スメクタイトの物理・化学的特性およびNaCl溶液中でのH+との相互作用
Physico-chemical characteristics of purified Na-smectite and protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite surface in NaCl media
澁谷 朝紀; 小原 幸利*; 小田 治恵 
 ; 久保田 満*; 久野 義夫; 柴田 雅博
; 久保田 満*; 久野 義夫; 柴田 雅博 
Shibutani, Tomoki; Kohara, Yukitoshi*; Oda, Chie; Kubota, Mitsuru*; not registered; Shibata, Masahiro
高レベル放射性廃棄物地層処分の性能評価におけるベントナイト-地下水相互作用を把握するため、その主要構成鉱物であるNa型スメクタイトの物理化学的特性を評価するとともに、様々な濃度のNaCl溶液中でのH+との相互作用を評価した。Na型スメクタイトは、クニピアFから精製した。XRD測定を行った結果、若干石英(玉髄)の存在を示唆するピークが認められた。また、スメクタイト層間に介在する陽イオンは1価であり、均一に配列していること、全岩化学組成分析結果と合わせ、ほぼNa型であることが推定された。さらに、湿度制御およびエチレングリコール処理により、イライト化または緑泥石化されていない健全な膨張性を有するスメクタイトであることが分かった。アンモニウム酢酸塩を用いて測定した陽イオン交換容量は110.8meq/100gであった。N2-BET比表面積測定によるスメクタイトの表面積は50 58m2/gであった。0.01、0.1および0.5MNaCl溶液中でのスメクタイトとH+との相互作用は、滴定法によって評価した。その結果、H+消費量は、pH
58m2/gであった。0.01、0.1および0.5MNaCl溶液中でのスメクタイトとH+との相互作用は、滴定法によって評価した。その結果、H+消費量は、pH 6ではNaCl濃度に強く影響を受けるが、pH
6ではNaCl濃度に強く影響を受けるが、pH 6ではNaCl濃度の影響をほとんど受けないことがわかった。また、溶液分析から、pH
6ではNaCl濃度の影響をほとんど受けないことがわかった。また、溶液分析から、pH 4ではスメクタイト骨格の溶解に起因すると見られるFe、AlおよびMgの溶出が認められた。さらに、イオン交換モデルおよび表面錯体モデルを用いて0.1MNaCl溶液中でのスメクタイトに対するH+の収着のモデル化を試みた結果、スメクタイト結晶端におけるH+収着/解離反応およびスメクタイト層間におけるH+収着反応の平衡定数は以下のように得られた。
4ではスメクタイト骨格の溶解に起因すると見られるFe、AlおよびMgの溶出が認められた。さらに、イオン交換モデルおよび表面錯体モデルを用いて0.1MNaCl溶液中でのスメクタイトに対するH+の収着のモデル化を試みた結果、スメクタイト結晶端におけるH+収着/解離反応およびスメクタイト層間におけるH+収着反応の平衡定数は以下のように得られた。 SOH+H+
SOH+H+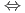 SOH2+ logK(+)=5.674
SOH2+ logK(+)=5.674  SOH
SOH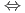 SO-+H+ logK(-)=-7.916 ZNa+H+
SO-+H+ logK(-)=-7.916 ZNa+H+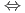 ZH+Na+logK(ZH)=1.88 本データを用いて、0.01および0.5MNaCl溶液中のスメクタイトに対するH+収着量を計算した結果、計算結果は実験結果とほぼ一致することが確認された。本計算結果から、低pH側ではH+が層間に収着することによってH+収着量にイオン強度依存性が生じたものと考えられた。
ZH+Na+logK(ZH)=1.88 本データを用いて、0.01および0.5MNaCl溶液中のスメクタイトに対するH+収着量を計算した結果、計算結果は実験結果とほぼ一致することが確認された。本計算結果から、低pH側ではH+が層間に収着することによってH+収着量にイオン強度依存性が生じたものと考えられた。
The physico-chemical characteristics of purified Na-smectite and protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite surface in different concentrations of NaCl solutions were studied to identify the reaction mechanism of smectite-water interaction for performance assessment of HLW geological disposal system. The Na-smectite was purified from Kunipia F (obtained from Kunimine Industries Co. Ltd. Japan). In this smectite, small amount of quartz was detected as an impurity by X-ray diffraction. As a result of XRD and chemical analysis of the smectite, it was found that exchangeable sites in smectite inter-layer were occupied by Na+. Cation exchange capacity (CEC) was measured as 1.108meq g by using ammonium acetate. The N
by using ammonium acetate. The N -BET surface area of smectite was 50
-BET surface area of smectite was 50 58m
58m g
g . Protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite was studied for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl by using titration and back titration method. Total amount of H
. Protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite was studied for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl by using titration and back titration method. Total amount of H consumption increased with decreasing pH for all NaCl concentrations, and the titration curves in these solutions showed similar trend in the pH range of 6-11. On the other hand, total amount of H
consumption increased with decreasing pH for all NaCl concentrations, and the titration curves in these solutions showed similar trend in the pH range of 6-11. On the other hand, total amount of H consumption increased with decreasing NaCl concentration in the pH range of 2-6. The dominant sorption mechanism of H
consumption increased with decreasing NaCl concentration in the pH range of 2-6. The dominant sorption mechanism of H on smectite was different between pH
on smectite was different between pH 6 and pH
6 and pH 6, and it can be considered that H
6, and it can be considered that H was sorbed on the same site as Na
was sorbed on the same site as Na for pH
for pH 6 and different site from Na
6 and different site from Na for pH
for pH 6. The prediction of protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl was carried out based on ion exchange and surface complexation models. The sorption sites were assumed as inter-layer and crystal edge site. The site concentrations for ion exchange and surface complexation were calculated from CEC. The reaction constants were consequently calculated by fitting of experimental results as follows. ...
6. The prediction of protonation/deprotonation behavior of smectite for 0.01, 0.1 and 0.5M NaCl was carried out based on ion exchange and surface complexation models. The sorption sites were assumed as inter-layer and crystal edge site. The site concentrations for ion exchange and surface complexation were calculated from CEC. The reaction constants were consequently calculated by fitting of experimental results as follows. ...