Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 irradiation
irradiation武内 伴照; 花川 裕規; 柴田 裕司; 上原 聡明; 上野 俊二; 熊原 肇*; 土谷 邦彦
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 33, 2015/03
水中でも伝送可能かつ耐放射線性をもつ可視光無線伝送システムの構築を目指して、LEDとフォトダイオード(PD)の 線照射効果の評価を行った。照射劣化を評価するため、照射前後で、LEDの電流電圧特性や全光束及びPDの暗電流や受光感度を測定した。その結果、照射後に、LEDは全光束が減少するとともに樹脂レンズ部が着色したが、電流電圧特性はほとんど変化は無かった。PDは、受光感度が減少するとともに窓材の樹脂が着色したが、暗電流は高々10nA以下と低い値のままであった。これらの結果から、両素子の特性劣化の主因は半導体部分の劣化ではなく、樹脂の着色によるものであることが示唆された。
線照射効果の評価を行った。照射劣化を評価するため、照射前後で、LEDの電流電圧特性や全光束及びPDの暗電流や受光感度を測定した。その結果、照射後に、LEDは全光束が減少するとともに樹脂レンズ部が着色したが、電流電圧特性はほとんど変化は無かった。PDは、受光感度が減少するとともに窓材の樹脂が着色したが、暗電流は高々10nA以下と低い値のままであった。これらの結果から、両素子の特性劣化の主因は半導体部分の劣化ではなく、樹脂の着色によるものであることが示唆された。
端 邦樹; 塙 悟史; 本岡 隆文; 塚田 隆
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 22, 2015/03
福島第一原子力発電所では事故後の対応として炉内や使用済燃料プールへの海水注入が実施された。注入された海水は放射線に曝されるため、水の放射線分解生成物が発生すると考えられる。放射線分解生成物の中でも過酸化水素(H O
O )は鉄鋼材料の腐食に影響を与える酸化剤である。本研究では、照射された海水中に発生する過酸化水素の濃度が海水中のどの成分によって決められるのかということを明らかにするため、
)は鉄鋼材料の腐食に影響を与える酸化剤である。本研究では、照射された海水中に発生する過酸化水素の濃度が海水中のどの成分によって決められるのかということを明らかにするため、 線照射した人工海水中のH
線照射した人工海水中のH O
O 濃度を調べ、これまでのラジオリシス計算結果と比較検討した。個々の海水成分を添加した水溶液についても同様に調べ、H
濃度を調べ、これまでのラジオリシス計算結果と比較検討した。個々の海水成分を添加した水溶液についても同様に調べ、H O
O 生成に寄与する成分の同定を試みた。その結果、海水の放射線分解におけるH
生成に寄与する成分の同定を試みた。その結果、海水の放射線分解におけるH O
O の生成がCl
の生成がCl とBr
とBr の照射下での振る舞いに起因することを示した。
の照射下での振る舞いに起因することを示した。
 -ray irradiated polyethylene with KOH treatment and SEM-EDS
-ray irradiated polyethylene with KOH treatment and SEM-EDS島田 明彦; 杉本 雅樹; 吉川 正人
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 30, 2015/03
原子力関連施設で用いられるケーブル絶縁材(高分子)の加速劣化試験を行うにあたって、高分子は酸素が行き届いた状態で放射線照射されたか、そうでないのかを把握しておくことは重要である。これを確かめる手法として、エチレンプロピレンゴム(EPR)については、70 CのKOH水溶液に5分間浸漬した後乾燥させて、SEM-EDSで観察することにより酸化領域(どの部分が酸化しているか)を調べる手法がある。本報告は、この手法をポリエチレン(PE)に適用するための技術改良について述べたものである。室温、2kGy/hの線量率で400時間
CのKOH水溶液に5分間浸漬した後乾燥させて、SEM-EDSで観察することにより酸化領域(どの部分が酸化しているか)を調べる手法がある。本報告は、この手法をポリエチレン(PE)に適用するための技術改良について述べたものである。室温、2kGy/hの線量率で400時間 線照射した厚さ2mmのPEシートについて、照射後のPEの断面を切り出した。予備試験の結果から浸漬時間を長くする必要があると考えられたので、浸漬時間を24時間とし、乾燥後断面をSEM-EDSで観察した。表面から約70
線照射した厚さ2mmのPEシートについて、照射後のPEの断面を切り出した。予備試験の結果から浸漬時間を長くする必要があると考えられたので、浸漬時間を24時間とし、乾燥後断面をSEM-EDSで観察した。表面から約70 mの範囲では、その内側に比べてK原子の強度が高かった。これはPEの酸化により生じたカルボン酸のH原子がK原子に置換されたことによってこの範囲のK原子の強度が高くなったためである。浸漬時間を24時間にすることにより、酸化したPEに対してKによる着色を行わせることができるとわかった。今後、酸化領域を完全に着色させるのに必要な時間を決定する必要がある。
mの範囲では、その内側に比べてK原子の強度が高かった。これはPEの酸化により生じたカルボン酸のH原子がK原子に置換されたことによってこの範囲のK原子の強度が高くなったためである。浸漬時間を24時間にすることにより、酸化したPEに対してKによる着色を行わせることができるとわかった。今後、酸化領域を完全に着色させるのに必要な時間を決定する必要がある。
 -ray irradiation facilities
-ray irradiation facilities上松 敬; 花屋 博秋; 山縣 諒平; 清藤 一; 長尾 悠人; 金子 広久; 山口 敏行*; 川島 郁男*; 八木 紀彦*; 高木 雅英*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 183, 2015/03
電子加速器及び 線照射施設を2013年度年間計画に基づいて照射利用に供した。電子線及び
線照射施設を2013年度年間計画に基づいて照射利用に供した。電子線及び 線照射施設の利用件数は2012年度と同様であった。東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故に対する復興対応関連の課題については、電子加速器では47件、
線照射施設の利用件数は2012年度と同様であった。東京電力福島第一原子力発電所の事故に対する復興対応関連の課題については、電子加速器では47件、 線照射施設においては91件の利用があった。
線照射施設においては91件の利用があった。
 -ray irradiation facilities
-ray irradiation facilities上松 敬; 花屋 博秋; 山縣 諒平; 清藤 一; 長尾 悠人; 金子 広久; 山口 敏行*; 川島 郁男*; 八木 紀彦*; 高木 雅英*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 182, 2015/03
電子・ 線照射施設はほぼ順調に稼動した。2013年度における運転時間は、電子加速器では1242時間、コバルト第1棟では18900時間、コバルト第2棟では11804時間、食品棟では6587時間であった。主要なメンテナンスは次の通りである。電子加速器ではSF
線照射施設はほぼ順調に稼動した。2013年度における運転時間は、電子加速器では1242時間、コバルト第1棟では18900時間、コバルト第2棟では11804時間、食品棟では6587時間であった。主要なメンテナンスは次の通りである。電子加速器ではSF ガス回収装置の更新を行った。コバルト施設の整備時にプール水を保管するための600m
ガス回収装置の更新を行った。コバルト施設の整備時にプール水を保管するための600m の貯水タンクを設置した。コバルト第1棟及び第2棟では線源の補充を行った。食品棟では定期整備を行った。
の貯水タンクを設置した。コバルト第1棟及び第2棟では線源の補充を行った。食品棟では定期整備を行った。
横山 彰人; 加田 渉*; 佐藤 隆博; 江夏 昌志; 山本 春也; 神谷 富裕; 横田 渉
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 168, 2015/03
サイクロトロンでは、数百MeV以上の重イオンマイクロビームを用いたシングルイオンヒット技術が生物細胞などの照射実験で利用されており、高精度位置検出が必要とされている。しかし、現状の固体飛跡検出器では 照射後の薬品による表面処理と顕微鏡での照射位置の観察に時間を要し、リアルタイムでの検出が困難であった。そこで、ビームモニタに利用されているZnS等の発光体などを試用したが発光強度や位置分解能が十分ではなかった。本研究では、単結晶サファイアに賦活剤として注入するEuイオンの量や熱処理条件等の調整により、強いイオンルミネッセンス(Ion Luminescence: IL)を発する試料の開発と発光検出装置の感度試験を行った。予備実験として調製試料の表面にレーザー照射することにより、電子励起過程を伴って発光するフォトルミネッセンス(Photoluminescence: PL)を測定した結果、表面から30nm 70nmにEuを7.5ions/nm
70nmにEuを7.5ions/nm を注入した後に、600
を注入した後に、600 Cで30分間熱処理した試料のPL強度が最大だった。また、同試料を用いた発光検出装置の感度試験では、260MeV Neイオンを1秒間に200個のフルエンス率で1点照射することによってILを捕えることができた。しかしながら、シングルイオンヒット実験では、ビーム電流量が数cps程度と低いことから、感度の向上のために賦活剤の濃度の調整などの改良を今後行う。
Cで30分間熱処理した試料のPL強度が最大だった。また、同試料を用いた発光検出装置の感度試験では、260MeV Neイオンを1秒間に200個のフルエンス率で1点照射することによってILを捕えることができた。しかしながら、シングルイオンヒット実験では、ビーム電流量が数cps程度と低いことから、感度の向上のために賦活剤の濃度の調整などの改良を今後行う。
 mutants to microbeam irradiation
mutants to microbeam irradiation坂下 哲哉; 鈴木 芳代; 服部 佑哉; 池田 裕子; 武藤 泰子*; 横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 浜田 信行*; 白井 花菜*; 小林 泰彦
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 74, 2015/03
昆虫・哺乳動物等を用いた実験から、放射線被ばくにより学習障害等の神経系への影響がもたらされることが示唆されている。我々は、神経系を研究するためのモデル生物として知られる線虫を用いて、化学走性学習が、特定の条件下においてのみコバルト60 線照射の影響を受けることを明らかにした。しかし、線虫のどの部位における放射線応答が、化学走性学習行動の変化を誘導するかは明らかでない。そこで、我々は、炭素イオンマイクロビームを用いて、線虫の化学走性学習に対する直接的な放射線の影響部位を明らかにすることを目的とした。マイクロビーム照射技術は、細胞あるいは組織レベルでの直接的な放射線の影響を調べるための有効なツールとして知られている。本報告では、2つの線虫変異体(
線照射の影響を受けることを明らかにした。しかし、線虫のどの部位における放射線応答が、化学走性学習行動の変化を誘導するかは明らかでない。そこで、我々は、炭素イオンマイクロビームを用いて、線虫の化学走性学習に対する直接的な放射線の影響部位を明らかにすることを目的とした。マイクロビーム照射技術は、細胞あるいは組織レベルでの直接的な放射線の影響を調べるための有効なツールとして知られている。本報告では、2つの線虫変異体(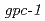 ,
, 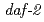 )に対して、マイクロビームの局部照射を行った結果について報告する。
)に対して、マイクロビームの局部照射を行った結果について報告する。
山本 春也; 箱田 照幸; 吉川 正人
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 129, 2015/03
白金(Pt),パラジウム(Pd)等は、有機水素化合物の脱水素触媒や高分子形燃料電池の酸素還元触媒などに用いられる触媒材料であり、高活性な触媒材料の研究開発を進めるためには、触媒反応過程を理解するとともに結晶方位を制御した高い結晶性のエピタキシャル膜が必要とされる。本研究では、サファイア単結晶基板上にスパッタリング法により成膜中の基板温度をパラメータとし、X線回折法及びラザフォード後方散乱(RBS)法により、作製した厚さ100nmのPt及びPdのエピタキシャル膜の結晶方位、深さ方向の結晶性を評価した。その結果、(0001)面のサファイア基板上に基板温度600 C及び500
C及び500 CでPt及びPdを蒸着することにより結晶性の高いPt(111)膜及びPd(111)膜が形成できることがわかった。さらに、基板温度600
CでPt及びPdを蒸着することにより結晶性の高いPt(111)膜及びPd(111)膜が形成できることがわかった。さらに、基板温度600 Cでサファイア基板上に厚さ約1nmのPt(111)のバッファー層を設けることより、基板温度300
Cでサファイア基板上に厚さ約1nmのPt(111)のバッファー層を設けることより、基板温度300 CでAu(111)膜が形成できることがわかった。
CでAu(111)膜が形成できることがわかった。
出崎 亮; 上地 宏樹*; 羽倉 吉彦*; 岸 肇*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 29, 2015/03
本研究では、J-PARCやITERに設置される超伝導磁石システム用電気絶縁材料として応用が期待されているシアネートエステル/エポキシ樹脂について、物理化学的特性変化の面から放射線照射効果を解明することを目的としている。これまでに、室温真空中において100MGyまでガンマ線を照射すると、水素, 一酸化炭素, 二酸化炭素が発生すること、樹脂のガラス転移温度が初期値の80%である180 Cまで低下することを明らかにしているが、本報では、放射線照射によって分解する化学構造の解明を核磁気共鳴法による分子構造解析により行なった。その結果、シアネートエステルとエポキシの間の架橋構造を構成するシアヌレート, イソシアヌレート, オキサゾリジノン骨格に結合するエーテル鎖が切断されていることが分かった。以上のことから、シアネートエステル/エポキシ樹脂に放射線を照射すると、シアネートエステルとエポキシの間で形成される架橋構造におけるエーテル鎖が切断され、ガス発生やガラス転移温度の低下が起こることが明らかになった。
Cまで低下することを明らかにしているが、本報では、放射線照射によって分解する化学構造の解明を核磁気共鳴法による分子構造解析により行なった。その結果、シアネートエステルとエポキシの間の架橋構造を構成するシアヌレート, イソシアヌレート, オキサゾリジノン骨格に結合するエーテル鎖が切断されていることが分かった。以上のことから、シアネートエステル/エポキシ樹脂に放射線を照射すると、シアネートエステルとエポキシの間で形成される架橋構造におけるエーテル鎖が切断され、ガス発生やガラス転移温度の低下が起こることが明らかになった。
菊地 正博; 鵜飼 光子*; 小林 泰彦
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 89, 2015/03
Electron spin resonance spectroscopy (ESR) has been utilized as a detection method of irradiated foods. However, there is a problem on ESR measurement for the water-rich foods. We have examined two techniques to solve the water problem. In two ESR detection methods for fresh fruits, dose response curves of signal intensities were obtained independently. Three responses show the direct proportional relationship, except for main peak signals of freeze-dried powders. In this study, we examined whether  -induced radicals of papaya fleshes are changed after different sample preparations. The right side peak intensity is good agreement with the estimation.
-induced radicals of papaya fleshes are changed after different sample preparations. The right side peak intensity is good agreement with the estimation.  -induced radicals of the side peak are not affected by the sample preparations. This study indicates that the ESR detection methods for fresh fruits are reliable as a quantitative measurement.
-induced radicals of the side peak are not affected by the sample preparations. This study indicates that the ESR detection methods for fresh fruits are reliable as a quantitative measurement.
岸田 敬吾*; 菊地 正博; 中村 秀夫*; 小林 泰彦; 鵜飼 光子*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 90, 2015/03
Radiation induced radicals in irradiated foods were analyzed with Pulse-ESR. The specimens were rice and wheat flour. We also analyzed 22 kinds of amino acids contained in foods to compare with the food specimens. Radiation dose level was 50,100 and 200 kGy. We could not detect any signals in all specimens before irradiation treatment. Upon radiation treatment one broad signal was detected. Using Pulse-ESR, we succeeded to detect field swept echo signal in some irradiated amino acid specimens and to analyze the relaxation times (T and T
and T ). It is concluded that ESR is very useful to analyze the radiation induced radicals in irradiated foods.
). It is concluded that ESR is very useful to analyze the radiation induced radicals in irradiated foods.
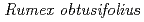 L. irradiated with ion beams
L. irradiated with ion beams宮城 敦子*; 北野 沙也佳*; 大野 豊; 長谷 純宏; 川合 真紀*; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 114, 2015/03
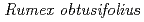 (Polygonaceae) is a weed, which spreads all over the world. It contains amino acids and ascorbate (Vitamin C) more than other edible
(Polygonaceae) is a weed, which spreads all over the world. It contains amino acids and ascorbate (Vitamin C) more than other edible 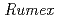 species (Miyagi et al., 2010). On the other hand, it highly accumulates soluble oxalate, which causes renal syndrome for vertebrates. Thus we aimed to lower oxalate contents in R. obtusifolius that can be used as a pasture by radiation breeding. In the present study, plant seeds irradiated with several doses of carbon ion beams (
species (Miyagi et al., 2010). On the other hand, it highly accumulates soluble oxalate, which causes renal syndrome for vertebrates. Thus we aimed to lower oxalate contents in R. obtusifolius that can be used as a pasture by radiation breeding. In the present study, plant seeds irradiated with several doses of carbon ion beams ( C
C ) were used to analyze effects of the radiation to oxalate contents and other metabolites using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry (CE-MS). Results showed that the oxalate contents of leaves were increased by the irradiation of ion beams on the contrary to the case of the irradiation with
) were used to analyze effects of the radiation to oxalate contents and other metabolites using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry (CE-MS). Results showed that the oxalate contents of leaves were increased by the irradiation of ion beams on the contrary to the case of the irradiation with  rays. High oxalate plants tended to contain high levels of organic acids. Amino acids and phosphorylated organic acids were decreased in these plants.
rays. High oxalate plants tended to contain high levels of organic acids. Amino acids and phosphorylated organic acids were decreased in these plants.
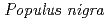 )
)Biswas, K. K.*; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 113, 2015/03
Species of the genus 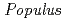 are ecologically important trees and often serving as a vegetative pioneer species because of their fast growth rates. The rapid growth of poplar is dependent on access to sufficient water in plantation sites and this is problematic. To overcome this problem, a forward genetics approach has been taken for developing salt/drought tolerant mutants by combination of radiation mutagenesis and in vitro regeneration in
are ecologically important trees and often serving as a vegetative pioneer species because of their fast growth rates. The rapid growth of poplar is dependent on access to sufficient water in plantation sites and this is problematic. To overcome this problem, a forward genetics approach has been taken for developing salt/drought tolerant mutants by combination of radiation mutagenesis and in vitro regeneration in 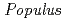 . Previously we screened regenerated
. Previously we screened regenerated  shoots regenerated from stems exposed with cobalt-60 source of
shoots regenerated from stems exposed with cobalt-60 source of  rays and isolated two mutant candidates named
rays and isolated two mutant candidates named 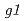 and
and 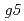 . Only about 25% stem segments of both lines produced roots in RIM with 75 mM NaCl. The low frequency in root production in NaCl medium may be attributed to that these plants are chimeric. We also successfully obtained at least 2 salt tolerant candidates regenerated from stem segments irradiated with 320 MeV
. Only about 25% stem segments of both lines produced roots in RIM with 75 mM NaCl. The low frequency in root production in NaCl medium may be attributed to that these plants are chimeric. We also successfully obtained at least 2 salt tolerant candidates regenerated from stem segments irradiated with 320 MeV  C
C ion beams.
ion beams.
 pink mutants through ion beam irradiation
pink mutants through ion beam irradiationZaiton, A.*; Affrida, A. H.*; Shakinah, S.*; Nurul Hidayah, M.*; 長谷 純宏; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 108, 2015/03
Developing new varieties of chrysanthemums is one of the emphases in Malaysian floriculture research as chrysanthemum is recognized as among the most important cut flower export for Malaysia. A combination of ion beam irradiation and  organ culture techniques is very efficient in generating new ornamental varieties with novel traits and wider mutation spectrum. Therefore, in this project, ray floret cultures of pink chrysanthemum variety were irradiated at various doses with 320 MeV
organ culture techniques is very efficient in generating new ornamental varieties with novel traits and wider mutation spectrum. Therefore, in this project, ray floret cultures of pink chrysanthemum variety were irradiated at various doses with 320 MeV  C
C ions, regenerated into plantlets and screened for morphological variations with an ultimate aim to produce mutants with useful horticultural traits. A series of screening was carried out at Nuclear Malaysia's glasshouse and MARDI Cameron Highlands. The mutants were selected and characterized morphologically. Based on these screenings, three mutants were identified based on their distinct flower and/or plant characteristics.
ions, regenerated into plantlets and screened for morphological variations with an ultimate aim to produce mutants with useful horticultural traits. A series of screening was carried out at Nuclear Malaysia's glasshouse and MARDI Cameron Highlands. The mutants were selected and characterized morphologically. Based on these screenings, three mutants were identified based on their distinct flower and/or plant characteristics.
鈴木 芳代; 服部 佑哉; 坂下 哲哉; 舟山 知夫; 横田 裕一郎; 池田 裕子; 小林 泰彦
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 88, 2015/03
The nematode  is a good
is a good  model system to examine radiation effects on vital functions such as locomotion, feeding, learning and memory. Using
model system to examine radiation effects on vital functions such as locomotion, feeding, learning and memory. Using  , we recently investigated the radiation effects on locomotion (snake-like crawling motion) and found that whole-body irradiation significantly reduced locomotion. Furthermore, we focused on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing), which is a rapid periodic motion, and found that the proportion of pumping-motion arrest increased after whole-body irradiation. As the next step, we started to examine whether or not the effects observed after whole-body irradiation could be induced by microbeam irradiation to a very limited region. In this report, we summarize the results of microbeam irradiation experiments we carried out in the past few years. Main findings in this study are the following: (1) Effects of the region-specific microbeam irradiation differ depending on types of motion, and (2) effects of whole-body irradiation tend to be more effective than those of the region-specific microbeam irradiation at the same irradiation dose. Further studies on the mechanisms underlying the radiation-induced changes of movements are required.
, we recently investigated the radiation effects on locomotion (snake-like crawling motion) and found that whole-body irradiation significantly reduced locomotion. Furthermore, we focused on the pharyngeal pumping motion (chewing and swallowing), which is a rapid periodic motion, and found that the proportion of pumping-motion arrest increased after whole-body irradiation. As the next step, we started to examine whether or not the effects observed after whole-body irradiation could be induced by microbeam irradiation to a very limited region. In this report, we summarize the results of microbeam irradiation experiments we carried out in the past few years. Main findings in this study are the following: (1) Effects of the region-specific microbeam irradiation differ depending on types of motion, and (2) effects of whole-body irradiation tend to be more effective than those of the region-specific microbeam irradiation at the same irradiation dose. Further studies on the mechanisms underlying the radiation-induced changes of movements are required.
横田 裕一郎; 舟山 知夫; 池田 裕子; 坂下 哲哉; 鈴木 芳代; 小林 泰彦
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 75, 2015/03
本研究では、異なる線量の 線あるいは炭素イオンビームによって誘発されるバイスタンダー効果の線量及び線質依存性と、一酸化窒素(NO)ラジカルの役割について調べた。ヒト正常繊維芽細胞を実験に用い、
線あるいは炭素イオンビームによって誘発されるバイスタンダー効果の線量及び線質依存性と、一酸化窒素(NO)ラジカルの役割について調べた。ヒト正常繊維芽細胞を実験に用い、 線あるいは炭素イオンを照射した細胞と非照射細胞を多孔性メンブレンの上側と下側で24時間培養した。培養後、非照射細胞の生存率は照射細胞に曝露した線量の増加とともに低下し、0.5Gy以上では下げ止まった。このことから、バイスタンダー効果は照射細胞に曝露した放射線の線量に依存するが、線質には依存しないことが明らかになった。さらに、NOラジカルの特異的消去剤であるc-PTIOをあらかじめ培養液に加えておくと、非照射細胞の生存率の低下が抑制された。以上の結果から、
線あるいは炭素イオンを照射した細胞と非照射細胞を多孔性メンブレンの上側と下側で24時間培養した。培養後、非照射細胞の生存率は照射細胞に曝露した線量の増加とともに低下し、0.5Gy以上では下げ止まった。このことから、バイスタンダー効果は照射細胞に曝露した放射線の線量に依存するが、線質には依存しないことが明らかになった。さらに、NOラジカルの特異的消去剤であるc-PTIOをあらかじめ培養液に加えておくと、非照射細胞の生存率の低下が抑制された。以上の結果から、 線や重イオンビームによって誘発されるバイスタンダー効果にNOラジカルが重要な役割を果たすことが示された。
線や重イオンビームによって誘発されるバイスタンダー効果にNOラジカルが重要な役割を果たすことが示された。
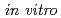 evaluation of
evaluation of  Cu-labeled peptide for tumor imaging
Cu-labeled peptide for tumor imaging須郷 由美; 佐々木 一郎; 渡辺 茂樹; 大島 康宏; 石岡 典子
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 100, 2015/03
MARSGL peptide (H-Met-Ala-Arg-Ser-Gly-Leu-OH) has high affinity to the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpressing in various tumor cells. Copper-64 ( Cu) is a useful radionuclide in nuclear medicine, and can be produced by the cyclotron. In this study, we designed and synthesized
Cu) is a useful radionuclide in nuclear medicine, and can be produced by the cyclotron. In this study, we designed and synthesized  Cu-labeled MARSGL peptide conjugated with 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) as a novel positron emission tomography (PET) imaging probe for HER2 overexpressing tumors. The formation of
Cu-labeled MARSGL peptide conjugated with 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid (DOTA) as a novel positron emission tomography (PET) imaging probe for HER2 overexpressing tumors. The formation of  Cu-DOTA-MARSGL was determined by TLC and HPLC compared with a non-radioactive preparation. It was confirmed that
Cu-DOTA-MARSGL was determined by TLC and HPLC compared with a non-radioactive preparation. It was confirmed that  Cu-DOTA-MARSGL was obtained in high radiochemical yield more than 94%. We also examined a stability of
Cu-DOTA-MARSGL was obtained in high radiochemical yield more than 94%. We also examined a stability of  Cu-DOTA-MARSGL
Cu-DOTA-MARSGL  . The chromatogram was not changed after incubation in physiological saline at 37
. The chromatogram was not changed after incubation in physiological saline at 37 C overnight. In order to evaluate the usefulness as a PET imaging probe, further
C overnight. In order to evaluate the usefulness as a PET imaging probe, further  studies on the stability in human or mice plasma and the cellular uptake are in progress.
studies on the stability in human or mice plasma and the cellular uptake are in progress.
渡辺 智; 橋本 和幸; 石岡 典子
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 102, 2015/03
As part of basic studies for the production of  Lu capable of labeling of
Lu capable of labeling of  Lu-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-N,N',N'',N'''-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-antibody,
Lu-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecan-N,N',N'',N'''-tetraacetic acid (DOTA)-antibody,  Lu complexation of DOTA and diethylenetriamine-N,N,N',N'',N''-pentaacetic acid (DTPA) was investigated in the presence of competing metals: Mg, Cu, and Yb in addition to Ca, Fe, and Zn. The inhibition of
Lu complexation of DOTA and diethylenetriamine-N,N,N',N'',N''-pentaacetic acid (DTPA) was investigated in the presence of competing metals: Mg, Cu, and Yb in addition to Ca, Fe, and Zn. The inhibition of  Lu complexation by the competing metals was in the order of Mg, Ca
Lu complexation by the competing metals was in the order of Mg, Ca  Fe
Fe  Yb
Yb  Cu, Zn and Mg, Ca
Cu, Zn and Mg, Ca  Zn
Zn  Fe
Fe  Cu
Cu  Yb with DOTA and DTPA, respectively. Consequently, the elimination of Mg and Ca from the
Yb with DOTA and DTPA, respectively. Consequently, the elimination of Mg and Ca from the  Lu final solution produced was not found to be necessary, while the elimination of Cu, Fe, Zn and Yb from the
Lu final solution produced was not found to be necessary, while the elimination of Cu, Fe, Zn and Yb from the  Lu final solution was found to be necessary. On the basis of the knowledge obtained, the method of elimination of the competing metals will be developed.
Lu final solution was found to be necessary. On the basis of the knowledge obtained, the method of elimination of the competing metals will be developed.
松尾 洋一*; 長谷 純宏; 竹下 大樹*; 納富 麻子*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 111, 2015/03
中生ウンシュウミカンは、多胚性種子のために交雑育種による品種改良には多数の制約がある。このため新品種の開発は、雑種実生による品種改良は少なく、枝変わりもしくは珠心胚実生の中から突然変異個体を選抜している。通常の珠心胚実生の選抜試験では、特定の形質を得ることは困難であるため、イオンビーム照射を実施した珠心胚実生より突然変異個体を効率的に誘発するために、品種毎に試料の前処理方法を検討した。前処理方法として、実生の胚軸及び根部を切断してプラ壺へ移植する方法、ならびに組織の切断部位を少なくするために胚軸部のみを切断し、スチロールケースに配置して根部は水分を含ませた支持体で固定する方法の2通りを試験した。イオンビーム照射後の再分化率を比較した結果、前者の方法の方が再分化率が高いことがわかった。
 radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater
radiolysis on pit initiation of Zircaloy-2 in artificial seawater本岡 隆文; 小松 篤史; 塚田 隆; 山本 正弘
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 18, 2015/03
人工海水でのジルカロイ2の孔食発生に対する 線照射による水質変化の影響を調査した。人工海水への
線照射による水質変化の影響を調査した。人工海水への 線照射により生成した過酸化水素が不動態被膜を形成し、その不動態被膜により孔食発生が困難になっていることを、溶液分析、電気化学試験並びに表面分析の結果から明らかにした。
線照射により生成した過酸化水素が不動態被膜を形成し、その不動態被膜により孔食発生が困難になっていることを、溶液分析、電気化学試験並びに表面分析の結果から明らかにした。