Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Osaka*
JAEA-Review 2025-040, 111 Pages, 2025/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2023, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge for screening of nuclear fuel debris by innovative spectral imaging and its verification by LIBS mapping" conducted in FY2023. The present study aims to develop a remote-sensing technique to identify the in-reactor materials by a combination of Hyper Spectral Imaging (HSI) and Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS). HSI analyzes spectral information of more than 100 colors, and is being applied to classify various materials. On the other hand, material composition cannot be directly evaluated by HSI. Therefore, we thought that the combination of HSI and LIBS could be an accurate and wide-ranging visualization technique. In order to demonstrate the HSI and LIBS, it is necessary to prepare standard materials that simulate in-reactor materials, and to acquire and accumulate training data on them. In this study, the University of Osaka is in charge of the preparation of standard materials and HSI data analysis, Nuclear Fuel Development (NFD) is in charge of the preparation of uranium bearing materials and HSI/LIBS measurements, and JAEA is in charge of LIBS development. On the UK side, the Univ. of Strathclyde, National Nuclear Laboratory (NNL), and Lancaster University participate in the joint research project. The compositions of the standard samples were determined from past experiments and thermodynamic calculation results. Several samples such as UO based composites and concrete were prepared. The HSI data were obtained using a hyperspectral camera installed in the NFD. For LIBS, we worked on the automatic optimization of focal distance as part of the development of remote operation technology.
based composites and concrete were prepared. The HSI data were obtained using a hyperspectral camera installed in the NFD. For LIBS, we worked on the automatic optimization of focal distance as part of the development of remote operation technology.
Dechenaux, B.*; Brovchenko, M.*; Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Suyama, Kenya
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 223, p.111555_1 - 111555_11, 2025/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Institute of Science Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-026, 72 Pages, 2025/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of effects of nano interfacial phenomena on dissolution aggregation of alpha nanoparticles by using micro nano technologies" conducted in FY2023. To ensure the safety of retrieval and storage management of nuclear fuel debris generated by the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, understanding of dissolution-denaturation behavior of the fuel debris alpha particles is one of the most crucial issues. This research aims to create novel microfluidic real-time measurement device for elucidating dissolution, aggregation, and denaturation processes of metal oxide nanoparticles under various solution environments, and clarify their nano-size and interfacial effects. In this year, we conducted bulk and micro dissolution tests of simulated fuel debris particles (UO mechanical-treated nanoparticles, UO
mechanical-treated nanoparticles, UO chemical-treated nanoparticles, and (U,Zr)O
chemical-treated nanoparticles, and (U,Zr)O nanoparticles), and successfully clarified that the effects of particle sizes, reaction times, and H
nanoparticles), and successfully clarified that the effects of particle sizes, reaction times, and H O
O concentrations on the dissolution behavior of each nanoparticle. In particular, it was found that (U,Zr)O
concentrations on the dissolution behavior of each nanoparticle. In particular, it was found that (U,Zr)O nanoparticles have different degrees of Zr catalytic reactions depending on H
nanoparticles have different degrees of Zr catalytic reactions depending on H O
O concentrations, resulting in the generation of different amounts of gas and U. Moreover, we developed a new microfluidic device which enables to instantly react the nanoparticles with H
concentrations, resulting in the generation of different amounts of gas and U. Moreover, we developed a new microfluidic device which enables to instantly react the nanoparticles with H O
O solutions, and determined dynamic aggregation and dissolution rates of the nanoparticles. The research was carried out in close collaboration with UK researchers, and achieved the expected goal of this year.
solutions, and determined dynamic aggregation and dissolution rates of the nanoparticles. The research was carried out in close collaboration with UK researchers, and achieved the expected goal of this year.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Institute of Science Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-012, 96 Pages, 2025/10
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Uncertainty reduction of the FPs transport mechanism and debris degradation behavior and evaluation of the reactor contamination of debris state on the basis of the accident progression scenario of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station unit 2 and 3" conducted from FY2021 to FY2023. The present study aims to elucidate the cause of the high dosage under shield plug by clarification of to the cesium behavior of migration, adhesion to structure and deposition as well as evaluate the properties of metal-rich debris predeceasing melted through the materials science approach based on the most probable scenario of accident progression of Unit 2 and 3. Through three years investigation, chemi-absorption configuration of Cs has been elucidated to change with acidity of steel surface during oxidation in humid atmosphere and Cs O trapping compound as well as penetration depth have found to be importantly considered. For metallic debris, solid oxidation was found to be controlled by Fe
O trapping compound as well as penetration depth have found to be importantly considered. For metallic debris, solid oxidation was found to be controlled by Fe O
O formation and molten state was found to tend to preferentially yield ZrO
formation and molten state was found to tend to preferentially yield ZrO resulting in formation of slate structure during solidification. Present findings obtained are contributing to better improve the accuracy of accident progression scenario in FDNPP in viewpoint of backward analysis.
resulting in formation of slate structure during solidification. Present findings obtained are contributing to better improve the accuracy of accident progression scenario in FDNPP in viewpoint of backward analysis.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-008, 134 Pages, 2025/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on water stopping, repair and stabilization of lower PCV by geopolymer, etc." conducted from FY2021 to FY2023. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2023, the results for 3 fiscal years were summarized. In order to retrieve fuel debris, it is necessary to shut off the water at the bottom of the dry well and repair it in order to control the PCV water level. Therefore, in this study, we evaluated a construction method of stopping the water of the jet deflector with an improved geopolymer and repairing the lower part of the dry well by experiments and simulations. In addition, after understanding the properties of the fuel debris coated with the geopolymer, the long-term life of the waste body was evaluated. As a result, it was predicted that by utilizing geopolymers, it is possible to stop water and repair the lower part of the PCV in consideration of steps from construction to waste management.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Institute of Science Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2025-010, 62 Pages, 2025/08
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Fuel debris criticality analysis technology using non-contact measurement method" conducted from FY2021 to FY2023. The purpose of research was to improve the fuel debris criticality analysis technology using non-contact measurement method by the development of the fuel debris criticality characteristics measurement system and the multi-region integral kinetic analysis code. It was performed by Institute of Science Tokyo, Tokyo City University, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, and Nagaoka University of Technology. We developed the fuel debris criticality characteristics measurement system which has a two layer structure surrounding a canister containing fuel debris fragments with  He proportional counters. The operational validation and performance evaluation were performed on the developed detector system. We have demonstrated the feasibility and accuracy of measuring the amount of fissile material and water content. MIK2.0-MVP code, which can calculate fission reaction rate attributed to both prompt and delayed neutrons and also can take the movement of fuel debris into calculation, was developed. After parallelizing the tally process of C
He proportional counters. The operational validation and performance evaluation were performed on the developed detector system. We have demonstrated the feasibility and accuracy of measuring the amount of fissile material and water content. MIK2.0-MVP code, which can calculate fission reaction rate attributed to both prompt and delayed neutrons and also can take the movement of fuel debris into calculation, was developed. After parallelizing the tally process of C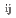 (
( ) function, MIK2.0-MVP code will be applicable to weakly coupled reactors which include moving fuel debris particles if a supercomputer will be used for the tally process of C
) function, MIK2.0-MVP code will be applicable to weakly coupled reactors which include moving fuel debris particles if a supercomputer will be used for the tally process of C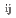 (
( ) function and if the coupling of MIK2.0-MVP code with MPS will be weak.
) function and if the coupling of MIK2.0-MVP code with MPS will be weak.
Nguyen, H. H.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 218, p.111361_1 - 111361_9, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study examined the criticality characteristics of a partially damaged reactor model, in which fuels located at the core center melt into fuel debris of varying shapes, while fuels situated at the core edges remain intact. The investigation was conducted using the Serpent code with the JENDL-5 nuclear data library. The results of the calculations indicate that when the volume of fuel debris is small and maintained at a constant level, the shape of the fuel debris does not result in significant alterations in the variation law of k of the system. In contrast, for the scenario in which the volume of the fuel debris is variable, the k
of the system. In contrast, for the scenario in which the volume of the fuel debris is variable, the k variation law can be divided into two groups for the reference case with a system temperature of 300 K and no boron in the water. The first group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are cuboid and cylindrical, while the second group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are spherical, cone-shaped, and truncated cone-shaped.
variation law can be divided into two groups for the reference case with a system temperature of 300 K and no boron in the water. The first group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are cuboid and cylindrical, while the second group comprises fuel debris with shapes that are spherical, cone-shaped, and truncated cone-shaped.
Sakamoto, Masahiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Kanno, Ikuo; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kaneko, Junichi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(8), p.756 - 765, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Yuki, Kohei*; Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Yuki, Kazuhisa*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 12(4), p.24-00451_1 - 24-00451_8, 2025/08
Fuel debris at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station is typically cooled under immersion. However, an unexpected significant drop in water level results in coolant contact with high-temperature fuel debris having porous structure. In such scenarios, rapid cooling is essential, yet the thermal behavior at the liquid-solid interface, including capillary phenomena, is not well understood. This paper presents basic research evaluating the evaporation characteristics of droplets upon contact with metallic porous media featuring small pores under 1 mm. We conducted experiments using bronze or stainless steel porous media with pore diameters of 1, 40, or 100  m to derive lifetime curves for droplets. Our findings indicate that Leidenfrost effect is mitigated on porous surfaces as the vapor can escape through the pores. Moreover, in bronze porous media, as the temperature increases, oxide film with a fine structure facilitates capillary action. In contrast, the low wettability of stainless steel porous media prevents capillary action, inhibiting droplet absorption and dispersion into the pores. Consequently, rapid cooling via the capillary action is unlikely if the fuel debris shares similar characteristics with steel porous media. Therefore, for risk management, the cooling system should be established assuming that capillary force does not act in the fuel debris.
m to derive lifetime curves for droplets. Our findings indicate that Leidenfrost effect is mitigated on porous surfaces as the vapor can escape through the pores. Moreover, in bronze porous media, as the temperature increases, oxide film with a fine structure facilitates capillary action. In contrast, the low wettability of stainless steel porous media prevents capillary action, inhibiting droplet absorption and dispersion into the pores. Consequently, rapid cooling via the capillary action is unlikely if the fuel debris shares similar characteristics with steel porous media. Therefore, for risk management, the cooling system should be established assuming that capillary force does not act in the fuel debris.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2024-064, 118 Pages, 2025/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2023. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of extremely small amount analysis technology for fuel debris analysis" conducted from FY2019 to FY2023. Understanding the properties of fuel debris is necessary for handling, criticality control, storage control, etc. A key technique is the chemical analysis of actinide nuclides. We developed sample pretreatment technology and separation / analysis process required for chemical analysis. The purpose of this study is to streamline future planned fuel debris analysis. To promote 1F decommissioning, we will train human resources through on-the-job training. In particular, we applied the extremely small amount analysis (ICP-MS/MS), which has recently been successful in the fields of analytical chemistry and radiochemistry, to the nuclear field. This method allows high-accuracy analysis without pretreatment to isolate the nuclide to be measured. The separation pretreatment can be skipped and a rapid analysis process can be established.
Nagatani, Taketeru; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Sagara, Hiroshi*; Nakaguki, Sho; Nomi, Takayoshi; Okumura, Keisuke
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 7, p.41 - 46, 2025/03
Matsumura, Taichi; Okumura, Keisuke; Sakamoto, Masahiro; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kondo, Kazuhiro*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 432, p.113791_1 - 113791_9, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) 100 m fiber-coupled microchip laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for remote elemental analysis applications
100 m fiber-coupled microchip laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for remote elemental analysis applicationsBatsaikhan, M.; Oba, Hironori; Wakaida, Ikuo
Optics Express (Internet), 32(25), p.45158 - 45170, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.84(Optics)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2024-021, 126 Pages, 2024/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on water stopping, repair and stabilization of lower PCV by geopolymer, etc" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to propose a construction method to stop jet deflectors by improved geopolymer and ultra-heavy muddy water, and to repair the lower part of the dry well. In addition, in order to increase the options for on-site construction in unknown situations such as deposition conditions, we will examine a wide range of construction outside the pedestal, and evaluate the feasibility of the construction method by the latest thermal flow simulation method.
Batsaikhan, M.; Oba, Hironori; Karino, Takahiro; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Optics Express (Internet), 32(24), p.42624 - 42638, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Optics)Yuki, Kohei*; Horiguchi, Naoki; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Yuki, Kazuhisa*
Proceedings of 31st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE31) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/11
Fuel debris in the Fukushima Nuclear Power Station is cooled under immersion condition. However, in the event of an unexpected decrease in water level, coolant contacts high-temperature fuel debris having porous structure. In this event, although fuel debris needs to be cooled rapidly, thermal behavior at liquid-solid contact, such as capillary phenomenon, remains unclear. In this paper, as basic research, we evaluate droplet evaporation characteristics after contact with metal porous media with small pores less than 1 mm. In experiment, to obtain life time curve of a droplet, bronze or stainless steel porous media having 1, 40, or 100  m pore diameter are utilized. Experimental results show that Leidenfrost phenomenon is suppressed on the porous surfaces because generated vapor can be discharged from the pores. Further, for bronze porous media, capillary phenomenon is observed as the temperature of the porous media increase because of generation of oxide film having fine structure. On the other hand, due to low wettability of stainless steel porous media, capillary phenomenon does not occur, and the droplet was not sucked and spread into pore. This indicates that rapid cooling by the capillary phenomenon can not be expected if fuel debris has the same characteristics as the stainless steel porous media.
m pore diameter are utilized. Experimental results show that Leidenfrost phenomenon is suppressed on the porous surfaces because generated vapor can be discharged from the pores. Further, for bronze porous media, capillary phenomenon is observed as the temperature of the porous media increase because of generation of oxide film having fine structure. On the other hand, due to low wettability of stainless steel porous media, capillary phenomenon does not occur, and the droplet was not sucked and spread into pore. This indicates that rapid cooling by the capillary phenomenon can not be expected if fuel debris has the same characteristics as the stainless steel porous media.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2024-026, 80 Pages, 2024/10
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Study on degradation of fuel debris by combined effects of radiological, chemical, and biological functions" conducted from FY2019 to FY2022. In the project, radiochemists, nuclear chemists, nuclear physicists, material scientists, and environmental biologists are teamed to elucidate the mechanism of the degradation of fuel debris by combined effects of radiological, chemical, and biological functions.
Nakashima, Shinsuke*; Moro, A.*; Komatsu, Ren*; Faragasso, A.*; Matsuhira, Nobuto*; Woo, H.*; Kawabata, Kuniaki; Yamashita, Atsushi*; Asama, Hajime*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2024-022, 59 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2022, this report summarizes the research results of the "Investigation of effects of nano interfacial phenomena on dissolution aggregation of alpha nanoparticles by using micro nano technologies" conducted in FY2022. To ensure the safety of retrieval and storage management of nuclear fuel debris generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident, understanding of dissolution-denaturation behavior of the fuel debris alpha particles is one of the most crucial issues. This research aims to create novel microfluidic real-time measurement device for elucidating dissolution, aggregation, and denaturation processes of metal oxide nanoparticles under various solution environments, and clarify their nano-size and interfacial effects.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; National Institute of Maritime, Port and Aviation Technology*
JAEA-Review 2024-020, 77 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Research and development of the sample-return technique for fuel debris using the unmanned underwater vehicle" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to develop a fuel debris sampling device that comprises a neutron detector with radiation resistance and enhanced neutron detection efficiency, an end-effector with powerful cutting and collection capabilities, and a manipulator under the Japan-UK joint research team. We will also develop a fuel debris sampling system that can be mounted on an unmanned vehicle.