Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kinoshita, Junichi; Sakamoto, Yu; Suzuki, Ichiro; Nakajima, Ryota; Morita, Yusuke; Irie, Hirobumi
JAEA-Technology 2024-027, 55 Pages, 2025/05
The Waste Treatment Facility No.2 has equipment that can process solid waste with relatively high radioactive levels generated within the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. This facility had been constructed under the old Building Standards Act. Seismic evaluation based on a new regulatory requirements enforced in December 2013 was executed, thereby, it was found that the seismic resistance requirements was insufficient according to the current Building Standards Act. Therefore, seismic reinforcement works was carried out from November 2018 to February 2020. In this report, seismic reinforcement design, works, test and inspection was complied.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2024-012, 122 Pages, 2024/09
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (hereafter referred to "1F"), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge of novel hybrid-waste-solidification of mobile nuclei generated in Fukushima Nuclear Power Station and establishment of rational disposal concept and its safety assessment" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to establish the rational waste disposal concept of a variety of wastes generated in 1F based on the hybrid-waste-solidification by the Hot Isostatic Press (HIP) method. The ceramics form with target elements, mainly iodine, which is difficult to immobilize, and Minor actinides such as Am, an alphaemitter and heat source, are HIPed with well-studied materials such as SUS and zircaloy, which make the long-term stability evaluation and safety assessment possible.
 inferred from muon study
inferred from muon studyKadono, Ryosuke*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Koda, Akihiro*; Ito, Takashi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285503_1 - 285503_13, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.20(Physics, Condensed Matter)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-072, 116 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge of novel hybrid-waste-solidification of mobile nuclei generated in Fukushima Nuclear Power Station and establishment of rational disposal concept and its safety assessment" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to establish the rational waste disposal concept of a variety of wastes generated in 1F by the novel hybrid-waste-solidification. The phosphate form of ALPS sediment wastes containing Eu , Ce
, Ce , Sr
, Sr and Cs
and Cs were synthesized as well as radioactive
were synthesized as well as radioactive  Sr,
Sr,  Cs and
Cs and  I which are both
I which are both  emitters, AREVA sludge and Iodine Calcium apatite were synthesized, and they were processed to the stabilization treatment such as sintering and Spark Plasma ...
emitters, AREVA sludge and Iodine Calcium apatite were synthesized, and they were processed to the stabilization treatment such as sintering and Spark Plasma ...
Sato, Takumi; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki; Quaini, A.*; Gu neau, C.*
neau, C.*
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 79, p.102481_1 - 102481_11, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.57(Thermodynamics) and CrUO
and CrUO
Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Kumagai, Yuta; Nakada, Masami; Watanabe, Masayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nagai, Takayuki; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kirishima, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:53.26(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)FeUO , CrUO
, CrUO , and Fe
, and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO
are monouranates containing pentavalent U. Even though these compounds have similar crystal structures, their formation conditions and thermal stability are significantly different. To determine the factors causing the difference in thermal stability between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO , their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm
, their crystal structures were evaluated in detail. A Raman band was observed at 700 cm in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe
in all the samples. This Raman band was derived from the stretching vibration of the O-U-O axis band, indicating that Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M
was composed of a uranyl-like structure in its lattice regardless of its "x"' value. M ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO
ssbauer measurements indicated that the Fe in FeUO and Fe
and Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe
were trivalent. Furthermore, Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO lost its symmetry around Fe
lost its symmetry around Fe with increasing electron densities around Fe
with increasing electron densities around Fe , as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO
, as the abundance of Cr increased. These results suggested no significant structural differences between FeUO and CrUO
and CrUO . Thermogravimetric measurements for UO
. Thermogravimetric measurements for UO , FeUO
, FeUO , and CrUO
, and CrUO showed that the temperature at which FeUO
showed that the temperature at which FeUO decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800
decomposed under an oxidizing condition (approximately 800  C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO
C) was significantly lower than the temperature at which the decomposition of CrUO started (approximately 1250
started (approximately 1250  C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO
C). Based on these results, we concluded that the decomposition of FeUO was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
was triggered by an "in-crystal" redox reaction, i.e., Fe
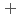 U
U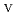
 Fe
Fe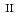
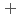 U
U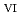 , which would not occur in the CrUO
, which would not occur in the CrUO lattice because Cr
lattice because Cr could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr
could never be reduced under the investigated condition. Finally, the existence of Cr in FexCr
in FexCr UO
UO effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe
effectively suppressed the decomposition of the Fe Cr
Cr UO
UO crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
crystal, even at a very low Cr content.
Nakashio, Nobuyuki*; Osugi, Takeshi; Kurosawa, Shigenobu; Ishikawa, Joji; Hemmi, Ko; Iketani, Shotaro; Yokobori, Tomohiko
JAEA-Technology 2022-016, 47 Pages, 2022/08
The Nuclear Science Research Institute (NSRI) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started operation of the Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities (AVWF) for production of waste packages for disposal of low-level radioactive solid wastes (LLW). To clarify the operating conditions for homogenization of non-metallic LLW, preliminary tests were carried out using the plasma melting furnace of the non-metal melting unit. The fluidity of molten waste influences homogenization conditions of solidified products. It was clarified that the viscosity, which is determined by the chemical composition and the melting temperature, influence the fluidity of molten waste greatly through previous literature review and the small-scale melting tests. In the preliminary tests, the simulated waste with a cold tracer loaded in 200 L drums were melted. Using the waste chemical components (basicity, iron oxide concentration) as an experimental parameter, the homogeneity of the chemical components of the solidified product was investigated and the homogenization conditions of melting tests were examined. The retention ratio of the tracer in the molten bath was also confirmed. The viscosity of the molten wastes was measured and the correlation with homogeneity was examined. In addition, the technical requirements that should be concerned in advance for future actual operation were discussed.
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:29.12(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Shibaura Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-008, 116 Pages, 2022/06
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of the sintering solidification method for spent zeolite to long-term stabilization" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021 (this contract was extended to FY2021). Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop a new sintering solidification method in which glass is added as a binder to spent zeolite which is adsorbed radionuclides such as Cs and the nuclides are immobilized by sintering them. In this project, the optimum conditions for sintering solidification and the basic performance of the sintered solidified body will be evaluated by cold tests, and they will be demonstrated by hot tests.
 GeP
GeP S
S by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurements
by quasi-elastic neutron scattering measurementsHori, Satoshi*; Kanno, Ryoji*; Kwon, O.*; Kato, Yuki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Matsuura, Masato*; Yonemura, Masao*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Kawakita, Yukinobu
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 126(22), p.9518 - 9527, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.11(Chemistry, Physical)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2021-077, 217 Pages, 2022/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of stable solidification technique of ALPS sediment wastes by apatite ceramics" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to establish an apatite solidification process of radioactive sediment wastes, which were generated from the ALPS process manipulating the large amount of contaminated water from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. In FY2020, the synthetic scheme and elemental composition were updated to precipitation method to accept the actual ALPS sediment wastes in engineering scale. The synthesis of apatite or phosphate wastes and their molding conditions were surveyed, and the relations among elemental compositions, structures and chemical properties were clarified.
Sato, Junya; Shiota, Kenji*; Takaoka, Masaki*
Zairyo, 70(5), p.406 - 411, 2021/05
An aluminosilicate solid is an inorganic material that has the property of immobilizing heavy metals or radionuclides in the matrix. In this study, aluminosilicates with a Si/Al molar ratio of 0.5 was synthesized from a chemical reagent in order to produce aluminosilicate solids with a low Si/Al molar ratio, which were expected to improve the immobilization of heavy metals and radionuclides contained in the matrix. The synthesized Si-Al gel with a Si/Al molar ratio of 0.5 had little impurity content and was in an amorphous phase. In addition, the compressive strength of the aluminosilicate solid produced by the synthesized Si-Al gel showed a 5 MPa or more, confirming that it can be used as a raw material for aluminosilicate solids. The aluminosilicate solid with a Si/Al molar ratio of 1.25 had a dense surface structure from the result of BSE images and had the highest compressive strength among all samples.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-060, 116 Pages, 2021/02
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of Stable Solidification Technique of ALPS Sediment Wastes by Apatite Ceramics" conducted in FY2019.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2020-054, 72 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Safe, efficient cementation of challenging radioactive wastes using alkali activated materials with high-flowability and high-anion retention capacity". The purpose of this study is to find safe, efficient cementation of challenging radioactive wastes using alkali activated materials with high-flowability and high-anion retention capacity, and to propose the concept of a manufacturing apparatus that is established as an actual plant. As a result of study in this year, it was revealed that the K-based alkali activated material has high-flowability and quick curing, and that high-iodine retention capacity is achieved by incorporating silver ions during manufacturing of solidified waste.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Shibaura Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2020-049, 78 Pages, 2021/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of the Sintering Solidification Method for Spent Zeolite to Long-term Stabilization" conducted in FY2019.
 Zr and
Zr and  Mo in concrete rubble
Mo in concrete rubbleDo, V. K.; Furuse, Takahiro; Murakami, Erina; Aita, Rena; Ota, Yuki; Sato, Soichi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(1), p.543 - 553, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:49.08(Chemistry, Analytical)A new HCl-free chromatographic separation procedure has been developed for sequential separation of Zr and Mo from concrete matrices. Accordingly,  Zr and
Zr and  Mo could be sensitively and selectively measured by ICP-MS/MS using ammonia reaction gas. The recoveries of greater than 90% for Zr and Mo from concretes could be achieved. The measurement condition was optimized for complete suppression of interferences from
Mo could be sensitively and selectively measured by ICP-MS/MS using ammonia reaction gas. The recoveries of greater than 90% for Zr and Mo from concretes could be achieved. The measurement condition was optimized for complete suppression of interferences from  Nb and peak tailing from abundant isotopes of Zr and Mo in concrete matrices. The removal of interferences was verified by measurement of radio-contamination-free concretes used as a sample matrix blank. Method detection limits of 1.7 mBq g
Nb and peak tailing from abundant isotopes of Zr and Mo in concrete matrices. The removal of interferences was verified by measurement of radio-contamination-free concretes used as a sample matrix blank. Method detection limits of 1.7 mBq g and 0.2 Bq g
and 0.2 Bq g were achieved for
were achieved for  Zr and
Zr and  Mo, respectively, in the concrete matrices. The interference removal factor for Nb (equivalent to the decontamination factor in radiochemical separation) was of the order of 10
Mo, respectively, in the concrete matrices. The interference removal factor for Nb (equivalent to the decontamination factor in radiochemical separation) was of the order of 10 , and the abundance sensitivity was of the order of 10
, and the abundance sensitivity was of the order of 10 , indicating that the developed method is reliable for verifying the presence of ultralow concentrations of
, indicating that the developed method is reliable for verifying the presence of ultralow concentrations of  Zr and
Zr and  Mo. The present method is suitable for the rapid assessment of
Mo. The present method is suitable for the rapid assessment of  Zr and
Zr and  Mo for radioactivity inventory of concrete rubble.
Mo for radioactivity inventory of concrete rubble.
Kitamura, Akira; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Goto, Takahiro*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.58 - 71, 2020/12
Evaluation and estimation of solubility values are required for a performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes. Selection of solubility-limiting solid phases (SSPs) that control the solubility of radionuclides is necessary for the evaluation and estimation of solubility values. The authors have developed a methodology for selection of the SSP through a calculation of saturation indices (SIs) using thermodynamic database to show a transparent procedure for the selection. Literature survey should be performed to confirm decision of the SSP from candidate SSPs which generally have larger SIs from realistic point of view for precipitation and solubility control. The authors have selected the SSPs for the elements of interest for the latest Japanese performance assessment in bentonite and cement porewaters after grouping various water compositions.
Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake; Sato, Fuminori; Matsushima, Ryotatsu; Kataoka, Shoji; Okada, Shota; Sasaki, Toshiki; Inoue, Junya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(11), p.658 - 663, 2020/11
, 62(11), p.658 - 663, 2020/11
no abstracts in English
Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-006, 70 Pages, 2020/08
Radioactive wastes which generated from research and testing reactors in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried at the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes by the time it starts disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JPDR and JRR-4. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 19 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of those samples.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Shibaura Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2019-028, 71 Pages, 2020/03
JAEA/CLADS, had been conducting the Center of World Intelligence Project for Nuclear Science/Technology and Human Resource Development (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2018. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of the Sintering Solidification Method for Spent Zeolite to Long-term Stabilization". The present study aims to develop the sintering solidification method for zeolites (spent zeolites) that adsorbs continuously generated radionuclides such as cesium. The sintering solidification method is able to stabilize adsorbed radionuclides such as cesium in zeolites by adding a glass as a binder to spent zeolite and sintered it. It is expected that the sintering solidification method is significantly reduce the volume of the solidified body compare with the glass solidification method and to form a stable solidified body equivalent to the calcination solidification method. In this project, we planned to select a glass suitable for the sintering solidification method and optimize the sintering temperature, etc. using non-radioactive nuclides (cold tests), and verify it by using radioactive nuclides (hot tests). In FY2018, we investigated the thermal properties of candidate glasses for binder and the effect of heating atmosphere on the sintering solidification method. Irradiated fuel for preparing simulated contaminated water containing radionuclides was selected and the condition of it was observed. In addition, we surveyed existing research results and latest research trends about solidification of zeolite, calcination solidification and so on.