Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 町田 昌彦
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2024 (WM2024) (Internet), 15 Pages, 2024/03
原子炉建屋の廃炉を安全に行うためには、放射線源分布の位置を特定することが非常に重要なる。これまでにも、同じ形状のセルで表現されているモデルに対して、LASSOを用いることで観測した空間線量から線源分布を推定できることが報告されている。さらに、セルが同じ形状でない場合でも、隣接セル間の濃度差を考慮した評価関数をfused LASSOを用いて最小化することで分布の推定ができる。しかし、モデルの構造データの精度の関係で、あるセル群が周囲のセル群と接していないとみなされている場合、そのようなセル群において推定される線源濃度が非常に高くなることかある。この問題を避けるため、新しい評価関数を提案し、テスト問題でその有効性を確認した。さらに、この提案した評価関数を用いることで、原子力機構のJMTRのプールカナル循環系機器室の線源分布をこれまでよりも正確に推定することに成功した。
町田 昌彦; 山田 進; Kim, M.; 奥村 雅彦; 宮村 浩子; 志風 義明; 佐藤 朋樹*; 沼田 良明*; 飛田 康弘*; 山口 隆司; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)建屋内には、原子炉内から漏洩した放射性物質の汚染により高い放射線量を示す地点が多数存在し、廃炉作業を円滑に進める上での大きな障害の一つとなっている。この課題解決に資するため、日本原子力研究開発機構(JAEA)は、経済産業省の廃炉・汚染水対策事業費補助金「原子炉建屋内の環境改善のための技術の開発(被ばく低減のための環境・線源分布のデジタル化技術の開発)」を受託し、令和3年度より2年間に渡り、放射線源の逆推定と推定線源に対する対策を仮想空間で実施可能とするためのデジタル技術の研究開発を実施してきた。本記事では、上記プロジェクトの成果(以下、前期プロジェクトと呼び、その2年間の研究開発の成果)を紹介する他、令和5年度4月より、新たに開始した継続プロジェクト(以下、後期プロジェクトと呼ぶ)の計画についても報告する。前期プロジェクトにて当初予定していた機械学習技術(LASSO)については、建屋内の複雑な構造情報と汚染源の性質を反映した一つの派生版手法へと結実させた成果を報告する他、実際の原子炉施設での検証結果を示す。更に、開発技術を集約したプラットフォームとしての機能を持つソフトウエア:3D-ADRES-Indoorを紹介し、継続して実施する予定の後期プロジェクトの研究開発計画も紹介する。
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)空間線量率のモニタリングに基づいて原子炉建屋内の放射源分布を予測することは、原子力発電所の廃止措置に向けた最も重要なステップの一つである。しかし、この問題は、一般には数学的には計算を行うには条件が足りない不良設定問題になり、解くことが困難である。そこで、このような不良設定問題でも線源分布の逆推定を成功させるために、損失関数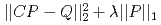 を最小化する機械学習手法であるLASSOの有効性を調査する。ここで、
を最小化する機械学習手法であるLASSOの有効性を調査する。ここで、 および
および はそれぞれ建屋の表面メッシュ上で定義された放射線源により構成されたベクトルおよび室内で観測された空間線量で構成されたベクトルである。また、
はそれぞれ建屋の表面メッシュ上で定義された放射線源により構成されたベクトルおよび室内で観測された空間線量で構成されたベクトルである。また、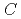 はPHITSを用いて計算された建屋の表面メッシュと観測点の寄与率で構成される行列である。CandesとTaoの理論に基づき、線源分布を正しく予測するための観測点の個数に関する条件を数学的に見出し、実際に、LASSOでは、観測点数がこの条件を満たす限り、実際に高い可能性で線源の分布を示すことができることを確認した。さらに、検出点数が基準値より少ない場合でも、線源分布の一部が示されることを見出した。さらに、現実的な実験モデルにおいても、放射線源が逆推定できることを確認する。最後に、逆推定における予測可能性を高めるために、観測点と線源間の距離のような影響因子を調査する。以上の実証結果から、LASSOスキームは福島第一原子力発電所のような損傷した原子力発電所で見られるホットスポットを探索するのに非常に有用な方法であることを示す。
はPHITSを用いて計算された建屋の表面メッシュと観測点の寄与率で構成される行列である。CandesとTaoの理論に基づき、線源分布を正しく予測するための観測点の個数に関する条件を数学的に見出し、実際に、LASSOでは、観測点数がこの条件を満たす限り、実際に高い可能性で線源の分布を示すことができることを確認した。さらに、検出点数が基準値より少ない場合でも、線源分布の一部が示されることを見出した。さらに、現実的な実験モデルにおいても、放射線源が逆推定できることを確認する。最後に、逆推定における予測可能性を高めるために、観測点と線源間の距離のような影響因子を調査する。以上の実証結果から、LASSOスキームは福島第一原子力発電所のような損傷した原子力発電所で見られるホットスポットを探索するのに非常に有用な方法であることを示す。
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Clarification of radioactive source distributions is one of the most important steps in initial decommissioning of not only normally shutdown reactors but also damaged ones by accidents like Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants (FDNPP). Generally, since radioactive hot spots are restricted into specific areas in normal operating conditions, the clarification scheme can be mapped onto the inverse estimation in sparse source distributions. On the other hand, the fact that radioactive hot spots are largely spread in unknown manner as seen in FDNPP motivates to construct an inversion scheme in non-sparse source conditions. Thus, a reconstruction scheme applicable to both sparse and non-sparse radioactive distributions is highly in demand. In addition, a variety of radionuclides is produced in reactors. Thus, we also need a scheme to distinguish each source distribution in mixed multi radionuclides. In this paper, we confirm that the inverse estimation scheme using Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) method with spectral information commonly shows excellent performance in the above all situations. The proposed LASSO scheme with the spectral information enables to reduce the number of measurement points in sparse conditions, while information proliferation by sensing the spectrum makes it possible to directly reconstruct source distribution as almost solvable problems in non-sparse ones. Moreover, the LASSO scheme allows to reconstruct the source distribution of each potential radionuclide in multi-radionuclide coexisting situations. Consequently, we confirm that the LASSO scheme to reconstruct radioactive sources is promising for the future nuclear decommissioning projects widely from normally shutdown reactors to damaged ones like FDNPP.
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Clarifying hot spots of radioactive sources inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps in decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is regarded as a rather difficult task, because information obtained by air dose rate measurements is generally not enough to inversely estimate contaminated distribution among a tremendous number of potential distributions inside complex reactor building rooms as far as one uses the conventional ways. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on source distributions even in such ill-posed circumstances, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) is a promising scheme. Subsequently, we construct a simple room model and employ Monte Carlo simulation code, Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Systems (PHITS) to numerically test feasibility of LASSO inverse estimation scheme. Consequently, we confirm high reconstruction performance of the LASSO scheme in successfully predicting radioactive source distributions. In addition, we carry out uncertainty analysis for the inverse estimation and derive an error function describing uncertainty of the inverse estimation as a useful error estimator. Finally, we find that additional use of spectral information in the measurements can significantly decrease the number of measurement points for the present inverse estimation. In conclusion, LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore radioactive hot spots toward the future decommissioning of nuclear power plants.
町田 昌彦; Shi, W.*; 山田 進; 宮村 浩子; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司; 青木 勇斗; 伊藤 倫太郎; 山口 隆司; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
In order to find radioactive hot spots inside reactor building rooms from structural data together with air dose rate measurement data, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) has been recently suggested as a promising scheme. The scheme has been examined in simplified room models and its high estimation feasibility has been confirmed by employing Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) as a radiation simulation code. In this paper, we apply the scheme to complex room models inside real reactor buildings. The target rooms are pool canal circulation system room and main circulation system room in Japan Materials Testing Reactor (JMTR) at Oarai area, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In these real rooms, we create STL format structural data based on Computer Aided Design (CAD) models made directly from their point group data measured by laser scanning devices, and we notice that the total number of their surface meshes in these real rooms reaches to the order of 1 million. Then, this order of the mesh number clearly indicates that one needs a simplified radiation simulation code considering only direct transmission of gamma ray as a radiation calculation instead of PHITS demanding high computational costs. By developing such a simplified code and customizing it to perform LASSO scheme, we consequently confirm that LASSO scheme driven by the simplified simulation can also successfully predict unknown radioactive hot spots on real structural models.
吉田 亨次*; 井上 拓也*; 鳥越 基克*; 山田 武*; 柴田 薫; 山口 敏男*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 149(12), p.124502_1 - 124502_10, 2018/09
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:17.83(Chemistry, Physical)異なる幾つかの、グリシン濃度, pH、および充填率(=グリシン溶液の質量/MCM-41の乾燥質量))をパラメーターとして、メソポーラスシリカ(MCM-41)に閉じ込められたグリシン水溶液の示差走査熱量測定、X線回折および準弾性中性子散乱(QENS)を305-180Kの温度範囲で実施して、グリシン水溶液の熱的挙動, 構造、および動的特性に対する閉じ込め効果を検討した。
伊藤 健一*; 宮原 英隆*; 氏家 亨*; 武島 俊達*; 横山 信吾*; 中田 弘太郎*; 永野 哲志; 佐藤 努*; 八田 珠郎*; 山田 裕久*
日本原子力学会和文論文誌, 11(4), p.255 - 271, 2012/04
放射性セシウムで汚染された土壌の減容化を検討するために、福島県飯舘村の農地土壌やグラウンド土壌に対し土壌分級洗浄実験を行った。その結果、水田,畑の土壌については分級洗浄により放射性セシウムの7, 8割を0.075mm以下の濁水として回収できること、また、グラウンドの砂質土壌については粗粒画分にも有意な量が分布しているが、分級洗浄の前に分散,振動,研磨などの処理を行うことにより、放射性セシウムをより細かい画分より回収できることを明らかにした。
中川 和道*; 金子 房恵*; 大田 佳実*; 田中 真人*; 北田 朋*; 安居院 あかね; 藤井 健太郎; 横谷 明徳; 渡辺 一寿*; 山田 亨*
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 144-147, p.271 - 273, 2005/06
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:50.37(Spectroscopy)円偏光と物質の相互作用の研究は、シンクロトロン放射の発展によって新たな発展の時期を迎えている。アミノ酸は鏡像体が容易に入手可能でありそれらが互いに反対の符号の円二色性を示すはずであるので、実験的にも理論的にも手堅い研究を可能にする研究素材である。われわれは、アミノ酸蒸着膜を試料として産総研TERASではVUV領域で、SPring-8では窒素・酸素K殻領域で円二色性測定を試み、SPring-8では、軟X線領域での円二色性検出に初めて成功した。産総研NIJI-2では固相で初めて不斉分解反応の検出に成功した。
 SiO
SiO determined by high
determined by high 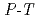 in situ X-ray diffractometry
in situ X-ray diffractometry桂 智男*; 山田 均*; 新名 亨*; 久保 敦*; 小野 重明*; 神崎 正美*; 米田 明*; Walter, M. J.*; 伊藤 英司*; 浦川 啓*; et al.
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 136(1-2), p.11 - 24, 2003/04
被引用回数:173 パーセンタイル:93.74(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Mg SiO
SiO のポストスピネル相転移境界をKawai型高圧装置と放射光を組合せた高温高圧下その場X線回折実験により再決定した。その結果、1550
のポストスピネル相転移境界をKawai型高圧装置と放射光を組合せた高温高圧下その場X線回折実験により再決定した。その結果、1550 2100Kにおける相境界は、約22GPaであり、地球内部660Km不連続が想定されている圧力より1
2100Kにおける相境界は、約22GPaであり、地球内部660Km不連続が想定されている圧力より1 1.5GPa低かった。
1.5GPa低かった。
長谷川 登*; 錦野 将元*; 三上 勝大*; 岡田 大*; 近藤 修司*; 河内 哲哉*; 島田 義則*; 倉橋 慎理*; 北村 俊幸*; Kotyaev, O.*; et al.
no journal, ,
急峻な地形を有する我が国にはトンネルや橋梁をはじめとするコンクリートを使用した社会インフラが数多く利用されている。特にトンネルの総延長は鉄道・道路を合わせて約8,000kmにも及んでおり、その中には築50年を越えたものも多く、事故を未然に防ぐための定期的な点検・補修を行うことが社会的な急務となっている。現在のコンクリート構造物の保守保全作業は訓練を受けた作業員による手作業に委ねられており、近接目視・触診・打音検査により欠陥を診断し、必要に応じて叩き落とし等の補修を行っている。これらは全て対象に近接する必要があるため時間がかかる事に加え、検査員に危険も伴う。そこで、高速・非接触・遠隔操作が可能な新しい保守保全技術の開発が盛んに行われている。本研究では、3種類のレーザー技術を用いることで、トンネルコンクリートを対象とした近接目視・触診・打音・叩き落としの一連の作業を遠隔・自動化を行うことを目的とし、屋外における実証試験を開始しており、この結果を中心に紹介する。
Shi, W.*; 町田 昌彦; 山田 進; 吉田 亨*; 長谷川 幸弘*; 岡本 孝司
no journal, ,
A mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on LASSO theory is developed for ill-posed radioactive source reconstruction. We employ Monte Carlo simulation to demonstrate and verify the feasibility of LASSO. Moreover, an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation is also examined.
町田 昌彦; Shi, W.*; 山田 進; 宮村 浩子; 沼田 良明*; 佐藤 朋樹*; 飛田 康弘*; 吉田 亨*; 柳 秀明*; 古立 直也*; et al.
no journal, ,
東京電力福島第一原子力発電所(以下「1F」)における燃料デブリ取り出し作業の本格的な実施に先立ち、線量率の高い原子炉建屋(以下「R/B」)内でのアクセスルート構築を、安全,効率的に行うための環境改善が必要であり、このための除染・遮へい戦略の検討をサイバー空間上で柔軟に実施できるシステムの開発を実施している。本報告では、上記システムの中核を成す、線源逆推定・線量率推定・可視化を担当する各エンジンの役割や研究開発計画とその進捗について報告する。
鈴木 政浩; 町田 昌彦; 山口 隆司; 宮村 浩子; 山田 進; 岡本 孝司; 長谷川 幸弘*; 吉田 亨*; Wei, S.*
no journal, ,
In order to promote decommissioning in 1F, it is crucial to find out strong radioactive hot spots inside reactor building rooms based on environmental measurement data composed of structural surface model data and distribution data of air dose rates. Such hot spot prediction allows to reduce radiation risks of persons working inside 1F and consequently to safely construct access routes to remove fuel debris. We introduce a new scheme to inversely estimate radioactive source distributions using LASSO. The scheme is composed of multiple steps, e.g., one of the most essential steps is to select measurement points of air dose rates. In addition, we develop the other engines calculating 3D distributions of air dose rates from the estimated source distributions together with a tool simulating virtual countermeasures and visualizing various outputs of the above engines in 3D space. In the present paper, we overview R&D project to integrate the above three engines.