Electronic structure of EuAl studied by photoelectron spectroscopy
studied by photoelectron spectroscopy
光電子分光によるEuAl の電子状態
の電子状態
小畠 雅明 
 ; 藤森 伸一
; 藤森 伸一 

 ; 竹田 幸治
; 竹田 幸治 

 ; 岡根 哲夫
; 岡根 哲夫 
 ; 斎藤 祐児
; 斎藤 祐児 
 ; 小林 啓介*; 山上 浩志; 仲村 愛*; 辺土 正人*; 仲間 隆男*; 大貫 惇睦*
; 小林 啓介*; 山上 浩志; 仲村 愛*; 辺土 正人*; 仲間 隆男*; 大貫 惇睦*
Kobata, Masaaki; Fujimori, Shinichi; Takeda, Yukiharu; Okane, Tetsuo; Saito, Yuji; Kobayashi, Keisuke*; Yamagami, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Ai*; Hedo, Masato*; Nakama, Takao*; Onuki, Yoshichika*
The electronic structure of a divalent 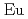 compound EuAl
compound EuAl , which shows the charge density wave transition at
, which shows the charge density wave transition at 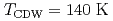 , was studied by the hard X-ray angle-integrated photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) and the soft X-ray angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES). The valence band and core-level spectra obtained by the HAXPES are consistent with the divalent nature of Eu atoms in EuAl
, was studied by the hard X-ray angle-integrated photoelectron spectroscopy (HAXPES) and the soft X-ray angle resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (ARPES). The valence band and core-level spectra obtained by the HAXPES are consistent with the divalent nature of Eu atoms in EuAl . Furthermore, the Fermi surface as well as the band structure in the vicinity of the Fermi Energy (
. Furthermore, the Fermi surface as well as the band structure in the vicinity of the Fermi Energy (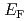 ) of EuAl
) of EuAl are very similar to those of its isostructural divalent
are very similar to those of its isostructural divalent 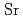 compound SrAl
compound SrAl , which does not have
, which does not have 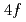 electrons. These suggest that Eu atoms are divalent in EuAl
electrons. These suggest that Eu atoms are divalent in EuAl , and
, and 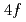 electrons are completely localized with
electrons are completely localized with 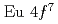 electronic configuration in the ground state. The ARPES spectra measured along the
electronic configuration in the ground state. The ARPES spectra measured along the  -
-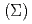 -Z high-symmetry line did not show significant temperature dependences above and below
-Z high-symmetry line did not show significant temperature dependences above and below 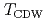 within the energy resolution of
within the energy resolution of 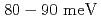 . Moreover, the Fermi surface mapping along the
. Moreover, the Fermi surface mapping along the 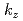 direction showed that both of EuAl
direction showed that both of EuAl and SrAl
and SrAl have highly three-dimensional electronic structures, suggesting that the nesting of Fermi surface is not straightforward. The Fermi surface and band structure of SrAl
have highly three-dimensional electronic structures, suggesting that the nesting of Fermi surface is not straightforward. The Fermi surface and band structure of SrAl were well explained by the band-structure calculation based on the local density approximation.
were well explained by the band-structure calculation based on the local density approximation.