Mechanisms responsible for adsorption of molybdate ions on alumina for the production of medical radioisotopes
医療用放射性同位体の製造のためのアルミナへのモリブデン酸イオンの吸着に関与するメカニズム
藤田 善貴 

 ; 新関 智丈*; 福光 延吉*; 有賀 克彦*; 山内 悠輔*; Malgras, V.*; Kaneti, Y. V.*; Liu, C.-H.*; 籏野 健太郎*; 末松 久幸*; 鈴木 達也*; 土谷 邦彦
; 新関 智丈*; 福光 延吉*; 有賀 克彦*; 山内 悠輔*; Malgras, V.*; Kaneti, Y. V.*; Liu, C.-H.*; 籏野 健太郎*; 末松 久幸*; 鈴木 達也*; 土谷 邦彦 
Fujita, Yoshitaka; Niizeki, Tomotake*; Fukumitsu, Nobuyoshi*; Ariga, Katsuhiko*; Yamauchi, Yusuke*; Malgras, V.*; Kaneti, Y. V.*; Liu, C.-H.*; Hatano, Kentaro*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Tsuchiya, Kunihiko
本研究では、異なるpHの様々なモリブデン酸イオン種を含む溶液に浸したアルミナの各種表面分析(FTIR, XPS,ラマン分光法)により、アルミナへのモリブデン酸イオンの吸着メカニズムを考察した。得られた結果は、モリブデン酸イオンを含む酸性溶液にアルミナを浸すと、表面に存在するヒドロキシル基が除去されて正に帯電したサイトが生成され、モリブデン酸イオン(MoO
 またはAlMo
またはAlMo O
O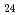 H
H
 )が静電相互作用によって吸着されることを示した。アルミナは酸性溶液にわずかに溶解してAlMo
)が静電相互作用によって吸着されることを示した。アルミナは酸性溶液にわずかに溶解してAlMo O
O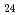 H
H
 を形成し、これはMoO
を形成し、これはMoO
 よりも容易に脱離する。さらに、アルミナ表面を多くの-OH基で濃縮し、Mo溶液を最適化してアルミナへMoO
よりも容易に脱離する。さらに、アルミナ表面を多くの-OH基で濃縮し、Mo溶液を最適化してアルミナへMoO
 としてモリブデン酸イオンを吸着させることで、アルミナのMo吸着および脱離特性を向上できる可能性が示唆された。これらの発見は、医療用放射性同位体(
としてモリブデン酸イオンを吸着させることで、アルミナのMo吸着および脱離特性を向上できる可能性が示唆された。これらの発見は、医療用放射性同位体( Mo/
Mo/ Tc)ジェネレータ用の、より効率的で安定したアルミナベースのMo吸着剤の開発に貢献できる。
Tc)ジェネレータ用の、より効率的で安定したアルミナベースのMo吸着剤の開発に貢献できる。
In this work, the mechanisms responsible for the adsorption of molybdate ions on alumina are investigated using in-depth surface analyses carried out on alumina specimens immersed in solutions containing different molybdate ions at different pH values. The obtained results reveal that when alumina is immersed in an acidic solution containing molybdate ions, the hydroxyl groups present on the surface are removed to generate positively charged sites, and molybdate ions (MoO
 or AlMo
or AlMo O
O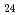 H
H
 ) are adsorbed by electrostatic interaction. Alumina dissolves slightly in an acidic solution to form AlMo
) are adsorbed by electrostatic interaction. Alumina dissolves slightly in an acidic solution to form AlMo O
O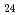 H
H
 , which is more easily desorbed than MoO
, which is more easily desorbed than MoO
 . Furthermore, the enhancement in the Mo adsorption or desorption property may be achieved by enriching the surface of the alumina adsorbent with many -OH groups and optimizing Mo solution to adsorb molybdate ions on alumina as MoO
. Furthermore, the enhancement in the Mo adsorption or desorption property may be achieved by enriching the surface of the alumina adsorbent with many -OH groups and optimizing Mo solution to adsorb molybdate ions on alumina as MoO
 ions. These findings will assist researchers in engineering more efficient and stable alumina-based adsorbents for molybdenum adsorption used in medical radioisotope (
ions. These findings will assist researchers in engineering more efficient and stable alumina-based adsorbents for molybdenum adsorption used in medical radioisotope ( Mo/
Mo/ Tc) generators.
Tc) generators.