原 悟
Biophysics and Physicobiology (Internet), 12, p.145 - 158, 2015/12
Troponin (Tn), consisting of three subunits, TnC, TnI, and TnT, is a protein that plays a major role in regulation of muscle contraction. Various mutations of Tn cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Here we focus on the mutations E244D and K247R of TnT, which induce an increase in the maximum tension of cardiac muscle without changes in Ca -sensitivity, and carried out small-angle X-ray scattering experiments on the Tn core domain containing the wild type subunits and those containing the mutant TnT in the absence and presence of Ca
-sensitivity, and carried out small-angle X-ray scattering experiments on the Tn core domain containing the wild type subunits and those containing the mutant TnT in the absence and presence of Ca . Changes in the overall shape induced by the mutations were detected for the first time by the changes in the radius of gyration and the maximum dimension between the wild type and the mutants. Analysis by model calculations shows that TnC adopts a dumbbell structure regardless of the mutations, and that the mutations change the distributions of the conformational ensembles so that the flexible N- and C-terminal regions of TnT become close to the center of the whole molecule.
. Changes in the overall shape induced by the mutations were detected for the first time by the changes in the radius of gyration and the maximum dimension between the wild type and the mutants. Analysis by model calculations shows that TnC adopts a dumbbell structure regardless of the mutations, and that the mutations change the distributions of the conformational ensembles so that the flexible N- and C-terminal regions of TnT become close to the center of the whole molecule.
迫田 晃弘; 石森 有; 山岡 聖典*; 片岡 隆浩*; 光延 文裕*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 52(3), p.389 - 395, 2013/08
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:43.11(Biology)本研究では、気道内腔の空気中ラドンに起因した肺への吸収線量を計算した。本計算は、ラドン曝露実験でよく使用されてきたマウスとラットを対象に行ったが、参考のため、ヒトに対しても行った。まず、気道内腔と環境中のラドン濃度が等しいと仮定して、気道における子孫核種の生成やクリアランスをモデル化し、子孫核種の放射能を計算した。これより、分泌細胞と基底細胞を標的細胞として考え、3つに分割した肺の各領域又は全肺における吸収線量率を求めた。その結果、いずれの吸収線量率も、ヒト,ラット,マウスの順で高かった。例えば、ヒト,ラット,マウスの全肺の線量率はそれぞれ、59.9, 41.7, 25.4pGy/(Bq/m )/hであった。これら数値は、他の2種類のラドン曝露形態による線量率とも比較した。いずれの生物種においても、環境中のラドン子孫核種を直接吸入した場合で線量率が最も高いことを確認した。本研究で求めた肺の吸収線量率は、子孫核種の直接吸入によるそれと比べて、マウスで550倍、ラットで200倍、ヒトで70倍ほど低かった。本計算結果の数値は比較的小さいが、ラドンや子孫核種の吸入による線量の理解にも貢献すると考えられる。
)/hであった。これら数値は、他の2種類のラドン曝露形態による線量率とも比較した。いずれの生物種においても、環境中のラドン子孫核種を直接吸入した場合で線量率が最も高いことを確認した。本研究で求めた肺の吸収線量率は、子孫核種の直接吸入によるそれと比べて、マウスで550倍、ラットで200倍、ヒトで70倍ほど低かった。本計算結果の数値は比較的小さいが、ラドンや子孫核種の吸入による線量の理解にも貢献すると考えられる。
松尾 龍人; 荒田 敏昭*; 小田 俊郎*; 藤原 悟
Biophysics, 9, p.99 - 106, 2013/07
Hydration structures around F-actin and myosin subfragment-1 (S1), which play central roles as counterparts in muscle contraction, were investigated by small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). The radius of gyration of S1 was evaluated to be 41.3  1.1
1.1  for SAXS, 40.1
for SAXS, 40.1  3.0
3.0  for SANS in H
for SANS in H O, and 37.8
O, and 37.8  0.8
0.8  for SANS in D
for SANS in D O, respectively. The values of the cross-sectional radius of gyration of F-actin were 25.4
O, respectively. The values of the cross-sectional radius of gyration of F-actin were 25.4  0.03
0.03  for SAXS, 23.4
for SAXS, 23.4  2.4
2.4  for SANS in H
for SANS in H O, and 22.6
O, and 22.6  0.6
0.6  for SANS in D
for SANS in D O, respectively. Analysis showed that the hydration shell of S1 has the average density 10-15% higher than bulk water, being the typical hydration shell, while the hydration shell of F-actin has the average density more than 19% higher than bulk water, indicating that F-actin has a denser, unusual hydration structure. The results indicate a difference in the hydration structures around F-actin and S1.
O, respectively. Analysis showed that the hydration shell of S1 has the average density 10-15% higher than bulk water, being the typical hydration shell, while the hydration shell of F-actin has the average density more than 19% higher than bulk water, indicating that F-actin has a denser, unusual hydration structure. The results indicate a difference in the hydration structures around F-actin and S1.
椎名 卓也; 渡辺 立子; 白石 伊世; 鈴木 雅雄*; 菅谷 雄基; 藤井 健太郎; 横谷 明徳
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 52(1), p.99 - 112, 2013/03
被引用回数:23 パーセンタイル:63.72(Biology)Plasmid DNA was irradiated with carbon ions or X-rays in solutions containing several concentrations of Tris (0.66-200 mM) to determine the yield of abasic (AP) sites and the effect of scavenging capacity. The yield of AP sites, detected as single strand breaks (SSB) after digestion with E. coli endonucrease IV (Nfo), was compared with that of SSB and base lesions. At higher concentrations of Tris, the yields of single or clustered AP sites were significantly lower than those of single or clustered base lesions. The dependence of the yield of AP sites on scavenging capacity was similar to that of prompt strand breaks. These results indicate that the reaction of water radiolysis products, presumably OH radicals, with the sugar-phosphate moieties in the DNA backbone induces both AP sites and SSB with similar efficiency.
斎藤 公明; 石榑 信人*; Petoussi-Henss, N.*; Schlattl, H.*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 51(4), p.411 - 423, 2012/11
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:70.76(Biology)In order to provide fundamental data required for dose evaluation due to environmental exposures, effective dose conversion coefficients were calculated for a number of potentially important radionuclides, assuming exponential distribution in ground, over a wide range of relaxation depths. The conversion coefficients were calculated for adults and a new-born baby on the basis of dosimetric methods that the authors and related researchers have previously developed, using Monte Carlo simulations and anthropomorphic computational phantoms. The differences in effective dose conversion coefficients due to body size between the adult and the baby were found to lie within 50%, for most cases. It was shown that the implementation into the computation of the tissue weighting factors and the adult reference computational phantoms of ICRP Publication 103 does not significantly influence the effective dose conversion coefficients of the environment.
迫田 晃弘; 石森 有; 深尾 光佑*; 山岡 聖典*; 片岡 隆浩*; 光延 文裕*
Radiation and Environmental Biophysics, 51(4), p.425 - 442, 2012/11
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:55.94(Biology)ラドン子孫核種への曝露に対する生体応答が動物実験で検討されてきたが、マウスの肺の吸収線量は評価例がない。本研究では、マウスにおける吸入ラドン子孫核種の肺線量を評価した。すなわち、粒子の気道沈着,除去、及びターゲット組織へのアルファ線の沈着エネルギー割合を体系的に計算した。参考のため、ラットとヒトに対しても同様に行った。まず、気管支,気管支,胞領域,全肺について、平衡等価ラドン濃度1Bq m (平衡係数0.4、非付着成分比0.01)の下で、単分散ラドン粒子径に対する吸収線量を評価した。この結果に基づき、(1)標準的な鉱山環境、及び(2)先行動物実験の曝露条件における吸収線量を求めた。鉱山環境におけるマウス,ラット,ヒトの全肺の線量は34.8, 20.7, 10.7nGy(Bq m
(平衡係数0.4、非付着成分比0.01)の下で、単分散ラドン粒子径に対する吸収線量を評価した。この結果に基づき、(1)標準的な鉱山環境、及び(2)先行動物実験の曝露条件における吸収線量を求めた。鉱山環境におけるマウス,ラット,ヒトの全肺の線量は34.8, 20.7, 10.7nGy(Bq m )
) h
h 、同様に動物実験条件においては16.9, 9.9, 6.5nGy(Bq m
、同様に動物実験条件においては16.9, 9.9, 6.5nGy(Bq m )
) h
h であった。両曝露条件において、マウスの数値はラットの約2倍、ヒトの約3倍であった。ラットとヒトの数値を文献値と比較すると、許容範囲内で一致しており、本研究でマウスに適用したモデルが妥当であると示唆された。今後は、マウスへの適用モデルをより高度化し、解剖学的・生理学的・環境パラメータが線量へ及ぼす影響を検討することが望まれる。
であった。両曝露条件において、マウスの数値はラットの約2倍、ヒトの約3倍であった。ラットとヒトの数値を文献値と比較すると、許容範囲内で一致しており、本研究でマウスに適用したモデルが妥当であると示唆された。今後は、マウスへの適用モデルをより高度化し、解剖学的・生理学的・環境パラメータが線量へ及ぼす影響を検討することが望まれる。
石橋 松二郎*; 内野 真奈美*; 新井 栄揮; 黒木 良太; 荒川 力*; 徳永 正雄*
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 525(1), p.47 - 52, 2012/09
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:19.80(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)高度好塩菌Halobacterium salinarum由来ヌクレオシド二リン酸キナーゼ(HsNDK)は、立体構造の安定化に高濃度の塩を必要とする。しかし、アスパラギン酸148番目をシステインに置換したD148C変異型HsNDKは、0.2M NaClの低塩濃度条件下において野生型HsNDKよりも10 C以上熱安定性が向上することが判明した。また、熱変性後の巻き戻りには、野生型では2M NaClを必要とするのに対し、D148C変異型では0.1M NaClで巻き戻ることができた。HsNDKは二量体どうしが会合した六量体構造を形成するが、D148C変異導入は六量体内の二量体間に3か所のジスルフィド架橋を形成させて構造を安定化し、本来構造安定化に必要な塩要求性を低減することができたと考えられる。
C以上熱安定性が向上することが判明した。また、熱変性後の巻き戻りには、野生型では2M NaClを必要とするのに対し、D148C変異型では0.1M NaClで巻き戻ることができた。HsNDKは二量体どうしが会合した六量体構造を形成するが、D148C変異導入は六量体内の二量体間に3か所のジスルフィド架橋を形成させて構造を安定化し、本来構造安定化に必要な塩要求性を低減することができたと考えられる。