Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
横田 祥*; 中後 大輔*; 橋本 洋志*; 川端 邦明
Proceedings of 25th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, p.910 - 911, 2016/08
本論文の目的は、パーソナルモビリティのサドルタイプインタフェースの入力あそびに関する特性の実験的検証と制御スキームへの実装である。プロトタイプにより実験した結果について述べた。
 is characterized as Type II bacterial topoisomerase and its activity is differentially regulated by PprA in vitro
is characterized as Type II bacterial topoisomerase and its activity is differentially regulated by PprA in vitroKota, S.*; Rajpurohit, Y. S.*; Charaka, V. K.*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*; Misra, H, S.*
Extremophiles, 20(2), p.195 - 205, 2016/03
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:40.92(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The multipartite genome of  forms toroidal structure. It encodes topoisomerase IB and both the subunits of DNA gyrase (DrGyr) while lacks other bacterial topoisomerases. Recently, PprA a pleiotropic protein involved in radiation resistance in
forms toroidal structure. It encodes topoisomerase IB and both the subunits of DNA gyrase (DrGyr) while lacks other bacterial topoisomerases. Recently, PprA a pleiotropic protein involved in radiation resistance in  has been suggested for having roles in cell division and genome maintenance. In vivo interaction of PprA with topoisomerases has also been shown. DrGyr constituted from recombinant gyrase A and gyrase B subunits showed decatenation, relaxation and supercoiling activities. Wild type PprA stimulated DNA relaxation activity while inhibited supercoiling activity of DrGyr. Thus, we showed that DrGyr confers all three activities of bacterial type IIA family DNA topoisomerases, which are differentially regulated by PprA, highlighting the significant role of PprA in DrGyr activity regulation and genome maintenance in
has been suggested for having roles in cell division and genome maintenance. In vivo interaction of PprA with topoisomerases has also been shown. DrGyr constituted from recombinant gyrase A and gyrase B subunits showed decatenation, relaxation and supercoiling activities. Wild type PprA stimulated DNA relaxation activity while inhibited supercoiling activity of DrGyr. Thus, we showed that DrGyr confers all three activities of bacterial type IIA family DNA topoisomerases, which are differentially regulated by PprA, highlighting the significant role of PprA in DrGyr activity regulation and genome maintenance in  .
.
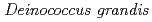 , isolated from freshwater fish in Japan
, isolated from freshwater fish in Japan佐藤 勝也; 小野寺 威文*; 面曽 宏太*; 武田-矢野 喜代子*; 片山 豪*; 大野 豊; 鳴海 一成*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 4(1), p.e01631-15_1 - e01631-15_2, 2016/01
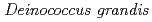 was isolated as a gram-negative, red-pigmented, radioresistant, rod-shaped bacterium from freshwater fish. The draft genome sequence of
was isolated as a gram-negative, red-pigmented, radioresistant, rod-shaped bacterium from freshwater fish. The draft genome sequence of  ATCC 43672 was 4,092,497 bp, with an average G+C content of 67.5% and comprised of 4 circular contigs and 3 linear contigs that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BCMS00000000. The draft genome sequence indicates that
ATCC 43672 was 4,092,497 bp, with an average G+C content of 67.5% and comprised of 4 circular contigs and 3 linear contigs that was deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/Genbank under the accession number BCMS00000000. The draft genome sequence indicates that  possesses a DNA damage response regulator (encoded by
possesses a DNA damage response regulator (encoded by  homolog) and radiation-desiccation response regulons (
homolog) and radiation-desiccation response regulons ( ,
, 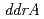 ,
, 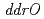 ,
,  and
and 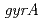 homologs etc.), which are involved in the unique radiation-desiccation response system in
homologs etc.), which are involved in the unique radiation-desiccation response system in  . As it is for
. As it is for  ,
, 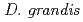 seems to employ the same radioresistant mechanisms. In future, the draft genome sequence of
seems to employ the same radioresistant mechanisms. In future, the draft genome sequence of 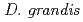 will be useful for elucidating the common principles of the radioresistance based on the extremely efficient DNA repair mechanisms in Deinococcus species by the comparative analysis of genomic sequences.
will be useful for elucidating the common principles of the radioresistance based on the extremely efficient DNA repair mechanisms in Deinococcus species by the comparative analysis of genomic sequences.
 ion beam entering a narrow gap between two cylindrical glass surfaces
ion beam entering a narrow gap between two cylindrical glass surfaces本橋 健次*; 齋藤 勇一; 宮脇 信正; 松尾 祐太郎*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(7), p.076301_1 - 076301_6, 2013/07
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:18.35(Physics, Applied)The transmission properties of a 4-MeV C ion beam entering a narrow gap between a pair of convex and concave glass rods facing each other are investigated in order to inspect the possibility to guide the ion beam with the tilting curved gap. The curvature of both rods was R = 155.70 mm, the gap was 1.2 mm. The entire setup can be tilted around the z-axis passing through the center of the gap at the entrance side. The tilt angle
ion beam entering a narrow gap between a pair of convex and concave glass rods facing each other are investigated in order to inspect the possibility to guide the ion beam with the tilting curved gap. The curvature of both rods was R = 155.70 mm, the gap was 1.2 mm. The entire setup can be tilted around the z-axis passing through the center of the gap at the entrance side. The tilt angle  was defined positive for clockwise rotation. The ion transmission of 42-59% obtained at a tilt angle
was defined positive for clockwise rotation. The ion transmission of 42-59% obtained at a tilt angle  = 3
= 3 was 20-30 times larger than the value of 2% estimated from the cross section of the narrow gap. About 10% of the ions transmitted even at
was 20-30 times larger than the value of 2% estimated from the cross section of the narrow gap. About 10% of the ions transmitted even at  = 3.4
= 3.4 in which almost no ions can pass through the gap without interacting with the cylindrical glass surfaces, according to the results of laser-transmission experiment. No significant loss in their initial energies was observed in the angular range of -3
in which almost no ions can pass through the gap without interacting with the cylindrical glass surfaces, according to the results of laser-transmission experiment. No significant loss in their initial energies was observed in the angular range of -3 

 +3.4
+3.4 . These results show an evidence of a guide effect of the carved gap to swift heavy ion beams.
. These results show an evidence of a guide effect of the carved gap to swift heavy ion beams.
 ions
ions本橋 健次*; 齋藤 勇一; 宮脇 信正; 神谷 富裕
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 135, 2013/01
We studied the mechanism of collisions between 1-2-MeV carbon ions and polarity-controlled ZnO surfaces in order to investigate the efficient reflection of swift ions on solid surfaces for transportation of ion beams without magnetic and/or electrostatic beam handling. The intensities of ions scattered on three different surfaces of Zn and O faces of the ZnO crystals and a polycrystalline Au film were measured by a Si surface barrier detector. As a result, the intensity on the Zn face of the ZnO crystals significantly increased at 2-MeV comparing to that at 1-MeV, although there was a small increase in intensity in the case of the O face of the ZnO and Au surfaces. The details of this finding have not been clarified yet. However, efficient reflection of MeV ions is expected on polarity-controlled ZnO surfaces.
 ion sputtering of Ti surface under O
ion sputtering of Ti surface under O environment
environment本橋 健次*; 齋藤 勇一; 北澤 真一
Applied Surface Science, 257(13), p.5789 - 5792, 2011/04
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:20.88(Chemistry, Physical)Visible light emission from atoms and ions sputtered on a polycrystalline Ti surface was observed under irradiation of 30 keV Ar ions. A number of atomic lines of Ti I and II were observed in the wavelength of 250 to 850 nm. The intensity of Ti II emission increased 1.3-5.6 times by introducing oxygen molecules at a pressure of 5.8
ions. A number of atomic lines of Ti I and II were observed in the wavelength of 250 to 850 nm. The intensity of Ti II emission increased 1.3-5.6 times by introducing oxygen molecules at a pressure of 5.8 10
10 Pa, whereas that of Ti I decreased 0.5-0.8 times. Factors enhancing or reducing photon intensities were plotted as a function of energy of the corresponding electrons in the excited states for Ti atoms and Ti
Pa, whereas that of Ti I decreased 0.5-0.8 times. Factors enhancing or reducing photon intensities were plotted as a function of energy of the corresponding electrons in the excited states for Ti atoms and Ti ions. As a result, neither the bond-breaking model nor the kinetic model was applicable to the intensity change. It is considered that the local band structure model is appropriate for understanding the Ti I and II emissions.
ions. As a result, neither the bond-breaking model nor the kinetic model was applicable to the intensity change. It is considered that the local band structure model is appropriate for understanding the Ti I and II emissions.
本橋 健次*; 齋藤 勇一; 宮脇 信正
no journal, ,
重元素終端された有極性半導体結晶による表面散乱を利用した、電磁石や静電場を必要としない簡便なイオンビームガイディングの実現を目指し、その基盤研究を行っている。今回は、有極性半導体結晶表面におけるイオンビームの鏡面反射率を通常の金属表面と比較し、その特性を調べた。1MeV及び2MeVの炭素イオンビームを標的(GaN(単結晶Ga面),GaN(単結晶N面),ZnO(単結晶Zn面),ZnO(単結晶O面),Au(多結晶))表面に対し2 で入射し、散乱角3
で入射し、散乱角3 と4
と4 における散乱イオンの強度測定及びエネルギー分析を、半導体検出器を用いて行った。その結果、Au面と比較して有極性半導体結晶面は鏡面反射率が高いことがわかった。さらに、GaNではGa面がN面より高い、また、ZnOではZn面がO面より高い反射率を示した。これらから、有極性半導体結晶の重元素終端面がイオンビームの反射(ガイディング)に有効であることが示唆された。
における散乱イオンの強度測定及びエネルギー分析を、半導体検出器を用いて行った。その結果、Au面と比較して有極性半導体結晶面は鏡面反射率が高いことがわかった。さらに、GaNではGa面がN面より高い、また、ZnOではZn面がO面より高い反射率を示した。これらから、有極性半導体結晶の重元素終端面がイオンビームの反射(ガイディング)に有効であることが示唆された。
本橋 健次*; 齋藤 勇一; 宮脇 信正; 神谷 富裕
no journal, ,
近年、金属表面に高速イオンを微小角入射で照射したときに鏡面角付近で100%近い反射が起こることが確認されたが、そのメカニズムの詳細は不明である。われわれは、この現象のイオンビーム輸送への応用を検討するため、高速イオンが微小角で入射したときの固体表面での反射(散乱)に関する研究を行っている。今回、最表面の原子を選択可能な有極性酸化亜鉛単結晶(ZnO)を標的として、そのZn面とO面を用いて、散乱ビームのエネルギー及び強度を比較した。その結果、1MeV炭素イオンを照射した場合、積分散乱強度はどちらの表面でもほとんど同じであるにもかかわらず、O面に比べてZn面の方がエネルギー損失の大きな散乱粒子が多かった。また、2MeV炭素イオンを照射した場合のZnOのZn面,O面と、多結晶金表面の3つの表面での散乱イオン強度を比較した結果、Zn面入射の場合に、散乱イオン強度が顕著に増大した。これらから、標的の最表面原子が、散乱に大きく影響することが示唆された。また、有極性材料の反射を利用したビーム輸送の可能性が示された。
本橋 健次*; 齋藤 勇一; 宮脇 信正
no journal, ,
近年、ガラスキャピラリーを透過するMeVエネルギーイオンビームに対して、ガラス表面近傍原子との小角散乱やチャージアップに起因すると考えられる集束効果が発見された。われわれは、同様の現象をMeVエネルギーイオンビームの偏向に応用することを考え、曲率を持つガラス面上に小角で入射した際のイオンの散乱について研究を行っている。今回、曲率半径175mmの光学用ガラス凸レンズと凹レンズを1.2mmの間隔で対向させて、湾曲した経路(経路長:約20mm)を作製した。そこに2MeVの炭素イオンビームを入射し、その入射ビーム軸に対する経路の角度を入射口を中心に回転させることにより変えて、ビームの透過率を測定する実験を行った。その結果、幾何学的にはビームが透過できない角度(10 )のときでも電流透過率が約10%になることを確認した。これにより、曲面ガラスを利用したビーム偏向の可能性が示された。
)のときでも電流透過率が約10%になることを確認した。これにより、曲面ガラスを利用したビーム偏向の可能性が示された。
本橋 健次*; 齋藤 勇一; 宮脇 信正
no journal, ,
近年、金を蒸着した表面に2.5MeVプロトンを微小角入射で照射させたときに100%近い反射が起こることが報告された。われわれは、固体表面との反射を利用した高速イオンビームの効率的な輸送方法の開発を目的に、高速イオンを微小角で入射させたときの固体表面での反射(散乱)に関する研究を行っている。今回、最表面の原子を選択可能な有極性酸化亜鉛単結晶(ZnO)を標的として、散乱ビーム(2MeV炭素イオン:入射角2度、散乱角3度、ここで入射角及び散乱角は、それぞれのターゲット表面に対する角度及びビーム軸に対する角度で定義)のエネルギー及び強度をそのZn面とO面で比較した。その結果、O面に比べてZn面の方が散乱イオンの強度が高く、エネルギー損失が大きいことがわかった。これらから、微小角入射の場合、標的の最表面原子の種類が入射イオンの散乱に大きく影響することがわかり、それを選択することでビームのエネルギー及び強度を制御可能なことが示唆された。
本橋 健次*; 鈴木 優紀*; 齋藤 勇一; 宮脇 信正; 的場 史朗; 神谷 富裕
no journal, ,
近年、ガラスキャピラリーを透過するMeVエネルギーイオンビームに対して、ガラス表面近傍原子との小角散乱やチャージアップに起因すると考えられる偏向・集束効果が発見された。我々は、この現象に着目して、MeVエネルギーイオンビームの偏向に応用することを考え、固体表面を利用した高速重イオンの偏向効果を検証することを目的に、一対の凸凹ガラス円筒面の隙間(面間チャネル)に4MeV炭素イオンを入射した際の透過率とエネルギーのガラス円筒面に対するビーム入射角(チルト角)依存性を調べた。曲率半径155.70mm奥行き20mmの凸凹ガラス円筒光学レンズを1.2mmの間隔で対向した面間チャネルに、直径1mmの4MeV-C イオンを入射し、面間チャネル入口を中心としてチルト回転したときの透過イオンを表面障壁型半導体検出器で検出し、そのイオン透過率とエネルギーを測定した。その結果、幾何学的にはビームが透過できない角度の時でも電流透過率が約10%になることを確認した。これにより、曲面ガラスを利用してビームを偏向できることが示された。
イオンを入射し、面間チャネル入口を中心としてチルト回転したときの透過イオンを表面障壁型半導体検出器で検出し、そのイオン透過率とエネルギーを測定した。その結果、幾何学的にはビームが透過できない角度の時でも電流透過率が約10%になることを確認した。これにより、曲面ガラスを利用してビームを偏向できることが示された。
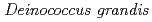 における突然変異を誘発する遺伝子の機能解析
における突然変異を誘発する遺伝子の機能解析面曽 宏太*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
放射線抵抗性細菌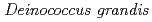 には、DNAポリメラーゼの
には、DNAポリメラーゼの サブユニットをコードする
サブユニットをコードする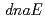 (
(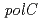 )遺伝子に相同性のある遺伝子が2つ存在する(
)遺伝子に相同性のある遺伝子が2つ存在する(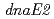 および
および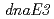 )。
)。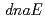 相同遺伝子は、突然変異を誘発する機能をもつことが示唆されている。しかし、放射線抵抗性細菌における
相同遺伝子は、突然変異を誘発する機能をもつことが示唆されている。しかし、放射線抵抗性細菌における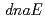 相同遺伝子の機能についてはよく分かっていない。そこで、本研究では
相同遺伝子の機能についてはよく分かっていない。そこで、本研究では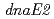 および
および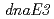 遺伝子が突然変異誘発に関わっているのかどうか、あるいは役割分担があるのかどうか、遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学的解析を行った。
遺伝子が突然変異誘発に関わっているのかどうか、あるいは役割分担があるのかどうか、遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学的解析を行った。
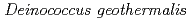 における
における 遺伝子の遺伝子破壊解析
遺伝子の遺伝子破壊解析島田 岳*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
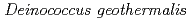 は、至適生育温度が通常30
は、至適生育温度が通常30 Cである
Cである 属細菌においては例外的に、至適生育温度が45から50
属細菌においては例外的に、至適生育温度が45から50 Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、
Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、 の
の 遺伝子を薬剤耐性マーカーとすげ替えた形の
遺伝子を薬剤耐性マーカーとすげ替えた形の 遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、
遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、 遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して
遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して 遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原(
遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原( 線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで
線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで における
における 遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、
遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、 遺伝子は
遺伝子は においても変異原耐性に関与しており、
においても変異原耐性に関与しており、 が関与するDNA修復機構は他の
が関与するDNA修復機構は他の 属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
 の機能解析
の機能解析黒澤 飛翔*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
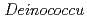 属細菌は、放射線, UV, アルキル化剤, 酸化剤, 乾燥等で誘発される様々なDNA損傷に対する修復能力を有している。
属細菌は、放射線, UV, アルキル化剤, 酸化剤, 乾燥等で誘発される様々なDNA損傷に対する修復能力を有している。 を用いたこれまでの研究で、DNA修復を促進する多面的タンパク質PprA (pleiotropic protein promoting DNA repair)とDNA修復時における
を用いたこれまでの研究で、DNA修復を促進する多面的タンパク質PprA (pleiotropic protein promoting DNA repair)とDNA修復時における 遺伝子の発現誘導を活性化する制御タンパク質PprI (inducer of PprA)が発見されている。本研究は、PprIタンパク質に着目し、
遺伝子の発現誘導を活性化する制御タンパク質PprI (inducer of PprA)が発見されている。本研究は、PprIタンパク質に着目し、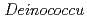 属細菌のDNA修復機構の共通原理を見出すことを目的とした。
属細菌のDNA修復機構の共通原理を見出すことを目的とした。 及び
及び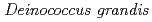 の
の 遺伝子破壊株を作製し、紫外線, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素, ナリジクス酸に対する感受性を野生株と比較した。
遺伝子破壊株を作製し、紫外線, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素, ナリジクス酸に対する感受性を野生株と比較した。
 の機能解析
の機能解析黒澤 飛翔*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
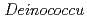 属細菌は、放射線、UV、アルキル化剤、酸化剤、乾燥等で誘発される様々なDNA損傷に対する修復能力を有している。
属細菌は、放射線、UV、アルキル化剤、酸化剤、乾燥等で誘発される様々なDNA損傷に対する修復能力を有している。 を用いたこれまでの研究で、DNA修復を促進する多面的タンパク質PprA (pleiotropic protein promoting DNA repair)とDNA修復時における
を用いたこれまでの研究で、DNA修復を促進する多面的タンパク質PprA (pleiotropic protein promoting DNA repair)とDNA修復時における 遺伝子の発現誘導を活性化する制御タンパク質PprI (inducer of PprA)が発見されている。本研究は、PprIタンパク質に着目し、
遺伝子の発現誘導を活性化する制御タンパク質PprI (inducer of PprA)が発見されている。本研究は、PprIタンパク質に着目し、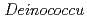 属細菌のDNA修復機構の共通原理を見出すことを目的とした。
属細菌のDNA修復機構の共通原理を見出すことを目的とした。 及び
及び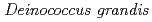 の
の 遺伝子破壊株を作製し、DNA変異原に対する感受性を野生株と比較した。
遺伝子破壊株を作製し、DNA変異原に対する感受性を野生株と比較した。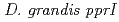 遺伝子破壊株は、
遺伝子破壊株は、 遺伝子破壊株と同様に、
遺伝子破壊株と同様に、 線, 紫外線, MMCに対して野生株よりも感受性を示した。これに加えて、
線, 紫外線, MMCに対して野生株よりも感受性を示した。これに加えて、 遺伝子破壊株は、ブレオマイシンと過酸化水素にも感受性を示した。これらのことから、PprIタンパク質は両菌種において、DNAに誘発された鎖切断, 酸化損傷, ピリミジンダイマー, アルキル化及び鎖間架橋の修復に関わっていると考えられた。
遺伝子破壊株は、ブレオマイシンと過酸化水素にも感受性を示した。これらのことから、PprIタンパク質は両菌種において、DNAに誘発された鎖切断, 酸化損傷, ピリミジンダイマー, アルキル化及び鎖間架橋の修復に関わっていると考えられた。
 における
における 遺伝子破壊解析
遺伝子破壊解析島田 岳*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
 は、至適生育温度が45から50
は、至適生育温度が45から50 Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、
Cの中等度好熱菌である。本研究では、 の
の 遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、
遺伝子欠失株を作製するとともに、 遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して
遺伝子を発現させたプラスミドDNAを遺伝子欠失株に導入して 遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原(
遺伝子相補株を作製した。また、これらの株を用いて、各種変異原( 線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで
線, UV, マイトマイシンC, ブレオマイシン, 過酸化水素など)に対する耐性を野生株と比較することで における
における 遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、
遺伝子の機能を調査した。その結果、欠失株は野生株と比べて生存率が低下し、相補株では耐性が野生株と同等にまで復帰するという結果が得られた。このことから、 遺伝子は
遺伝子は においても変異原耐性に関与しており、
においても変異原耐性に関与しており、 が関与するDNA修復機構は他の
が関与するDNA修復機構は他の 属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
属細菌に広く保存されていることが示唆された。
 における突然変異を誘発する遺伝子の機能解析
における突然変異を誘発する遺伝子の機能解析面曽 宏太*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成*
no journal, ,
放射線抵抗性細菌 には、複製型DNAポリメラーゼの
には、複製型DNAポリメラーゼの サブユニットをコードする
サブユニットをコードする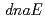 遺伝子に相同性のある遺伝子が2つ存在する(
遺伝子に相同性のある遺伝子が2つ存在する(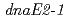 および
および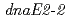 )。
)。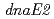 相同遺伝子は、突然変異を誘発する機能をもつことが示唆されている。しかし、放射線抵抗性細菌における
相同遺伝子は、突然変異を誘発する機能をもつことが示唆されている。しかし、放射線抵抗性細菌における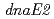 相同遺伝子の機能についてはよく分かっていない。そこで、本研究では
相同遺伝子の機能についてはよく分かっていない。そこで、本研究では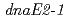 および
および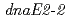 遺伝子が突然変異誘発に関わっているのかどうか、あるいは役割分担があるのかどうか、遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学的解析を行った。その結果、2つの
遺伝子が突然変異誘発に関わっているのかどうか、あるいは役割分担があるのかどうか、遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学的解析を行った。その結果、2つの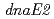 遺伝子は紫外線照射後の突然変異誘発に大きく関わっていることが示唆された。さらに、
遺伝子は紫外線照射後の突然変異誘発に大きく関わっていることが示唆された。さらに、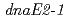 遺伝子過剰発現株では、紫外線照射前後で、野生株よりも突然変異率の上昇が見られたことから、
遺伝子過剰発現株では、紫外線照射前後で、野生株よりも突然変異率の上昇が見られたことから、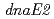 遺伝子は突然変異誘発遺伝子として機能することが明らかになった。
遺伝子は突然変異誘発遺伝子として機能することが明らかになった。