Hydrogen occupation and hydrogen-induced volume expansion in Fe Ni
Ni D
D at high
at high 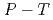 conditions
conditions
高温高圧下におけるFe Ni
Ni D
D の水素占有サイトと水素誘起体積膨張
の水素占有サイトと水素誘起体積膨張
市東 力*; 鍵 裕之*; 柿澤 翔*; 青木 勝敏*; 小松 一生*; 飯塚 理子*; 阿部 淳*; 齋藤 寛之*; 佐野 亜沙美 

 ; 服部 高典
; 服部 高典 


Shito, Chikara*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Abe, Jun*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
Fe Ni
Ni H
H (D
(D )の12GPa, 1000Kまでの高温高圧下における相関係と結晶構造をその場X線及び中性子回折測定により明らかにした。今回実験した温度圧力下において、Fe
)の12GPa, 1000Kまでの高温高圧下における相関係と結晶構造をその場X線及び中性子回折測定により明らかにした。今回実験した温度圧力下において、Fe Ni
Ni H
H (D
(D )ではFeH
)ではFeH (D
(D )とは異なり、重水素原子は面心立方構造(fcc)中の四面体サイトを占有しないことが明らかになった。単位重水素あたりの水素誘起膨張体積
)とは異なり、重水素原子は面心立方構造(fcc)中の四面体サイトを占有しないことが明らかになった。単位重水素あたりの水素誘起膨張体積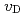 は、fcc相で2.45(4)
は、fcc相で2.45(4) 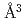 、hcp相で3.31(6)
、hcp相で3.31(6) 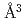 であり、FeD
であり、FeD におけるそれぞれの値より著しく大きいことが明らかになった。また、
におけるそれぞれの値より著しく大きいことが明らかになった。また、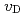 は温度の上昇に伴いわずかに増加した。この結果は、鉄に10%ニッケルを添加するだけで、金属中の水素の挙動が劇的に変化することを示唆している。
は温度の上昇に伴いわずかに増加した。この結果は、鉄に10%ニッケルを添加するだけで、金属中の水素の挙動が劇的に変化することを示唆している。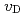 が圧力に関係なく一定であると仮定すると、地球内核の最大水素含有量は海洋の水素量の1-2倍であると推定される。
が圧力に関係なく一定であると仮定すると、地球内核の最大水素含有量は海洋の水素量の1-2倍であると推定される。
The phase relation and crystal structure of Fe Ni
Ni H
H (D
(D ) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under
) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under 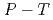 conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal (
conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal ( ) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe
) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe Ni
Ni D
D unlike fcc FeH
unlike fcc FeH (D
(D ). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium
). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium 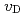 was determined as 2.45(4)
was determined as 2.45(4) 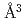 and 3.31(6)
and 3.31(6) 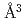 for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD
for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD . The
. The 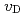 value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that
value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that 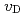 is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.