Evaluation of doped potassium concentrations in stacked two-Layer graphene using real-time XPS
X線光電子分光を使ったカリウムドープ積層2層グラフェン中のカリウム濃度の定量評価
小川 修一*; 津田 泰孝 

 ; 坂本 徹哉*; 沖川 侑揮*; 増澤 智昭*; 吉越 章隆
; 坂本 徹哉*; 沖川 侑揮*; 増澤 智昭*; 吉越 章隆  ; 虻川 匡司*; 山田 貴壽*
; 虻川 匡司*; 山田 貴壽*
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Sakamoto, Tetsuya*; Okigawa, Yuki*; Masuzawa, Tomoaki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abukawa, Tadashi*; Yamada, Takatoshi*
グラフェンのKOH溶液への浸漬により、SiO /Siウェハ上のグラフェンの移動度が改善される。これはK原子によるグラフェン修飾による電子ドーピングのためと考えられるが、このときのグラフェンに含まれるK濃度は不明だった。本研究では高輝度放射光を用いたXPS分析によりK濃度を求めた。リアルタイム観察によりK原子濃度の時間変化を求め、放射光未照射時のK原子濃度は0.94%と推定された。また、K原子の脱離に伴ってC 1sスペクトルが低結合エネルギー側にシフトした。これはグラフェンへの電子ドープ濃度が減少していることを示し、K原子はグラフェンに電子注入していることが実験的に確かめられた。
/Siウェハ上のグラフェンの移動度が改善される。これはK原子によるグラフェン修飾による電子ドーピングのためと考えられるが、このときのグラフェンに含まれるK濃度は不明だった。本研究では高輝度放射光を用いたXPS分析によりK濃度を求めた。リアルタイム観察によりK原子濃度の時間変化を求め、放射光未照射時のK原子濃度は0.94%と推定された。また、K原子の脱離に伴ってC 1sスペクトルが低結合エネルギー側にシフトした。これはグラフェンへの電子ドープ濃度が減少していることを示し、K原子はグラフェンに電子注入していることが実験的に確かめられた。
Immersion of graphene in KOH solution improves its mobility on SiO /Si wafers. This is thought to be due to electron doping by modification with K atoms, but the K atom concentration C
/Si wafers. This is thought to be due to electron doping by modification with K atoms, but the K atom concentration C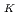 in the graphene has not been clarified yet. In this study, the C
in the graphene has not been clarified yet. In this study, the C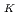 was determined by XPS analysis using high-brilliance synchrotron radiation. The time evolution of C
was determined by XPS analysis using high-brilliance synchrotron radiation. The time evolution of C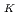 was determined by real-time observation, and the C
was determined by real-time observation, and the C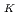 before irradiation of synchrotron radiation was estimated to be 0.94%. The C 1s spectrum shifted to the low binding energy side with the desorption of K atoms. This indicates that the electron doping concentration into graphene is decreasing, and it is experimentally confirmed that K atoms inject electrons into graphene.
before irradiation of synchrotron radiation was estimated to be 0.94%. The C 1s spectrum shifted to the low binding energy side with the desorption of K atoms. This indicates that the electron doping concentration into graphene is decreasing, and it is experimentally confirmed that K atoms inject electrons into graphene.