Biological nano-mineralization of Yb phosphate by 
酵母によるYbリン酸塩ナノ鉱物化
大貫 敏彦; Jiang, M.; 上石 瑛伍*; 宇都宮 聡*; 田中 万也 
 ; 香西 直文
; 香西 直文 

 ; 鈴木 義規*
; 鈴木 義規*
Onuki, Toshihiko; Jiang, M.; Kamiishi, Eigo*; Utsunomiya, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Suzuki, Yoshinori*
酵母を用いてYbの微生物による鉱物化機構を明らかにする実験を行った。溶液のpHを3, 4, 5に調整したYb溶液に酵母を添加して、溶液中のYb濃度,pH変化を調べた。さらに、酵母を電子顕微鏡で観察した。その結果、溶液中からYbが除かれて、酵母細胞表面でナノサイズの鉱物が生成することを明らかにした。溶液中にはリンを添加していないにもかかわらず、鉱物はリンを含んでいた。これらの結果は、Ybが細胞表面に吸着し、細胞から溶出したPと反応してナノサイズのYbリン酸塩鉱物が生成したことを示している。
We have investigated the association of heavy REE of Yb with yeast 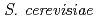 after exposure at pH of 3, 4 or 5. A variety of analytical techniques including FESEM-EDS, TEM, ICP-AES, XAFS have been employed to investigate the sequestration mechanism of Yb by yeast as a function of exposure time. Ytterbium concentrations in solutions decrease as the exposure time increases. FESEM, TEM, and XAFS analyses revealed that nano-sized blocky Yb phosphate with amorphous phase formed on the yeast cells surface after 24 h. These results suggest that the sorbed Yb on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside of the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of amorphous Yb phosphate.
after exposure at pH of 3, 4 or 5. A variety of analytical techniques including FESEM-EDS, TEM, ICP-AES, XAFS have been employed to investigate the sequestration mechanism of Yb by yeast as a function of exposure time. Ytterbium concentrations in solutions decrease as the exposure time increases. FESEM, TEM, and XAFS analyses revealed that nano-sized blocky Yb phosphate with amorphous phase formed on the yeast cells surface after 24 h. These results suggest that the sorbed Yb on the cell surfaces reacted with P released from inside of the yeast cell, resulting in the formation of amorphous Yb phosphate.