Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival
-sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on bacterial inoculants survival手島 光平*; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 112, 2013/01
Biofertilizer is a substance that holds beneficial microorganisms for plant growth in the carrier such as peat, perlite, charcoal and soil. To use biofertilizer more efficiently, it is necessary to keep the amount of viable inoculants in the biofertilizer for a definite period of time.  -irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of
-irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In this study, to demonstrate the effectiveness of  -sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria
-sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored for the nitrogen-fixing bacteria 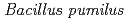 strain TUAT1 and
strain TUAT1 and 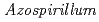 sp. strain MAFF210364.
sp. strain MAFF210364.
布柴 達男*; 平澤 佑啓*; 山内 理子*; 佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平*; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 111, 2013/01
The LOH (loss of heterozygosity) induction by various ion beam radiations was investigated in diploid  . The ion beams
. The ion beams  C
C ,
,  C
C ,
,  He
He and
and  Ar
Ar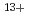 at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30-50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly (
at the lowest dose (75, 75, 200 and 150 Gy, respectively), which had 30-50% lethality, induced LOH with 10-fold higher frequency. The LOH induction was predominantly ( 90%) resulted from gene conversion or crossover through homologous recombination, and followed by chromosome loss through chromosome mis-segregation. Induction of LOH by
90%) resulted from gene conversion or crossover through homologous recombination, and followed by chromosome loss through chromosome mis-segregation. Induction of LOH by  C
C was also examined in
was also examined in 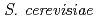 deficient in AP endonuclease (Apn1), translesion DNA polymerases Pol
deficient in AP endonuclease (Apn1), translesion DNA polymerases Pol encoded by Rad30 and Pol
encoded by Rad30 and Pol encoded by Rev3 and Rev7. Pol
encoded by Rev3 and Rev7. Pol may be involved in the induction of LOH, because a slight induction of LOH by
may be involved in the induction of LOH, because a slight induction of LOH by  C
C was observed in the Rev3-deficient strain.
was observed in the Rev3-deficient strain.
 USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation
USDA110 generated by ion-beam irradiation武田 喜代子; 手島 光平*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 107, 2013/01
We have tried to improve high temperature tolerance of  USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43
USDA110, which is a superior inoculant to soybean in temperate area, using ion beam breeding technology. Consequently, we have obtained 20 high-temperature tolerant mutants, which can survive at 43 C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30
C for at least 7 days. In this report, we show phenotypic characteristics of 3 mutants (strains M4, M5 and M6) that exhibit relatively higher tolerance among the mutants obtained. The colony of M4, M5 and M6 was smooth with glossy pale pink color unlike wild type. There might be a link between high temperature tolerance and these phenotypic changes. Therefore, we intend to identify factors causing these changes. The generation time of high-temperature tolerant mutants at 30 C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.
C was about 1.5 h shorter than that of wild type.

佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平*; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 103, 2013/01
 exhibits extraordinary resistance to the lethal effects of ionizing radiations. This resistance has been attributed to its highly proficient DNA repair capacity. In this study, we investigated antibiotics-resistant mutant frequencies for different LET radiations in
exhibits extraordinary resistance to the lethal effects of ionizing radiations. This resistance has been attributed to its highly proficient DNA repair capacity. In this study, we investigated antibiotics-resistant mutant frequencies for different LET radiations in  . Rifampicin is one of the antibiotics that inhibit RNA synthesis by directly interacting with the RNA polymerase beta subunit protein encoded by
. Rifampicin is one of the antibiotics that inhibit RNA synthesis by directly interacting with the RNA polymerase beta subunit protein encoded by 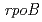 gene. By genetically altering the
gene. By genetically altering the 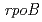 gene in genome, Rif
gene in genome, Rif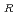 mutant can be generated. The Rif
mutant can be generated. The Rif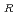 mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. The highest Rif
mutant frequencies increased depending on radiation dose. The highest Rif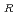 mutant frequencies were observed at a dose range that give 10
mutant frequencies were observed at a dose range that give 10 to 10
to 10 of surviving fraction. There is the possibility that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purposes.
of surviving fraction. There is the possibility that this dose range is the best dose to generate the mutants of interest for research and breeding purposes.
 RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination佐藤 勝也; 菊地 正博; Ishaque, A. M.*; 大庭 寛史*; 山田 貢; 手島 光平; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
DNA Repair, 11(4), p.410 - 418, 2012/04
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:60.32(Genetics & Heredity)放射線抵抗性細菌の相同組換え機構におけるRecFORタンパク質の役割を明らかにするために、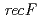 ,
, 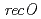 及び
及び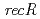 遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学及び分子生物学的解析を行った。
遺伝子破壊株を作製し、分子遺伝学及び分子生物学的解析を行った。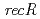 遺伝子破壊株では、形質転換効率の著しい低下が見られたことから、RecRタンパク質は、細胞内に取り込んだ外来DNAの安定性に関与していることがわかった。また、
遺伝子破壊株では、形質転換効率の著しい低下が見られたことから、RecRタンパク質は、細胞内に取り込んだ外来DNAの安定性に関与していることがわかった。また、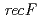 遺伝子破壊株は、他の遺伝子破壊株に比べて、
遺伝子破壊株は、他の遺伝子破壊株に比べて、 線,紫外線及びマイトマイシンCに非常に感受性を示した。これらの高い感受性は、RecFタンパク質が、組換え修復タンパク質RecAの活性化に重要な役割を担っていることに起因していることがわかった。以上のことから、放射線抵抗性細菌の効率的なDNA鎖切断修復を担うextended synthesis-dependent strand annealing(伸長合成依存的DNA鎖対合)経路の初期段階として、RecF及びRecRタンパク質は、RecAタンパク質の活性化とDNAの安定性にそれぞれ関与していることを明らかにした。
線,紫外線及びマイトマイシンCに非常に感受性を示した。これらの高い感受性は、RecFタンパク質が、組換え修復タンパク質RecAの活性化に重要な役割を担っていることに起因していることがわかった。以上のことから、放射線抵抗性細菌の効率的なDNA鎖切断修復を担うextended synthesis-dependent strand annealing(伸長合成依存的DNA鎖対合)経路の初期段階として、RecF及びRecRタンパク質は、RecAタンパク質の活性化とDNAの安定性にそれぞれ関与していることを明らかにした。
 -sterilization of carrier materials made with different types of soils on the shelf life of biofertilizer containing
-sterilization of carrier materials made with different types of soils on the shelf life of biofertilizer containing  strain USDA110
strain USDA110手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 横山 正*; 鳴海 一成
Radioisotopes, 61(4), p.161 - 171, 2012/04
バイオ肥料とは、植物生育を促進する細菌をピートや土壌などの担体に生きたまま保持した資材であり、施肥効果の高いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、保存中の接種菌数を長期間維持する技術が必要である。そこで、土着菌を 線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。担体として国内の代表的な土壌5種類を供試し、
線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。担体として国内の代表的な土壌5種類を供試し、 線滅菌(50kGy)及びオートクレーブ滅菌(121
線滅菌(50kGy)及びオートクレーブ滅菌(121 C, 40min)処理した後、ダイズ根粒菌
C, 40min)処理した後、ダイズ根粒菌 USDA110株を接種した。バイオ肥料を4
USDA110株を接種した。バイオ肥料を4 C及び30
C及び30 Cで1年間保存し、接種菌の生菌数の経時的推移を調べた。その結果、滅菌しない担体では接種菌が減少したが、滅菌した担体では接種菌の増加が見られた。供給安定性、低線量
Cで1年間保存し、接種菌の生菌数の経時的推移を調べた。その結果、滅菌しない担体では接種菌が減少したが、滅菌した担体では接種菌の増加が見られた。供給安定性、低線量 線照射での高い滅菌効果、接種菌密度の保持性を考慮すると、被検土壌の中でケト土がバイオ肥料担体として最も適していると考えられた。
線照射での高い滅菌効果、接種菌密度の保持性を考慮すると、被検土壌の中でケト土がバイオ肥料担体として最も適していると考えられた。

佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 106, 2012/01
In this study, we investigated lethal effects of different LET radiations in  and
and  gene disruptant strains and determined the relationship between LET and RBE. In both gene disruptant strains, radiosensitivities to four kinds of ion beams (
gene disruptant strains and determined the relationship between LET and RBE. In both gene disruptant strains, radiosensitivities to four kinds of ion beams ( He
He ,
,  C
C ,
,  C
C and
and  Ne
Ne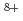 ) were almost equal to that of the
) were almost equal to that of the  rays. Both gene disruptant strains did not exhibit the dependence of LET on RBE at range of LET from about 0.2 to 441 keV/
rays. Both gene disruptant strains did not exhibit the dependence of LET on RBE at range of LET from about 0.2 to 441 keV/ m. These results indicate that RecA-mediated HR and PprA-mediated NHEJ mechanisms in
m. These results indicate that RecA-mediated HR and PprA-mediated NHEJ mechanisms in  play important roles in repairing the ion beams-induced clustered damage as well as the
play important roles in repairing the ion beams-induced clustered damage as well as the  ray-induced damage.
ray-induced damage.
 USDA 110 obtained by ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA 110 obtained by ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 110, 2012/01
In order to prevent deterioration in viability of inoculants in biofertilizers exposed to high temperature, we are trying to improve a phenotypic character concerning high temperature tolerance in  USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained 9 high temperature tolerant mutants that can survive at 45
USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained 9 high temperature tolerant mutants that can survive at 45 C for 5 days. These mutants were classified into 3 groups in terms of differences in colony morphology and colony size. We will carry out further characterization of those isolates in terms of temperature tolerant and symbiotic characters.
C for 5 days. These mutants were classified into 3 groups in terms of differences in colony morphology and colony size. We will carry out further characterization of those isolates in terms of temperature tolerant and symbiotic characters.
 -sterilized carriers
-sterilized carriers手島 光平; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 114, 2012/01
The inoculants survival in the biofertilizer could be affected by the physical and chemical properties of carrier materials and by the competition with native microbes in the carrier.  -irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In an effort to demonstrate the effectiveness of
-irradiation is expected to sterilize the carrier materials without changes in physical and chemical properties. In an effort to demonstrate the effectiveness of  -sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored to assess the shelf life of biofertilizer. The inoculants density after 12-month storage was greater than the initial density in biofertilizers made from sterilized carriers, while that was significantly decreased in biofertilizers made from non-sterilized carriers.
-sterilization, the survivals of inoculants were monitored to assess the shelf life of biofertilizer. The inoculants density after 12-month storage was greater than the initial density in biofertilizers made from sterilized carriers, while that was significantly decreased in biofertilizers made from non-sterilized carriers.  -sterilization was superior to autoclave-sterilization in enhancing the survival of inoculants. Because of the stability of supply, the high sterilization effect with lower radiation doses, and the high performance in maintaining the inoculants density, "Keto-tsuchi" was selected as one of the most suitable for a biofertilizer's carrier.
-sterilization was superior to autoclave-sterilization in enhancing the survival of inoculants. Because of the stability of supply, the high sterilization effect with lower radiation doses, and the high performance in maintaining the inoculants density, "Keto-tsuchi" was selected as one of the most suitable for a biofertilizer's carrier.
手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
土と微生物, 65(1), p.78 - 82, 2011/04
世界的な人口増加に伴い、食料の増産・安定的な供給及び地球環境の保全は非常に重要な課題である。世界の農業生産力は2004年をピークに減少し、食料の消費量が生産量を上回っており、自給率の低い我が国にとっては由々しい状況であるといえる。一方、地球環境汚染や地球温暖化の進行速度が近年ますます増加し、この現象に対して歯止めをかける必要がある。食料の増産・安定的な供給及び地球環境の保全を可能にするためには、環境耐性や新機能性を持つ生物資源の拡大が必要である。突然変異育種は、生物資源の拡大の基礎をなすものであり、日本原子力研究開発機構・量子ビーム応用研究部門では、世界最初の材料・バイオ研究のための専用施設として高崎量子応用研究所に設置されたイオンビーム照射研究施設TIARAのサイクロトロンを用いて、1990年からイオンビームを用いた突然変異育種の研究に取り組んできた。本解説では、イオンビームを用いた植物の突然変異育種と微生物育種への応用の現状を概説する。
 -sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on the density of rhizobial inoculants
-sterilization of biofertilizer's carrier on the density of rhizobial inoculants手島 光平; 鳴海 一成
FNCA Biofertilizer Newsletter, (9), P. 3, 2011/03
効率の良いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、接種菌の生存数を維持した状態で比較的長期間保存できることが必要不可欠である。バイオ肥料の保存中における接種菌密度の低下は、担体中に存在する微生物との競合も要因のひとつと考えられる。そこで、土壌を母材とした担体を用い、 線滅菌により競合相手となり得る微生物の密度を低下させた場合のバイオ肥料中での接種菌密度の変化を調べ、オートクレーブ滅菌及び非滅菌と比較した。その結果、滅菌担体では1, 2か月目に接種根粒菌密度の増加が見られ、その後徐々に低下するものの6か月後でも初期の菌密度を維持していた。1, 2か月目の接種根粒菌密度の増加は
線滅菌により競合相手となり得る微生物の密度を低下させた場合のバイオ肥料中での接種菌密度の変化を調べ、オートクレーブ滅菌及び非滅菌と比較した。その結果、滅菌担体では1, 2か月目に接種根粒菌密度の増加が見られ、その後徐々に低下するものの6か月後でも初期の菌密度を維持していた。1, 2か月目の接種根粒菌密度の増加は 線滅菌担体の方が大きい傾向が見られた。
線滅菌担体の方が大きい傾向が見られた。
 USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 75, 2011/01
Major constraint of biofertilizer utilization in agricultural practice is a serious deterioration of qualities in biofertilizers under both storage and transportation conditions. In order to prevent deterioration in variability of inoculants in biofertilizers exposed to high temperature, we are trying to improve a phenotypic character concerning high temperature tolerant in  USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained high temperature tolerant mutants of
USDA 110, which is a worldwide superior inoculant to soybean. In this study, ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology is used to generate high temperature tolerant mutants. We obtained high temperature tolerant mutants of  USDA 110, which can survive at 45
USDA 110, which can survive at 45 C for 5 days. Now, we are characterizing these mutants in terms of differences in several phenotypic properties.
C for 5 days. Now, we are characterizing these mutants in terms of differences in several phenotypic properties.

佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 80, 2011/01
In this study, we investigated lethal effects and relationship between LET and RBE for different LET radiation using the freeze-dried cells of the radioresistant bacterium  . The radioresistance of the cells to helium, carbon and neon ion beams were almost equal to that of
. The radioresistance of the cells to helium, carbon and neon ion beams were almost equal to that of  -irradiated cells. Unlike other organisms,
-irradiated cells. Unlike other organisms,  did not show the dependence of LET on RBE at a range of LET from about 0.2 to 441 keV/
did not show the dependence of LET on RBE at a range of LET from about 0.2 to 441 keV/ m. These results suggest that
m. These results suggest that  could repair the clustered damage effectively.
could repair the clustered damage effectively.
 -sterilization of carrier materials on the shelf life of biofertilizer
-sterilization of carrier materials on the shelf life of biofertilizer手島 光平; 横山 正*; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 83, 2011/01
バイオ肥料とは、窒素固定細菌や植物生長を促進する菌を泥炭(ピート)や土壌などの担体に生きたまま保持した資材であり、施肥効果の高いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、保存中における接種菌(原体微生物)の生存数を長期間維持する技術が必要である。そこで、土着の微生物を 線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。非滅菌担体では接種菌の密度は保存期間とともに低下していたが、30
線により滅菌した担体を用いてダイズ根粒菌のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。非滅菌担体では接種菌の密度は保存期間とともに低下していたが、30 C保存に比べ4
C保存に比べ4 C保存の方が緩やかに減少していた。一方、滅菌担体の接種菌密度は2か月目までは増加し、その後減少に転ずる傾向が見られた。特に、30
C保存の方が緩やかに減少していた。一方、滅菌担体の接種菌密度は2か月目までは増加し、その後減少に転ずる傾向が見られた。特に、30 C保存の
C保存の 線滅菌担体ではオートクレーブ滅菌担体よりも接種菌密度の増加量が大きかった。以上の結果から、バイオ肥料を低温で保存できない場合、滅菌処理した担体が接種菌の密度を維持するために有効であることが示された。また、
線滅菌担体ではオートクレーブ滅菌担体よりも接種菌密度の増加量が大きかった。以上の結果から、バイオ肥料を低温で保存できない場合、滅菌処理した担体が接種菌の密度を維持するために有効であることが示された。また、 線滅菌がより有効であることが示された。
線滅菌がより有効であることが示された。
武田 喜代子; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
現在、化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では根粒菌バイオ肥料の利用を奨励している。しかし、輸送や保存時の高温による接種菌の活性低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。そこで本研究では、イオンビーム突然変異育種法を用いてダイズ根粒菌高温耐性変異株を作出するとともに、作出した変異株の高温耐性能に関与する表現形質の探索を行った。その結果、イオンビーム照射により、43 Cで7日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を20株作出することに成功した。また、それら高温耐性株に再度イオンビーム照射を行った所、47
Cで7日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を20株作出することに成功した。また、それら高温耐性株に再度イオンビーム照射を行った所、47 Cで3日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を5株作出することができた。一方、高温耐性株のコロニー色がピンク色に変化することや、世代時間が野生株よりも約1.5時間短くなること等、高温耐性能とかかわりがあると推測される表現形質を幾つか発見することができた。
Cで3日間生存可能な高温耐性変異株を5株作出することができた。一方、高温耐性株のコロニー色がピンク色に変化することや、世代時間が野生株よりも約1.5時間短くなること等、高温耐性能とかかわりがあると推測される表現形質を幾つか発見することができた。
増淵 隆*; 上山 修*; 佐藤 勝也; 長谷 純宏; 手島 光平; 鳴海 一成; 小野寺 威文
no journal, ,
群馬県ではオリジナルの吟醸用清酒酵母として「群馬KAZE酵母」を既に実用化しているが、消費者の嗜好の変化に対応した新たな酵母の開発をすべく、平成20年度よりイオンビーム照射による変異処理を行い、優良株の選抜を試みている。22年度は、変異株の選抜を継続するとともに、それまでに得られた優良株の試験醸造を行い、醸造適性の確認を行った。選抜の指標は、吟醸酒の主要な香気成分であるカプロン酸エチルの生成能とした。23年度のイオンビーム照射は、きょうかい901号及びNo.227酵母(平成20年度に取得した優良株)を親株として用いた。発酵試験は計1,135株について実施した。良好な香気生成能を示す変異株は、主として100 150Gyの照射区分で得られた。発酵試験で良好な7株について、小仕込み試験を行った。そのうち6株は群馬KAZE2号酵母よりも高い香気生成能を示した。これらから官能評価などを考慮したうえで、150Gyの照射区分で得られたNo.1529を有望株として選抜し、試験醸造に供した。No.1529株は非常に高いカプロン酸エチル生成能を示すとともに、酢酸イソアミルをほとんど生成せず、独特の風味を呈した。しかし発酵力が弱く、目標のアルコール度・日本酒度に到達しないまま上槽せざるを得なかった。一方、No.227は昨年の試験と同様に発酵力も順調で、28日目でほぼ目標成分に達し、カプロン酸エチル生成能も良好であった。この株は既に実製造規模の試験も行っており、実用化が期待されている状況にある。
150Gyの照射区分で得られた。発酵試験で良好な7株について、小仕込み試験を行った。そのうち6株は群馬KAZE2号酵母よりも高い香気生成能を示した。これらから官能評価などを考慮したうえで、150Gyの照射区分で得られたNo.1529を有望株として選抜し、試験醸造に供した。No.1529株は非常に高いカプロン酸エチル生成能を示すとともに、酢酸イソアミルをほとんど生成せず、独特の風味を呈した。しかし発酵力が弱く、目標のアルコール度・日本酒度に到達しないまま上槽せざるを得なかった。一方、No.227は昨年の試験と同様に発酵力も順調で、28日目でほぼ目標成分に達し、カプロン酸エチル生成能も良好であった。この株は既に実製造規模の試験も行っており、実用化が期待されている状況にある。
佐藤 勝也; 手島 光平; 小野寺 威文; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
2011年までの研究で、放射線抵抗性細菌の野生株は、他の生物とは異なり生物学的効果比(RBE)がLET依存性を示さないことがわかった。本研究では、放射線抵抗性細菌の 及び
及び 遺伝子破壊株を用いて、異なるLET放射線に対する致死効果及びLETとRBEの関係について解析を行った。その結果、野生株と同様にLETが0.2から441keV/
遺伝子破壊株を用いて、異なるLET放射線に対する致死効果及びLETとRBEの関係について解析を行った。その結果、野生株と同様にLETが0.2から441keV/ mの範囲において、
mの範囲において、 及び
及び 遺伝子破壊株のRBEは、LET依存性を示さなかった。放射線抵抗性細菌のRecA及びPprAタンパク質がそれぞれ介在するHR及びNHEJ機構は、
遺伝子破壊株のRBEは、LET依存性を示さなかった。放射線抵抗性細菌のRecA及びPprAタンパク質がそれぞれ介在するHR及びNHEJ機構は、 線に誘発されるDNA損傷の修復と同様にイオンビームに誘発されるクラスター損傷の修復に対しても重要な役割を担っていると考えられた。
線に誘発されるDNA損傷の修復と同様にイオンビームに誘発されるクラスター損傷の修復に対しても重要な役割を担っていると考えられた。
 USDA110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA110 into a high temperature tolerant strain in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology武田 喜代子*; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
炭素イオンビーム照射による高温耐性ダイズ根粒菌の作出を試みた。はじめに、イオンビーム照射菌株の生存率、及びリファンピシン耐性をマーカーとした突然変異率を指標として、変異誘発に最適な炭素イオンビーム線量を決定した。その結果、100Gy 400Gy程度のエネルギー量が突然変異誘発に適した条件であると考えられた。次に、イオンビーム照射菌株を45
400Gy程度のエネルギー量が突然変異誘発に適した条件であると考えられた。次に、イオンビーム照射菌株を45 Cで5日間静置し、生存している菌株の選抜を行った。その結果、300Gy及び400Gy照射区から生存する菌株を6株取得した。得られた株を16S-rRNAのシークエンスの比較により同定した結果、すべての株がUSDA110株からの変異株と判定された。
Cで5日間静置し、生存している菌株の選抜を行った。その結果、300Gy及び400Gy照射区から生存する菌株を6株取得した。得られた株を16S-rRNAのシークエンスの比較により同定した結果、すべての株がUSDA110株からの変異株と判定された。
 USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain as a more applicable inoculant for biofertilizers in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology
USDA 110 into a high temperature tolerant strain as a more applicable inoculant for biofertilizers in terms of ion-beam microbial mutation-breeding technology横山 正*; 武田 喜代子; 手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 鳴海 一成
no journal, ,
バイオ肥料普及の大きな障害の一つに、保存及び輸送時における高温・乾燥によるバイオ肥料接種菌の死滅が上げられる。そこで、ダイズへの接種剤として世界的に優れている USDA 110株の表現形質を高温耐性に改良することを試みた。本研究では、高温耐性株を作出するために、イオンビーム微生物突然変異育種技術を用いた。原子力機構TIARAにて、炭素イオンビームを800Gyまで細胞に照射後、液体培地中45
USDA 110株の表現形質を高温耐性に改良することを試みた。本研究では、高温耐性株を作出するために、イオンビーム微生物突然変異育種技術を用いた。原子力機構TIARAにて、炭素イオンビームを800Gyまで細胞に照射後、液体培地中45 Cで5日間培養し、生き残った株を得た。高温耐性変異株は、コロニーの形状と増殖速度の違いから3グループに分けられた。3グループのうち、薄桃色の小型コロニーを形成するグループの高温耐性が最も高かった。根粒着生や窒素固定能といった共生能力は高温耐性変異株と親株で差異は認められなかった。
Cで5日間培養し、生き残った株を得た。高温耐性変異株は、コロニーの形状と増殖速度の違いから3グループに分けられた。3グループのうち、薄桃色の小型コロニーを形成するグループの高温耐性が最も高かった。根粒着生や窒素固定能といった共生能力は高温耐性変異株と親株で差異は認められなかった。
 線滅菌担体におけるバイオ肥料原体微生物の生存性
線滅菌担体におけるバイオ肥料原体微生物の生存性手島 光平; 佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子; 鳴海 一成; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
バイオ肥料とは、窒素固定細菌や植物生長を促進する菌を泥炭や土壌などの担体に生きたまま保持した資材である。施肥効果の高いバイオ肥料を開発するためには、保存中における接種菌(原体微生物)の生存数を長期間維持する技術が必要である。本研究では、土着の微生物を 線により滅菌した担体を用いて、窒素固定細菌
線により滅菌した担体を用いて、窒素固定細菌 TUAT1株及び
TUAT1株及び sp. MAFF210364株のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。その結果、接種菌の種類によって滅菌方法の影響が異なることが示された。
sp. MAFF210364株のバイオ肥料を作製し、保存中の接種菌密度の変化を調べた。その結果、接種菌の種類によって滅菌方法の影響が異なることが示された。