Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
豊田 実*; 解良 恭一*; 大島 康宏; 石岡 典子; 紫野 正人*; 坂倉 浩一*; 高安 幸弘*; 高橋 克昌*; 富永 英之*; 織内 昇*; et al.
British Journal of Cancer, 110(10), p.2506 - 2513, 2014/05
被引用回数:115 パーセンタイル:95.14(Oncology)Amino-acid transporters are necessary for the tumor cell growth and survival, and play a crucial role in the development of cancer. But, it remains unclear about the prognostic significance of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1), System ASC amino acid transporter 2 (ASCT2) and xCT expression in patients with tongue cancer. We conducted the clinicopathological study to investigate the protein expression of these amino acid transporters in tongue cancer. Eighty-five patients with surgically resected tongue cancer were evaluated. Tumor sections were stained by immunohistochemistry for LAT1, ASCT2, xCT, CD98, Ki-67, CD34 and p53. The expression of LAT1 and ASCT2 was significantly associated with disease staging, lymph node metastasis, lymphatic permeation, vascular invasion, CD98 expression and cell proliferation (Ki-67). xCT expression indicated a significant association with advanced stage and tumor factor, correlated with CD98. By univariate analysis, both LAT1 and ASCT2 had a significant relationship with prognosis. Multivariate analysis confirmed that LAT1 were independent prognostic factors for predicting poor prognosis. These results suggest that LAT1 and ASCT2 can serve as a significant prognostic factor for predicting worse outcome after surgical treatment and may play an important role in the development and pathogenesis for tongue cancer.
 -methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancer
-methyltyrosine (FAMT) uptake on PET in patients with oesophageal cancer鈴木 茂正*; 解良 恭一*; 大島 康宏; 石岡 典子; 宗田 真*; 横堀 武彦*; 宮崎 達也*; 織内 昇*; 富永 英之*; 金井 好克*; et al.
British Journal of Cancer, 110(8), p.1985 - 1991, 2014/04
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:59.10(Oncology)Fluorine-18- -methyltyrosine (FAMT) as an amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) is useful for detecting human neoplasms. FAMT is accumulated in tumor cells solely via L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1). This study was conducted to investigate the biological significance of FAMT uptake in patients with esophageal cancer. From April 2008 to December 2011, 42 patients with esophageal cancer underwent both FAMT PET and FDG PET before surgical treatment. The immunohistochemical analysis of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67, CD34, p53, p-Akt and p-mTOR was performed on the primary lesions.
-methyltyrosine (FAMT) as an amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) is useful for detecting human neoplasms. FAMT is accumulated in tumor cells solely via L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1). This study was conducted to investigate the biological significance of FAMT uptake in patients with esophageal cancer. From April 2008 to December 2011, 42 patients with esophageal cancer underwent both FAMT PET and FDG PET before surgical treatment. The immunohistochemical analysis of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67, CD34, p53, p-Akt and p-mTOR was performed on the primary lesions. 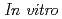 experiments were performed to examine the mechanism of FAMT uptake using LAT1 inhibitor, 2-aminobicyclo-(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH). High uptake of FAMT was significantly associated with advanced stage, lymph node metastasis and the expression of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67 and CD34. LAT1 expression yielded a statistically significant correlation with CD98 expression, cell proliferation, angiogenesis and glucose metabolism.
experiments were performed to examine the mechanism of FAMT uptake using LAT1 inhibitor, 2-aminobicyclo-(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH). High uptake of FAMT was significantly associated with advanced stage, lymph node metastasis and the expression of LAT1, CD98, Ki-67 and CD34. LAT1 expression yielded a statistically significant correlation with CD98 expression, cell proliferation, angiogenesis and glucose metabolism. 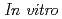 experiments revealed that FAMT was specifically transported by LAT1. The uptake of FAMT within tumor cells is determined by the LAT1 expression and correlated with cell proliferation and angiogenesis in esophageal cancer. The present experiments also confirmed the presence of LAT1 as an underlying mechanism of FAMT accumulation.
experiments revealed that FAMT was specifically transported by LAT1. The uptake of FAMT within tumor cells is determined by the LAT1 expression and correlated with cell proliferation and angiogenesis in esophageal cancer. The present experiments also confirmed the presence of LAT1 as an underlying mechanism of FAMT accumulation.
解良 恭一*; 須納瀬 豊*; 大島 康宏; 石岡 典子; 荒川 和久*; 小川 哲史*; 砂長 則明*; 清水 公裕*; 富永 英之*; 織内 昇*; et al.
BMC Cancer, 13, p.482_1 - 482_12, 2013/10
被引用回数:83 パーセンタイル:89.75(Oncology)The expression of L-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) has been described to play essential roles in tumor growth and survival. However, it remains unclear about the clinicopathological significance of LAT1 expression in biliary tract cancer. This study was conducted to determine clinical significance of LAT1 expression and investigate whether LAT1 could be a new therapeutic target for biliary tract cancer. A total of 139 consecutive patients with resected pathologic stage I-IV biliary tract adenocarcinoma were retrospectively reviewed. Tumor sections were stained by immunohistochemistry for LAT1, CD98, Ki-67, microvessel density determined by CD34 and p53. Further, anti-tumor activity of LAT inhibitor, 2-aminobicyclo-(2,2,1)-heptane-2-carboxylic acid (BCH) was investigated using cholangiocarcinoma cell line. The expression of LAT1 was recognized in 64% of total patients, and closely correlated with CD98 expression, lymphatic metastases, cell proliferation and angiogenesis, and was a significant indicator for predicting poor outcome after surgery. Experiments showed that BCH significantly suppressed the tumor growth and BCH yielded an additive therapeutic efficacy to gemcitabine and 5-FU. A cooperative high expression of LAT1 with CD98 is a promising pathological marker to predict the outcome in biliary tract adenocarcinoma. Inhibition of LAT1 may be an effective targeted therapy for this distressing disease.
 F]fluoro-
F]fluoro- -methyl-D-tyrosine (D-[
-methyl-D-tyrosine (D-[ F]FAMT) as a novel amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography
F]FAMT) as a novel amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography大島 康宏; 花岡 宏史*; 富永 英之*; 金井 好克*; 解良 恭一*; 山口 藍子*; 永森 收志*; 織内 昇*; 対馬 義人*; 遠藤 啓吾*; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 27(4), p.314 - 324, 2013/05
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:52.10(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)Since D-amino acid is not distributed much in the non-target organs and is rapidly excreted in the urine, radiotracer using D-amino acid would allow clear PET image of the tumor early after administration. In this study, we prepared 3-[ F]fluoro-
F]fluoro- -methyl-D-tyrosine (D-[
-methyl-D-tyrosine (D-[ F]FAMT) and evaluated its usefulness. In biodistribution studies, D-[
F]FAMT) and evaluated its usefulness. In biodistribution studies, D-[ F]FAMT showed rapid clearance from the blood, marked accumulation and retention in the tumor and low accumulation in non-target organs. The amount of D-[
F]FAMT showed rapid clearance from the blood, marked accumulation and retention in the tumor and low accumulation in non-target organs. The amount of D-[ F]FAMT in the tumor was also lowered, tumor-to-blood ratio and tumor-to-muscle ratio of D-[
F]FAMT in the tumor was also lowered, tumor-to-blood ratio and tumor-to-muscle ratio of D-[ F]FAMT were similar to those of correspondign L-isomer, 3-[
F]FAMT were similar to those of correspondign L-isomer, 3-[ F]fluoro-
F]fluoro- -methyl-L-tyrosine (L-[
-methyl-L-tyrosine (L-[ F]FAMT), at every timepoint. Consequently, PET imaging with D-[
F]FAMT), at every timepoint. Consequently, PET imaging with D-[ F]FAMT could not show clear image of the tumor early after the administration. However, D-[
F]FAMT could not show clear image of the tumor early after the administration. However, D-[ F]FAMT enabled higher tumor-to-background contrast than L-[
F]FAMT enabled higher tumor-to-background contrast than L-[ F]FAMT. In conclusions, D-[
F]FAMT. In conclusions, D-[ F]FAMT showed rapid blood clearance, low accumulation in non-target organs, and tumor-selective image compared with L-[
F]FAMT showed rapid blood clearance, low accumulation in non-target organs, and tumor-selective image compared with L-[ F]FAMT. Thus, D-[
F]FAMT. Thus, D-[ F]FAMT could potentially serve as a novel PET tracer for imaging malignant tumors.
F]FAMT could potentially serve as a novel PET tracer for imaging malignant tumors.
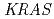 wild-type and
wild-type and 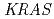 mutant colorectal cancer using
mutant colorectal cancer using  Cu-labeled cetuximab positron emission tomography
Cu-labeled cetuximab positron emission tomographyAchmad, A.*; 花岡 宏史*; 吉岡 弘樹*; 山元 進司*; 富永 英之*; 荒木 拓也*; 大島 康宏; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*
Cancer Science, 103(3), p.600 - 605, 2012/03
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:56.63(Oncology)Overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is common in colorectal cancer. However, cetuximab, an EGFR-targeting drug, is useful only for a subset of patients and no single predictor other than V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (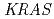 ) mutation status has been established. In this study, we investigated cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors using
) mutation status has been established. In this study, we investigated cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors using  In-DOTA-cetuximab, and evaluated the potential of positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of
In-DOTA-cetuximab, and evaluated the potential of positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of  Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. We found that
Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. We found that 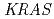 wild-type tumors had significantly higher
wild-type tumors had significantly higher  In-DOTA-cetuximab accumulation than
In-DOTA-cetuximab accumulation than 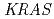 mutant tumors. Based on
mutant tumors. Based on 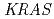 mutation status, a strong correlation was found between
mutation status, a strong correlation was found between  In-DOTA-cetuximab tumor uptake and EGFR expression level. Significant correlation was also found between tumor uptake of
In-DOTA-cetuximab tumor uptake and EGFR expression level. Significant correlation was also found between tumor uptake of  In-DOTA-cetuximab and
In-DOTA-cetuximab and  Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. PET imaging with
Cu-DOTA-cetuximab. PET imaging with  Cu-DOTA-cetuximab effectively visualized cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors with a wide variety of EGFR expression levels and different
Cu-DOTA-cetuximab effectively visualized cetuximab accumulation in colorectal tumors with a wide variety of EGFR expression levels and different 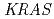 mutation status as commonly encountered in the clinical setting. Our findings suggest that this radioimmunoimaging can be clinically translated as an in vivo tool to predict cetuximab accumulation in colorectal cancer patients prior to cetuximab therapy.
mutation status as commonly encountered in the clinical setting. Our findings suggest that this radioimmunoimaging can be clinically translated as an in vivo tool to predict cetuximab accumulation in colorectal cancer patients prior to cetuximab therapy.
 Br]bromo-
Br]bromo- -methyl-L-tyrosine, a novel tyrosine analog for PET imaging of tumors
-methyl-L-tyrosine, a novel tyrosine analog for PET imaging of tumors大島 康宏; 花岡 宏史*; 渡邉 茂樹; 須郷 由美; 渡辺 智; 富永 英之*; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*; 石岡 典子
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 91, 2012/01
3-[ F]Fluoro-
F]Fluoro- -methyl-L-tyrosine ([
-methyl-L-tyrosine ([ F]FAMT) is a useful amino acid tracer for PET imaging of malignant tumors. FAMT analogs labeled with
F]FAMT) is a useful amino acid tracer for PET imaging of malignant tumors. FAMT analogs labeled with  Br, a positron emitter with a long half-life (t
Br, a positron emitter with a long half-life (t =16.1 h), could be widely used as tracers for tumor imaging. In this study, 3-[
=16.1 h), could be widely used as tracers for tumor imaging. In this study, 3-[ Br]bromo-
Br]bromo- -methyl-L-tyrosine ([
-methyl-L-tyrosine ([ Br]BAMT) was designed, and its usefulness was evaluated as a novel PET tracer for imaging malignant tumors. In this study, both [
Br]BAMT) was designed, and its usefulness was evaluated as a novel PET tracer for imaging malignant tumors. In this study, both [ Br]BAMT and [
Br]BAMT and [ Br]BAMT were prepared. [
Br]BAMT were prepared. [ Br]BAMT was stable in vitro, but was catabolized after administration in mice. Cellular accumulation and retention of [
Br]BAMT was stable in vitro, but was catabolized after administration in mice. Cellular accumulation and retention of [ Br]BAMT using LS180 colon adenocarcinoma cells were significantly higher than those of [
Br]BAMT using LS180 colon adenocarcinoma cells were significantly higher than those of [ F]FAMT. In biodistribution studies using LS180 tumor-bearing mice, the tumor accumulation of [
F]FAMT. In biodistribution studies using LS180 tumor-bearing mice, the tumor accumulation of [ Br]BAMT was higher than that of [
Br]BAMT was higher than that of [ F]FAMT. However, some level of debromination was seen, and this debromination caused more retention of radioactivity in the blood and organs than was seen with [
F]FAMT. However, some level of debromination was seen, and this debromination caused more retention of radioactivity in the blood and organs than was seen with [ F]FAMT. PET imaging with [
F]FAMT. PET imaging with [ Br]BAMT enabled clear visualization of the tumor. In conclusion, although an improvement in stability is still needed,
Br]BAMT enabled clear visualization of the tumor. In conclusion, although an improvement in stability is still needed,  Br-labeled FAMT analogs could potentially serve as PET tracers for the imaging of malignant tumors.
Br-labeled FAMT analogs could potentially serve as PET tracers for the imaging of malignant tumors.
 Br]bromo-
Br]bromo- -methyl-L-tyrosine, a novel tyrosine analog for positron emission tomography imaging of tumors
-methyl-L-tyrosine, a novel tyrosine analog for positron emission tomography imaging of tumors大島 康宏; 花岡 宏史*; 渡邉 茂樹; 須郷 由美; 渡辺 智; 富永 英之*; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*; 石岡 典子
Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 38(6), p.857 - 865, 2011/08
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:47.71(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)3-[ F]fluoro-
F]fluoro- -methyl-L-tyrosine ([
-methyl-L-tyrosine ([ F]FAMT) is a useful amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of malignant tumors. FAMT analogs labeled with
F]FAMT) is a useful amino acid tracer for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of malignant tumors. FAMT analogs labeled with  Br, a positron emitter with a long half-life (
Br, a positron emitter with a long half-life (
 =16.1 h), could be widely used as tracers for tumor imaging. In this study, 3-[
=16.1 h), could be widely used as tracers for tumor imaging. In this study, 3-[ Br]bromo-
Br]bromo- -methyl-L-tyrosine ([
-methyl-L-tyrosine ([ Br]BAMT) was designed, and its usefulness was evaluated as a novel PET tracer for imaging malignant tumors. In this study, both [
Br]BAMT) was designed, and its usefulness was evaluated as a novel PET tracer for imaging malignant tumors. In this study, both [ Br]BAMT and [
Br]BAMT and [ Br]BAMT were prepared. [
Br]BAMT were prepared. [ Br]BAMT was stable in vitro, but was catabolized after administration in mice. Cellular accumulation and retention of [
Br]BAMT was stable in vitro, but was catabolized after administration in mice. Cellular accumulation and retention of [ Br]BAMT using LS180 colon adenocarcinoma cells were significantly higher than those of [
Br]BAMT using LS180 colon adenocarcinoma cells were significantly higher than those of [ F]FAMT. In biodistribution studies using LS180 tumor-bearing mice, the tumor accumulation of [
F]FAMT. In biodistribution studies using LS180 tumor-bearing mice, the tumor accumulation of [ Br]BAMT was higher than that of [
Br]BAMT was higher than that of [ F]FAMT. However, some level of debromination was seen, and this debromination caused more retention of radioactivity in the blood and organs than was seen with [
F]FAMT. However, some level of debromination was seen, and this debromination caused more retention of radioactivity in the blood and organs than was seen with [ F]FAMT. PET imaging with [
F]FAMT. PET imaging with [ Br]BAMT enabled clear visualization of the tumor. In conclusion, although an improvement in stability is still needed,
Br]BAMT enabled clear visualization of the tumor. In conclusion, although an improvement in stability is still needed,  Br-labeled FAMT analogs could potentially serve as PET tracers for the imaging of malignant tumors.
Br-labeled FAMT analogs could potentially serve as PET tracers for the imaging of malignant tumors.
 Cu -labeled trastuzumab PET
Cu -labeled trastuzumab PETPaudyal, P.*; Paudyal, B.*; 花岡 宏史*; 織内 昇*; 飯田 靖彦*; 吉岡 弘樹*; 富永 英之*; 渡辺 智; 渡邉 茂樹; 石岡 典子; et al.
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 108, 2011/01
Non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC) overexpress the Her2/neu gene in approximately 59% of cases. Trastuzumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, interferes with Her2 signaling and is approved for the treatment of Her2/neu overexpressing breast cancer. However, its therapeutic use in Her2/neu overexpressing NSCLC remains obscure. The present study aimed to determine the role of  Cu-labeled trastuzumab positron emission tomography (PET) for non-invasive imaging of Her2/neu expression in NSCLC. Imaging of Her2/neu expression was performed in NCI-H2170 tumor-bearing mice with
Cu-labeled trastuzumab positron emission tomography (PET) for non-invasive imaging of Her2/neu expression in NSCLC. Imaging of Her2/neu expression was performed in NCI-H2170 tumor-bearing mice with  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab. PET studies revealed a significantly high accumulation of
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab. PET studies revealed a significantly high accumulation of  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab in the Her2/neu overexpressing NCI-H2170 tumor at 24 h and 48 h post-injection.
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab in the Her2/neu overexpressing NCI-H2170 tumor at 24 h and 48 h post-injection.  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab showed a very clear image of a Her2/neu positive tumor and appeared to be effective as a PET tracer for imaging of Her2/neu gene expression in NSCLC, suggesting its potential clinical use for identifying patients that might benefit from trastuzumab-based therapy.
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab showed a very clear image of a Her2/neu positive tumor and appeared to be effective as a PET tracer for imaging of Her2/neu gene expression in NSCLC, suggesting its potential clinical use for identifying patients that might benefit from trastuzumab-based therapy.
 Cu-labeled trastuzumab PET
Cu-labeled trastuzumab PETPaudyal, P.*; Paudyal, B.*; 花岡 宏史*; 織内 昇*; 飯田 靖彦*; 吉岡 弘樹*; 富永 英之*; 渡辺 智; 渡邉 茂樹; 石岡 典子; et al.
Cancer Science, 101(4), p.1045 - 1050, 2010/04
被引用回数:40 パーセンタイル:66.81(Oncology)Non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC) overexpress the Her2/neu gene in approximately 59% of cases. Trastuzumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody, interferes with Her2 signaling and is approved for the treatment of Her2/neu overexpressing breast cancer. However, its therapeutic use in Her2/neu overexpressing NSCLC remains obscure. The present study aimed to determine the role of  Cu-labeled trastuzumab positron emission tomography (PET) for non-invasive imaging of Her2/neu expression in NSCLC. Imaging of Her2/neu expression was performed in NCI-H2170 tumor-bearing mice with
Cu-labeled trastuzumab positron emission tomography (PET) for non-invasive imaging of Her2/neu expression in NSCLC. Imaging of Her2/neu expression was performed in NCI-H2170 tumor-bearing mice with  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab. PET studies revealed a significantly high accumulation of
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab. PET studies revealed a significantly high accumulation of  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab in the Her2/neu overexpressing NCI-H2170 tumor at 24 h and 48 h post-injection.
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab in the Her2/neu overexpressing NCI-H2170 tumor at 24 h and 48 h post-injection.  Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab showed a very clear image of a Her2/neu positive tumor and appeared to be effective as a PET tracer for imaging of Her2/neu gene expression in NSCLC, suggesting its potential clinical use for identifying patients that might benefit from trastuzumab-based therapy.
Cu-DOTA-trastuzumab showed a very clear image of a Her2/neu positive tumor and appeared to be effective as a PET tracer for imaging of Her2/neu gene expression in NSCLC, suggesting its potential clinical use for identifying patients that might benefit from trastuzumab-based therapy.
飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 渡辺 智; 渡邉 茂樹; 石岡 典子; 吉岡 弘樹*; 山元 進司*; Paudyal, P.*; Paudyal, B.*; 樋口 哲也*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 108, 2009/12
As antibody binds specifically to corresponding antigens, radiolabeled antibody also binds to cells expressing antigens on surface membranes. Large amounts of antibodies labeled with cytotoxic radionuclides are administered intravenously in cancer patients, after diagnostic imaging using the tracer amount of radiolabeled antibody. In this study, we developed this therapy, called radioimmunotherapy, for effective treatment in cancer patients without damaging normal cells which do not express antigens. We developed  Lu-DOTA-NuB2 using carrier-free
Lu-DOTA-NuB2 using carrier-free  Lu, and obtained remarkable results for decreasing tumor. Tumor specific radionuclide therapy using
Lu, and obtained remarkable results for decreasing tumor. Tumor specific radionuclide therapy using  Lu is effective therapy with less adverse reactions.
Lu is effective therapy with less adverse reactions.
 Cu-labeled DOTA-
Cu-labeled DOTA-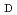 -Phe
-Phe -Tyr
-Tyr -octreotide (
-octreotide ( Cu-DOTA-TOC) for imaging somatostatin receptor-expressing tumors
Cu-DOTA-TOC) for imaging somatostatin receptor-expressing tumors花岡 宏史*; 富永 英之*; 山田 圭一*; Paudyal, P.*; 飯田 靖彦*; 渡邉 茂樹; Paudyal, B.*; 樋口 徹也*; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*
Annals of Nuclear Medicine, 23(6), p.559 - 567, 2009/08
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:50.64(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)In-111 ( In)-labeled octreotide has been clinically used for imaging somatostatin receptor-positive tumors, and radiolabeled octreotide analogs for positron emission tomography (PET) have been developed. The aim of this study is to produce and fundamentally examine a
In)-labeled octreotide has been clinically used for imaging somatostatin receptor-positive tumors, and radiolabeled octreotide analogs for positron emission tomography (PET) have been developed. The aim of this study is to produce and fundamentally examine a  Cu-labeled octreotide analog,
Cu-labeled octreotide analog,  Cu-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-
Cu-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid-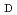 -Phe
-Phe -Tyr
-Tyr -octreotide (
-octreotide ( Cu-DOTA-TOC).
Cu-DOTA-TOC).  Cu-DOTA-TOC can be produced in amounts efficient for clinical study with high radiochemical yield.
Cu-DOTA-TOC can be produced in amounts efficient for clinical study with high radiochemical yield.  Cu-DOTA-TOC was stable in vitro, but time-dependent transchelation to protein was observed after injection into mice. In biodistribution studies, the radioactivity of
Cu-DOTA-TOC was stable in vitro, but time-dependent transchelation to protein was observed after injection into mice. In biodistribution studies, the radioactivity of  Cu was higher than that of
Cu was higher than that of  In in all organs except kidney. In tumor-bearing mice,
In in all organs except kidney. In tumor-bearing mice,  Cu-DOTA-TOC showed a high accumulation in the tumors, and the tumor-to-blood ratio reached as high as 8.81
Cu-DOTA-TOC showed a high accumulation in the tumors, and the tumor-to-blood ratio reached as high as 8.81  1.17 at 6 h after administration.
1.17 at 6 h after administration.  Cu-DOTA-TOC showed significantly higher accumulation in the tumor than
Cu-DOTA-TOC showed significantly higher accumulation in the tumor than  Cu-TETA-OC and
Cu-TETA-OC and  Cu-DOTA-OC. PET showed a very clear image of the tumor, which was comparable to that of
Cu-DOTA-OC. PET showed a very clear image of the tumor, which was comparable to that of  F-FDG PET and very similar to that of
F-FDG PET and very similar to that of  Cu-TETA-OC.
Cu-TETA-OC.  Cu-DOTA-TOC clearly imaged a somatostatin receptor-positive tumor and seemed to be a potential PET tracer in the clinical phase.
Cu-DOTA-TOC clearly imaged a somatostatin receptor-positive tumor and seemed to be a potential PET tracer in the clinical phase.
飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; Paudyal, P.*; Paudyal, B.*; 渡辺 智; 石岡 典子; 渡邉 茂樹; 松橋 信平; 吉岡 弘樹*; 樋口 徹也*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2008-055, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2007, P. 114, 2008/11
Optical imaging is recently developed for in vivo molecular imaging. It requires only a simple system, and has advantage of relatively low cost. Furthermore, optical imaging probes can provide the highest signal-to-noise ratio for molecular targeting, so optical imaging is ideal candidate for molecular imaging. In this study, we prepared a probe, which labeled with both radioisotope and fluorescent dye, and evaluated the difference of images from PET and optical imaging, and compare the characteristics of both imaging methods. From our results, multimodal imaging system can provide complementary information about the functional status of various tissues, and can improve the accuracy of tumor diagnosis.
飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 片渕 竜也*; 渡邉 茂樹; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 樋口 徹也*; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 128, 2008/03
PET is superior in quantitative measurement, so  F-FDG-PET is most valuable tool for tumor diagnosis. Although several positron emitters have been used for PET, their uses are limited for their short half-lives. Compared with these radionuclides,
F-FDG-PET is most valuable tool for tumor diagnosis. Although several positron emitters have been used for PET, their uses are limited for their short half-lives. Compared with these radionuclides,  Cu and
Cu and  Br have appropriate properties (
Br have appropriate properties ( Br: T
Br: T = 16.1hr,
= 16.1hr,  Cu: T
Cu: T = 12.7hr) and they may have great potentials for PET utility. In this study, we synthesized monoclonal antibody (mAb) labeled with
= 12.7hr) and they may have great potentials for PET utility. In this study, we synthesized monoclonal antibody (mAb) labeled with  Cu or
Cu or  Br and evaluated their potential for tumor diagnosis with PET. The results of tumor localization studies show that
Br and evaluated their potential for tumor diagnosis with PET. The results of tumor localization studies show that  Cu or
Cu or  Br labeled mAb were highly accumulated to tumor. From these data, the use of
Br labeled mAb were highly accumulated to tumor. From these data, the use of  Cu and
Cu and  Br has great advantage for PET utility.
Br has great advantage for PET utility.
飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 片渕 竜也*; 渡辺 智; 石岡 典子; 松橋 信平; 織内 昇*; 樋口 徹也*; 宮久保 満之*; 遠藤 啓吾*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 165, 2007/02
Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) becomes one of the most promising treatments for cancer therapy. Recently, because various radioisotopes are being used for RIT, the efficient tailor-made therapy is thought to be possible. The high energy  -particle-emitter, such as
-particle-emitter, such as  Y (2.28 MeV), seems particularly well suited for the treatment of relatively large tumor masses, but the middle energy
Y (2.28 MeV), seems particularly well suited for the treatment of relatively large tumor masses, but the middle energy  -particles, such as
-particles, such as  Cu (0.18-0.58 MeV), may have an advantage in treating small lesions. In this study, we prepared
Cu (0.18-0.58 MeV), may have an advantage in treating small lesions. In this study, we prepared  Cu and evaluated its potential of application for RIT in tumor bearing mice. Our results of tumor localization studies show that
Cu and evaluated its potential of application for RIT in tumor bearing mice. Our results of tumor localization studies show that  Cu was expected to be suitable for RIT.
Cu was expected to be suitable for RIT.
花岡 宏史*; 飯田 靖彦*; 樋口 徹也*; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*; 渡辺 智; 渡邉 茂樹; 石岡 典子
no journal, ,
近年、治療効果の増強を目的として抗体に放射性同位元素(RI)を結合したRI標識抗体を投与しがんを治療する放射免疫療法が注目されている。 線放出核種であるイットリウム-90で標識した抗CD20抗体(ゼヴァリン)は、悪性リンパ腫の治療薬として日本でも認可されており、新規治療薬として高い治療効果を示している。その一方で、放射免疫療法では十分な治療効果が得られていない場合も多く存在することから、治療成績の向上のためにさまざまな方策が考えられている。その一つとして、新規RIを用いた放射免疫療法が検討されている。抗体が腫瘍へ集積するまでには数日を要することから、6.7日と比較的長い半減期を有するルテチウム-177(
線放出核種であるイットリウム-90で標識した抗CD20抗体(ゼヴァリン)は、悪性リンパ腫の治療薬として日本でも認可されており、新規治療薬として高い治療効果を示している。その一方で、放射免疫療法では十分な治療効果が得られていない場合も多く存在することから、治療成績の向上のためにさまざまな方策が考えられている。その一つとして、新規RIを用いた放射免疫療法が検討されている。抗体が腫瘍へ集積するまでには数日を要することから、6.7日と比較的長い半減期を有するルテチウム-177( Lu)が新規核種として期待されている。そこで本研究では、
Lu)が新規核種として期待されている。そこで本研究では、 Lu標識抗体を用いた効果的な放射免疫療法を目指して、
Lu標識抗体を用いた効果的な放射免疫療法を目指して、 Lu標識抗体に関する基礎的検討を行った。
Lu標識抗体に関する基礎的検討を行った。 Yb(n,
Yb(n,  )
)  Yb
Yb
 Lu反応で製造した
Lu反応で製造した Luを用いて
Luを用いて Lu標識抗体による胆癌マウスを用いた治療実験を行った結果、投与早期より腫瘍が縮小し、6日後には腫瘍が消失したことから、
Lu標識抗体による胆癌マウスを用いた治療実験を行った結果、投与早期より腫瘍が縮小し、6日後には腫瘍が消失したことから、 Lu標識抗体の放射免疫療法薬剤としての有用性が示された。
Lu標識抗体の放射免疫療法薬剤としての有用性が示された。
飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 渡辺 智; 石岡 典子; 渡邉 茂樹; 松橋 信平; Paudyal, B.*; 織内 昇*; 樋口 徹也*; 遠藤 啓吾*
no journal, ,
Optical imaging is recently developed for in vivo molecular imaging. It requires only a simple system, and has advantage of relatively low cost. Furthermore, a probe for optical imaging can be designed to change its signal characteristic when it has interaction with the specific target. This property provides the highest signal-to-noise ratio for molecular targeting, so optical imaging is ideal candidate for molecular imaging. On the other hand, optical imaging is poor for tissue penetration and has limitation of deep tissue surveying. In this study, we prepared a probe, which labeled with both radioisotope and fluorescent dye, and evaluated the difference of images from PET and optical imaging, and compare the characteristics of both imaging methods. Anti-CD20 antibody, NuB2, was labeled with  Cu and fluorescent dye. For in vivo imaging studies, tumor bearing mice were used. After administration of this probe, imaging was performed with PET and optical imaging. For the results, optical imaging could not detect deep tissue, so optical image was different from PET image. Compared with data from extracted tissue activity, optical image does not reflect the accurate tissue distribution, but it has utility for evaluation of subcutaneous transplanted tumor.
Cu and fluorescent dye. For in vivo imaging studies, tumor bearing mice were used. After administration of this probe, imaging was performed with PET and optical imaging. For the results, optical imaging could not detect deep tissue, so optical image was different from PET image. Compared with data from extracted tissue activity, optical image does not reflect the accurate tissue distribution, but it has utility for evaluation of subcutaneous transplanted tumor.
飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 吉岡 弘樹*; 宮久保 満之*; Paudyal, B.*; 樋口 徹也*; 織内 昇*; 遠藤 啓吾*; 片渕 竜也*; 石岡 典子; et al.
no journal, ,
近年、がん診断における F標識グルコース(
F標識グルコース( F-FDG)の有用性が明らかとなり、多数の施設においてPETによる画像診断が行われるようになっている。しかしながら、現在PETに用いられている放射性同位元素はいずれも半減期が短く、その利用には制限があるのが現状である。そこで、製薬会社において製造し、医療現場への供給が可能な半減期を有する新規PET用核種の製造とそれを用いた放射性薬剤の開発・有効性の確認に関する研究を進めている。本シンポジウムにおいては、新規核種として開発を進めている、
F-FDG)の有用性が明らかとなり、多数の施設においてPETによる画像診断が行われるようになっている。しかしながら、現在PETに用いられている放射性同位元素はいずれも半減期が短く、その利用には制限があるのが現状である。そこで、製薬会社において製造し、医療現場への供給が可能な半減期を有する新規PET用核種の製造とそれを用いた放射性薬剤の開発・有効性の確認に関する研究を進めている。本シンポジウムにおいては、新規核種として開発を進めている、 Cu,
Cu,  Cu,
Cu,  Br,
Br,  Luについて、それぞれの核種の特徴及び研究開発の進捗を紹介する。
Luについて、それぞれの核種の特徴及び研究開発の進捗を紹介する。
 Cu for quantitative evaluation of radioimmunotherapy
Cu for quantitative evaluation of radioimmunotherapy飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 片渕 竜也*; 渡辺 智; 石岡 典子; 松橋 信平; 織内 昇*; 樋口 徹也*; 宮久保 満之*; 遠藤 啓吾*
no journal, ,
 Cu is one of the most attractive candidate emitter for radioimmunotherapy (RIT).
Cu is one of the most attractive candidate emitter for radioimmunotherapy (RIT).  Cu releases positron emitter (0.653 MeV, 18%) as well as middle energy
Cu releases positron emitter (0.653 MeV, 18%) as well as middle energy  -particles (0.578 MeV, 37%), so it can be applied for diagnostic imaging with PET. PET is superior in quantitative measurement and suitable for evaluation of therapeutic effect with RIT. PET can also directly estimate radiation dose of RIT. In this study, we prepared a radioimmunoconjugate, NuB2, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb), labeled with
-particles (0.578 MeV, 37%), so it can be applied for diagnostic imaging with PET. PET is superior in quantitative measurement and suitable for evaluation of therapeutic effect with RIT. PET can also directly estimate radiation dose of RIT. In this study, we prepared a radioimmunoconjugate, NuB2, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb), labeled with  Cu, and evaluated its potential for PET imaging with RIT. NuB2 was labeled with
Cu, and evaluated its potential for PET imaging with RIT. NuB2 was labeled with  Cu. For in vivo studies, SCID mice bearing CD20
Cu. For in vivo studies, SCID mice bearing CD20 tumor were used. After administration, biodistribution and PET imaging were performed. For the results of biodistribution,
tumor were used. After administration, biodistribution and PET imaging were performed. For the results of biodistribution,  Cu-NuB2 was highly accumulated to CD20
Cu-NuB2 was highly accumulated to CD20 tumor, and PET images could show the same results. From these date, the use of
tumor, and PET images could show the same results. From these date, the use of  Cu for PET imaging has potential for accurately evaluation of therapeutic effect of RIT.
Cu for PET imaging has potential for accurately evaluation of therapeutic effect of RIT.
 Cu for immuno-PET; In vivo measurement of radiation dose for radioimmunotherapy
Cu for immuno-PET; In vivo measurement of radiation dose for radioimmunotherapy飯田 靖彦*; 花岡 宏史*; 片渕 竜也*; 渡辺 智; 石岡 典子; 松橋 信平; 織内 昇*; 樋口 徹也*; 宮久保 満之*; 遠藤 啓吾*
no journal, ,
Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) becomes one of the most promising treatments for cancer therapy. Recently, RIT becomes available for clinical use and shows high efficacy, but it has some adverse effects for radiation to normal tissues and its therapeutic window is limited. So, assessment of radiation dose deliver to both tumor and normal tissues is very important for RIT. PET is superior in quantitative measurement and it can estimate radiation dose directly. Although representative positron emitter has short half-life, which is not good for labeling of antibody,  Cu has appropriate property, T
Cu has appropriate property, T = 12.7 hr, and it may have a great potential for immuno-PET. In this study, we prepared a radioimmunoconjugate, NuB2, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb), labeled with
= 12.7 hr, and it may have a great potential for immuno-PET. In this study, we prepared a radioimmunoconjugate, NuB2, anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (mAb), labeled with  Cu, and evaluated potential for in vivo quantitative measurement of radiation dose for RIT. NuB2 was labeled with
Cu, and evaluated potential for in vivo quantitative measurement of radiation dose for RIT. NuB2 was labeled with  Cu. For in vivo studies, SCID mice bearing CD20
Cu. For in vivo studies, SCID mice bearing CD20 tumor were used. After administration, biodistribution and PET imaging were performed. For the results of biodistribution,
tumor were used. After administration, biodistribution and PET imaging were performed. For the results of biodistribution,  Cu-NuB2 was highly accumulated to CD20
Cu-NuB2 was highly accumulated to CD20 tumor, and PET images could show the same results. From these date, the use of
tumor, and PET images could show the same results. From these date, the use of  Cu immuno-PET has potential for accurately measurement of radiation dose for RIT.
Cu immuno-PET has potential for accurately measurement of radiation dose for RIT.
石岡 典子; 花岡 宏史*; 飯田 靖彦*; 渡辺 智; 渡邉 茂樹; 織内 昇*; 樋口 徹也*; 橋本 和幸; 遠藤 啓吾*
no journal, ,
近年、治療効果の増強を目的としてRI標識抗体による治療(放射免疫療法)が注目されている。そこで、抗体が腫瘍へ集積するために十分な半減期を有するLu-177(T :6.7日)を用いて効果的な放射免疫療法を実施するために、
:6.7日)を用いて効果的な放射免疫療法を実施するために、 Lu標識抗体の作製,分析,体内動態に関する基礎的検討を行った。抗CD20抗体に2種類のキレート剤を結合させたDTPA-抗体及びDOTA-抗体を作製した。
Lu標識抗体の作製,分析,体内動態に関する基礎的検討を行った。抗CD20抗体に2種類のキレート剤を結合させたDTPA-抗体及びDOTA-抗体を作製した。 Lu標識を行ったところ、標識率はDTPA-抗体が92.4%, DOTA-抗体44.8%とDTPA-抗体の方が有意に高かった。CD20陽性のバーキットリンパ腫細胞を移植した担癌マウスを作製し、
Lu標識を行ったところ、標識率はDTPA-抗体が92.4%, DOTA-抗体44.8%とDTPA-抗体の方が有意に高かった。CD20陽性のバーキットリンパ腫細胞を移植した担癌マウスを作製し、 Lu標識抗体の体内分布を検討したところ、腫瘍への集積性は
Lu標識抗体の体内分布を検討したところ、腫瘍への集積性は Lu-DTPA-抗体の方が高かった。また同様のモデルに対して、
Lu-DTPA-抗体の方が高かった。また同様のモデルに対して、 Lu標識抗体による治療実験を行った結果、腫瘍サイズが小さいものでは明らかな腫瘍増殖抑制効果が認められた。また、
Lu標識抗体による治療実験を行った結果、腫瘍サイズが小さいものでは明らかな腫瘍増殖抑制効果が認められた。また、 Lu-DTPA-抗体を投与したマウスの一部に腫瘍の縮小が見られ、腫瘍全体が白く変色したことから腫瘍が壊死していることが示唆された。新規RIとして注目されている
Lu-DTPA-抗体を投与したマウスの一部に腫瘍の縮小が見られ、腫瘍全体が白く変色したことから腫瘍が壊死していることが示唆された。新規RIとして注目されている Luで標識した抗体を作製し、治療実験可能な放射能の
Luで標識した抗体を作製し、治療実験可能な放射能の Lu標識抗体を得ることができた。担癌マウスを用いた体内分布実験では
Lu標識抗体を得ることができた。担癌マウスを用いた体内分布実験では Lu標識抗体は腫瘍集積性を示し、また治療実験では抗腫瘍効果を認めた。以上の結果より、
Lu標識抗体は腫瘍集積性を示し、また治療実験では抗腫瘍効果を認めた。以上の結果より、 Lu標識抗体の放射免疫療法薬剤としての有用性が示された。
Lu標識抗体の放射免疫療法薬剤としての有用性が示された。