Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Song, Y.*; Xu, S.*; 佐藤 駿介*; Lee, I.*; Xu, X.*; 大森 俊洋*; 長迫 実*; 川崎 卓郎; 鬼柳 亮嗣; Harjo, S.; et al.
Nature, 638, p.965 - 971, 2025/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:88.78(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In advanced applications like aerospace and space exploration, materials must balance lightness, functionality, and extreme thermal fluctuation resistance. Shape-memory alloys show promise with strength, toughness, and substantial strain recovery due to superelasticity, but maintaining low mass and effective operation at cryogenic temperatures is challenging. We hereby introduce a novel shape-memory alloy that adheres to these stringent criteria. Predominantly composed of Ti and Al with a chemical composition of Ti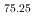 Al
Al Cr
Cr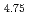 , this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36
, this alloy 25 is characterized by a low density (4.36 10
10 kg/m
kg/m ) and a high specific strength (185
) and a high specific strength (185 10
10 Pa
Pa m
m /kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
/kg) at room temperature, while exhibiting excellent superelasticity. The superelasticity, owing to a reversible stress-induced phase transformation from an ordered body-centered cubic parent phase to an ordered orthorhombic martensite, allows for a recoverable strain exceeding 7%. Remarkably, this functionality persists across a broad range of temperatures, from deep cryogenic 4.2 K to above room temperature, arising from an unconventional temperature dependence of transformation stresses. Below a certain threshold during cooling, the critical transformation stress inversely correlates with temperature. We interpret this behavior from the perspective of a temperature-dependent anomalous lattice instability of the parent phase. This alloy holds potential in everyday appliances requiring flexible strain accommodations, as well as components designed for extreme environmental conditions such as deep space and liquefied gases.
能崎 幸雄*; 介川 裕章*; 渡邉 紳一*; 柚木 清司*; 洞口 泰輔*; 中山 颯人*; 山野井 一人*; Wen, Z.*; He, C.*; Song, J.*; et al.
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 26(1), p.2428153_1 - 2428153_39, 2025/02
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a novel method for generating spin currents using the gyromagnetic effect, a phenomenon discovered over a century ago. This effect, crucial for understanding the origins of magnetism, enables the coupling between various macroscopic rotational motions and electron spins. While higher rotational speeds intensify the effect, conventional mechanical rotations, typically, below 10,000 RPM, produce negligible results comparable to geomagnetic fluctuations, limiting applied research. Our studies demonstrate that spin current generation comparable to that of rare metals can be achieved through atomic rotations induced by GHz- range surface acoustic waves and the rotational motion of conduction electrons in metallic thin films with nanoscale gradient modulation of electrical conductivity. These effects, termed the acoustic gyromagnetic effect and the current-vorticity gyromagnetic effect, are significant in different contexts.
 signatures in two-dimensional cone beam interferometry
signatures in two-dimensional cone beam interferometrySarenac, D.*; Gorbet, G.*; Clark, C. W.*; Cory, D. G.*; Ekinci, H.*; Henderson, M. E.*; Huber, M. G.*; Hussey, D. S.*; Kapahi, C.*; Kienzle, P. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.L032054_1 - L032054_8, 2024/09
Neutron interferometry has played a distinctive role in fundamental science and characterization of materials. Moir neutron interferometers are candidate next-generation instruments: they offer microscopy-like magnification of the signal, enabling direct camera recording of interference patterns across the full neutron wavelength spectrum. Here we demonstrate the extension of phase-grating moir
neutron interferometers are candidate next-generation instruments: they offer microscopy-like magnification of the signal, enabling direct camera recording of interference patterns across the full neutron wavelength spectrum. Here we demonstrate the extension of phase-grating moir interferometry to two-dimensional geometries. Our measurements of phase topologies and gravitationally induced phase shifts are in good agreement with theory.
interferometry to two-dimensional geometries. Our measurements of phase topologies and gravitationally induced phase shifts are in good agreement with theory.
Zhang, Z.*; 服部 高典; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(3), p.035105_1 - 035105_8, 2024/07
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:40.97(Physics, Applied)バロカロリック材料を用いた固体冷凍は、環境に優しく高効率であるため、過去10年間にわたり世界的に注目されてきた。ここでは、室温付近で立方晶から菱面体晶への相転移を起こすヘキサフルオロ燐酸ナトリウム(NaPF )とヘキサフルオロ砒酸ナトリウム(NaAsF
)とヘキサフルオロ砒酸ナトリウム(NaAsF )における巨大バロカロリック効果を報告する。われわれは中性子粉末回折により、NaPF
)における巨大バロカロリック効果を報告する。われわれは中性子粉末回折により、NaPF の低温相の構造が空間群R
の低温相の構造が空間群R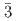 の菱面体構造であることを明らかにした。NaPF
の菱面体構造であることを明らかにした。NaPF とNaAsF
とNaAsF には3つのラマン振動モード(F
には3つのラマン振動モード(F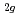 , E
, E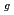 , A
, A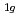 )が存在する。相転移温度はNaPF
)が存在する。相転移温度はNaPF 及びNaAsF
及びNaAsF においてそれぞれdT
においてそれぞれdT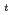 /dP=250K/GPa及び310K/GPaの割合で圧力とともに変化する。NaPF
/dP=250K/GPa及び310K/GPaの割合で圧力とともに変化する。NaPF とNaAsF
とNaAsF の圧力誘起エントロピー変化は、それぞれ約45.2Jkg
の圧力誘起エントロピー変化は、それぞれ約45.2Jkg K
K と35.6Jkg
と35.6Jkg K
K と決定された。飽和駆動圧力は約40MPaであった。高圧下の中性子粉末回折から、バロカロリック効果は立方晶から菱面体晶への圧力誘起相転移に関係していることが示唆された。
と決定された。飽和駆動圧力は約40MPaであった。高圧下の中性子粉末回折から、バロカロリック効果は立方晶から菱面体晶への圧力誘起相転移に関係していることが示唆された。
Sarenac, D.*; Gorbet, G.*; Kapahi, C.*; Clark, C. W.*; Cory, D. G.*; Ekinci, H.*; Garrad, D. V.*; Henderson, M. E.*; Huber, M. G.*; Hussey, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(2), p.023260_1 - 023260_15, 2024/06
Phase-grating moire interferometers (PGMIs) have emerged as promising candidates for the next generation of neutron interferometry, enabling the use of a polychromatic beam and manifesting interference patterns that can be directly imaged by existing neutron cameras. However, the modeling of the various PGMI configurations is limited to cumbersome numerical calculations and backward propagation models which often do not enable one to explore the setup parameters. Here we generalize the Fresnel scaling theorem to introduce a k-space model for PGMI setups illuminated by a cone beam, thus enabling an intuitive forward propagation model for a wide range of parameters and experimental setups.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionZhou, Y.*; Song, W.*; Zhang, F.*; Wu, Y.*; Lei, Z.*; Jiao, M.*; Zhang, X.*; Dong, J.*; Zhang, Y.*; Yang, M.*; et al.
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 971, p.172635_1 - 172635_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:12.80(Chemistry, Physical)The grain orientation-dependent lattice strain evolution of a (TiZrHfNb)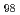
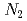 refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using
refractory high-entropy alloy (HEA) during tensile loading has been investigated using  neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary
neutron diffraction. The equivalent strain-hardening rate of each of the primary 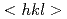 -oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
-oriented grain families was found to be relatively low, manifesting the macroscopically weak work-hardening ability of such a body-centered cubic (BCC)-structured HEA. This finding is indicative of a dislocation planar slip mode that is confined in a few single-slip planes and leads to in-plane softening by high pile-up stresses.
 Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; 梶本 亮一; 池内 和彦*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:62.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)TbMn Sn
Sn is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn
is a correlated topological magnet with a Mn-based kagome lattice, in which a Chern gap opens at the Dirac point at low temperatures. The magnetic moment direction of the ferrimagnetic order changes from in the kagome plane to the out-of-plane upon cooling, which is essential for generating the Chern gap, but the underlying mechanism for the spin reorientation remains elusive. Here, we investigate the spin-reorientation transition in TbMn Sn
Sn using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb
using neutron scattering. We provide direct evidence for the spin-reorientation transition and unveil the coexistence of two Tb modes at 200 K. To account for these results, we put forward a model based on SU(N) spin-wave theory, in which there is a temperature evolution of the ground state Tb 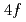 orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn
orbitals, driven by the crystalline electric field, single-ion anisotropy, and exchange interactions between Tb and Mn ions. Our findings shed light on the complex magnetism of TbMn Sn
Sn , despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
, despite its relatively simple ground state magnetic structure, and provide insights into the mechanisms for tuning magnetic topological materials.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
被引用回数:19 パーセンタイル:94.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The magnetization of a quantum magnet can be pinned at a fraction of its saturated value by collective effects. One example of such a plateau phase is found in spin-1/2 triangular-lattice antiferromagnets. They feature strong geometrical frustration and the plateau phase therein is often interpreted as arising from an order-by-disorder mechanism driven by quantum fluctuations. Here we observe a one-third magnetization plateau under an applied magnetic field in the spin-1 antiferromagnet Na Ni
Ni BiO
BiO with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
with a honeycomb lattice, which, with conventional magnetic interactions, would not be geometrically frustrated. Based on our elastic neutron scattering measurements, we propose the spin structure of the plateau phase to be an unusual partial spin-flop ferrimagnetic order. Our theoretical calculations indicate that bond-anisotropic Kitaev interactions are the source of frustration that produces the plateau. These results suggest that Kitaev interactions provide a different route to frustration and phases driven by quantum fluctuations in high-spin magnets.
Liu, B.*; Feng, R.*; Busch, M.*; Wang, S.*; Wu, H.*; Liu, P.*; Gu, J.*; Bahadoran, A.*; 松村 大樹; 辻 卓也; et al.
ACS Nano, 16(9), p.14121 - 14133, 2022/09
被引用回数:97 パーセンタイル:98.70(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Pt single-atom materials possess an ideal atom economy but suffer from limited intrinsic activity and side reaction of producing H O
O in catalyzing the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Here, we demonstrate that anchoring platinum alloys on single-atom Pt-decorated carbon (Pt- SAC) surmounts their inherent deficiencies, thereby enabling a complete four-electron ORR pathway catalysis with high efficiency and durability. Pt
in catalyzing the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). Here, we demonstrate that anchoring platinum alloys on single-atom Pt-decorated carbon (Pt- SAC) surmounts their inherent deficiencies, thereby enabling a complete four-electron ORR pathway catalysis with high efficiency and durability. Pt Co@Pt-SAC demonstrates an exceptional mass and specific activities 1 order of magnitude higher than those of commercial Pt/C. They are durable throughout 50000 cycles, showing only a 10 mV decay in halfwave potential. The superior durability is attributed to the shielding effect of the Pt-SAC coating, which significantly mitigates the dissolution of Pt
Co@Pt-SAC demonstrates an exceptional mass and specific activities 1 order of magnitude higher than those of commercial Pt/C. They are durable throughout 50000 cycles, showing only a 10 mV decay in halfwave potential. The superior durability is attributed to the shielding effect of the Pt-SAC coating, which significantly mitigates the dissolution of Pt Co cores.
Co cores.
Tang, J.*; Seo, O.*; Rivera Rocabado, D. S.*; 小板谷 貴典*; 山本 達*; 難波 優輔*; Song, C.*; Kim, J.*; 吉越 章隆; 古山 通久*; et al.
Applied Surface Science, 587, p.152797_1 - 152797_8, 2022/06
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:67.59(Chemistry, Physical)水素貯蔵材料として重要な立方体形状Pdナノ粒子の水素吸収と拡散メカニズムをX線光電子分光とDFT計算を用いて調べた。表面領域では粒子の大きさによらず、ほぼ同様の水素吸収挙動を示した。四面体サイトよりも八面体サイトの水素占有率が大きいことがわかった。表面の乱れによってPd-H結合が弱くなるため、小さいサイズのPdナノ粒子に吸収された水素原子は、より活発に粒子内部に拡散することが分かった。これが低水素圧での水素吸着に重要な役割を果たしている。
 near
near 
Song, T.*; Gubler, P.; Hong, J.*; Lee, S. H.*; 森田 健司*
Physics Letters B, 813, p.136065_1 - 136065_5, 2021/02
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:35.67(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We calculate the mass shift and thermal decay width of the J/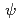 near the QCD transition temperature
near the QCD transition temperature  by imposing two independent constraints on these variables that can be obtained first by solving the Schrodinger equation and second from the QCD sum rule approach. While the real part of the potential is determined by comparing the QCD sum rule result for charmonium and the D meson to that from the potential model result, the imaginary potential is taken to be proportional to the perturbative form multiplied by a constant factor, which in turn can be determined by applying the two independent constraints. The result shows that the binding energy and the thermal width becomes similar in magnitude at around T = 1.09
by imposing two independent constraints on these variables that can be obtained first by solving the Schrodinger equation and second from the QCD sum rule approach. While the real part of the potential is determined by comparing the QCD sum rule result for charmonium and the D meson to that from the potential model result, the imaginary potential is taken to be proportional to the perturbative form multiplied by a constant factor, which in turn can be determined by applying the two independent constraints. The result shows that the binding energy and the thermal width becomes similar in magnitude at around T = 1.09  , above which the sum rule analysis also becomes unstable, strongly suggesting that the J/
, above which the sum rule analysis also becomes unstable, strongly suggesting that the J/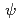 will melt slightly above
will melt slightly above  .
.
仲吉 彬; Rempe, J. L.*; Barrachin, M.*; Bottomley, D.; Jacquemain, D.*; Journeau, C.*; Krasnov, V.; Lind, T.*; Lee, R.*; Marksberry, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 369, p.110857_1 - 110857_15, 2020/12
被引用回数:12 パーセンタイル:37.42(Nuclear Science & Technology)福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の各ユニットの燃料デブリの最終状態位置については、まだ多くは不明である。不確実性の低減に向けた最初のステップとして、OECD/NEAは、燃料デブリ分析予備的考察(PreADES)プロジェクトが立ち上げた。PreADESプロジェクトのタスク1の一環として、関連情報をレビューし、燃料デブリの状態の推定図の正確さを確認した。これは、将来の燃料デブリの分析を提案するための基礎となる。具体的にタスク1では2つのアクティビティを実施した。第一に、1Fでの廃止措置活動に資するTMI-2とチェルノブイリ原子力発電所4号機での重大事故の関連知識、プロトタイプ試験とホットセル試験の結果の知見を収集した。第二に、プラント情報とBSAFプロジェクトのシビアアクシデントコード分析からの関連知識が組み込まれている1F燃料デブリの原子炉内の状態に関する現状の推定図を見直した。この報告は、PreADESプロジェクトのタスク1の洞察に焦点を当て、1Fの将来の除染および廃止措置活動に情報を提供するだけでなく、シビアアクシデント研究、特にシビアアクシデントにより損傷した原子力サイトの長期管理に関する重要な視点を提供する。
Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Lind, T.*; 丸山 結; Gauntt, R.*; Bixler, N.*; Morreale, A.*; Dolganov, K.*; Sevon, T.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 206(9), p.1449 - 1463, 2020/09
被引用回数:42 パーセンタイル:97.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)The OECD/NEA Benchmark Study at the Accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (BSAF) project, which started in 2012 and continued until 2018, was one of the earliest responses to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi. The project, divided into two phases addressed the investigation of the accident at Unit 1, 2 and 3 by Severe Accident (SA) codes until 500 h focusing on thermal-hydraulics, core relocation, Molten Corium Concrete Interaction (MCCI) and fission products release and transport. The objectives of BSAF were to make up plausible scenarios based primarily on SA forensic analysis, support the decommissioning and inform SA codes modeling. The analysis and comparison among the institutes have brought up vital insights regarding the accident progression identifying periods of core meltdown and relocation, Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV) and Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) leakage/failure through the comparison of pressure, water level and CAMS signatures. The combination of code results and inspections (muon radiography, PCV inspection) has provided a picture of the current status of the debris distribution and plant status. All units present a large relocation of core materials and all of them present ex-vessel debris with Unit 1 and Unit 3 showing evidences of undergoing MCCI. Uncertainties have been identified in particular on the time and magnitude of events such as corium relocation in RPV and into cavity floor, RPV and PCV rupture events. Main uncertainties resulting from the project are the large and continuous MCCI progression predicted by basically all the SA codes and the leak pathways from RPV to PCV and PCV to reactor building and environment. The BSAF project represents a pioneering exercise which has set the basis and provided lessons learned not only for code improvement but also for the development of new related projects to investigate in detail further aspects of the Fukushima Daiichi accident.
 dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy
dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopySong, C.*; Seo, O.*; 松村 大樹; 廣井 慧*; Cui, Y.-T.*; Kim, J.*; Chen, Y.*; Tayal, A.*; 草田 康平*; 小林 浩和*; et al.
RSC Advances (Internet), 10(34), p.19751 - 19758, 2020/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)To unveil the origin of the hydrogen-storage properties of rhodium nanoparticles (Rh NPs), we investigated the dynamical structural change of Rh NPs using  dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (XAFS). The variation of the Rh-Rh interatomic distance and Debye-Waller factor of Rh NPs with a size of 4.0 and 10.5 nm during hydrogen absorption and desorption suggested that they have a different mechanism for hydrogen absorption, which is that the hydrogen absorption on the inner site has a greater contribution than that on a surface for Rh 4.0 nm. In the case of Rh 10.5 nm, it is opposed to Rh 4.0 nm. This study demonstrates a powerful
dispersive X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy (XAFS). The variation of the Rh-Rh interatomic distance and Debye-Waller factor of Rh NPs with a size of 4.0 and 10.5 nm during hydrogen absorption and desorption suggested that they have a different mechanism for hydrogen absorption, which is that the hydrogen absorption on the inner site has a greater contribution than that on a surface for Rh 4.0 nm. In the case of Rh 10.5 nm, it is opposed to Rh 4.0 nm. This study demonstrates a powerful  XAFS method for observing small local structural changes of metal nanoparticles and its importance for understanding of the hydrogen-absorption properties of Rh NPs with an interesting hydrogenation mechanism.
XAFS method for observing small local structural changes of metal nanoparticles and its importance for understanding of the hydrogen-absorption properties of Rh NPs with an interesting hydrogenation mechanism.
仲吉 彬; Journeau, C.*; Rempe, J.*; Barrachin, M.*; Bottomley, D.; Nauchi, Y.*; Song, J. H.*
Proceedings of 2019 International Workshop on Post-Fukushima Challenges on Severe Accident Mitigation and Research Collaboration (SAMRC 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2019/11
In recognition of the broad international interest in learning from post-accident examinations and other activities related to the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Japan recommended, to the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development/Nuclear energy Agency/Committee on Safety of Nuclear Installations (OECD/NEA/CSNI) in 2013, that they identified and followed up on opportunities to address safety research gaps. The CSNI set up the Senior Expert Group (SEG) on Safety Research Opportunities Post-Fukushima (SAREF). In 2016-2017, Preparatory Study on Analysis of Fuel Debris (PreADES) project was recommended by the SEG on SAREF as a near-term project. The PreADES project will summarize the collected knowledge and expertise of debris characterization and identify the needs for debris analyses that will most contribute to the decommissioning of 1F. The project also aims to improve the understanding of severe accidents and reactor safety assessments as well as creating appropriate and optimal methodologies for future debris sampling, retrieval, and storage. Consequently, the project provides important input for a future international project of sample examination based on long-term considerations. The PreADES project launched discussions among interested organizations at the preliminary meeting in July 2017 about the objectives, scope, output, and direction of the project. The contents of the PreADES project were agreed as the three following tasks: Task 1: Joint study on fuel debris' expected properties and characterization, Task 2: Identifying needs and major issues for future fuel debris sampling, retrieval, and analyses, Task 3: Planning of future international R&D framework. Currently, 4th meeting took place on July in Tokyo Japan. Task 1 is almost completed and Task 2 will be summarized soon.
 resonances in a box
resonances in a box小野 章*; Xu, J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; Ko, C. M.*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Wolter, H.*; Zhang, Y.-X.*; Chen, L.-W.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(4), p.044617_1 - 044617_35, 2019/10
被引用回数:74 パーセンタイル:98.62(Physics, Nuclear)2017年4月に開催された国際会議Transport2017において、重イオン核反応モデルの国際的な比較が議論された。重イオン加速器の安全評価や宇宙飛行士の被ばく評価等で重要な役割を果たすため、世界中で重イオン核反応の様々な理論モデルが開発されている。本研究では、辺の長さが20fmの直方体に320個の中性子と陽子をランダム配置し、それらが70fm/cの間に起こす散乱の回数やエネルギーを計算した。ここでは、特にパイオンやその前駆体であるデルタ共鳴の生成に注目して比較を行った。参加コードは、個々の粒子の時間発展を追うQMD型コードと、粒子の位置や運動量の確率分布を決めておき、散乱や崩壊が発生したときそれらを乱数サンプリングするBUU型コードがあり、発表者が用いたJQMDは前者に属する。本研究により、計算における時間刻みが各コードによる結果の差の主な原因であることが分かった。さらに、今後のJQMDの改良方針の策定に有益な知見を得ることができた。
Pellegrini, M.*; Herranz, L.*; Sonnenkalb, M.*; Lind, T.*; 丸山 結; Gauntt, R.*; Bixler, N.*; Morreale, A.*; Dolganov, K.*; Sevon, T.*; et al.
Proceedings of 18th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-18) (USB Flash Drive), p.1147 - 1162, 2019/08
The OECD/NEA Benchmark Study at the Accident of the Fukushima Daiichi NPS project (BSAF) has started in 2012 until 2018 as one of the earliest responses to the accident at Fukushima Daiichi NPS. The project addressed the investigation of the accident at Units 1, 2 and 3 by severe accident (SA) codes focusing on thermal-hydraulics, core relocation, molten core/concrete interaction (MCCI) and fission products release and transport. The objectives of BSAF were to make up plausible scenarios based primarily on SA forensic analysis, support the decommissioning and inform SA codes modeling. The analysis and comparison among the institutes have brought up vital insights regarding the accident progression identifying periods of core meltdown and relocation, reactor vessel (RV) and primary containment vessel (PCV) leakage/failure through the comparison of pressure, water level and CAMS measurement. The combination of code results and inspections has provided a picture of the current state of the debris distribution and plant state. All units present a large relocation of core materials and all of them present ex-vessel debris with units 1 and 3 showing evidences of undergoing MCCI. Uncertainties have been identified in particular on the time and magnitude of events such as corium relocation in RV and into cavity floor, RV and PCV rupture events. Main uncertainties resulting from the project are the large and continuous MCCI progression predicted by basically all the SA codes and the leak pathways from RV to PCV and PCV to reactor building and environment. The BSAF project represents a pioneering exercise which has set the basis and provided lessons learned not only for code improvement but also for the development of new related projects to investigate in details further aspects of the Fukushima Daiichi NPS accident.
Tang, C.*; Song, Q.*; Chang, C.-Z.*; Xu, Y.*; 大沼 悠一; 松尾 衛*; Liu, Y.*; Yuan, W.*; Yao, Y.*; Moodera, J. S.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 4(6), p.eaas8660_1 - eaas8660_6, 2018/06
被引用回数:34 パーセンタイル:83.64(Multidisciplinary Sciences)This work demonstrates markedly modified spin dynamics of magnetic insulator (MI) by the spin momentum-locked Dirac surface states of the adjacent topological insulator (TI). As the Bi concentration  is systematically tuned in 5-nm-thick (Bi
is systematically tuned in 5-nm-thick (Bi Sb
Sb )
) Te
Te TI films, the weight of the surface relative to bulk states peaks at
TI films, the weight of the surface relative to bulk states peaks at  = 0.32 when the chemical potential approaches the Dirac point. At this concentration, the Gilbert damping constant of the precessing magnetization in 10-nm-thick Y
= 0.32 when the chemical potential approaches the Dirac point. At this concentration, the Gilbert damping constant of the precessing magnetization in 10-nm-thick Y Fe
Fe O
O MI films in the MI/TI heterostructures is enhanced by an order of magnitude, the largest among all concentrations. In addition, the MI acquires additional strong magnetic anisotropy that favors the in-plane orientation with similar Bi concentration dependence. These extraordinary effects of the Dirac surface states distinguish TI from other materials such as heavy metals in modulating spin dynamics of the neighboring magnetic layer.
MI films in the MI/TI heterostructures is enhanced by an order of magnitude, the largest among all concentrations. In addition, the MI acquires additional strong magnetic anisotropy that favors the in-plane orientation with similar Bi concentration dependence. These extraordinary effects of the Dirac surface states distinguish TI from other materials such as heavy metals in modulating spin dynamics of the neighboring magnetic layer.
Zhang, Y.-X.*; Wang, Y,-J.*; Colonna, M.*; Danielewicz, P.*; 小野 章*; Tsang, M. B.*; Wolter, H.*; Xu, J.*; Chen, L.-W.*; Cozma, D.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 97(3), p.034625_1 - 034625_20, 2018/03
被引用回数:116 パーセンタイル:98.99(Physics, Nuclear)2017年4月に開催された国際会議Transport2017において、重イオン核反応モデルの国際的な比較が議論された。重イオン加速器の安全評価や宇宙飛行士の被ばく評価等で重要な役割を果たすため、世界中で重イオン核反応の様々な理論モデルが開発されている。本研究はモデル間の共通点と差異を明らかにし、各モデルの問題点を明らかにした。比較において、辺の長さが20fmの直方体に320個の中性子と320個の陽子をランダム配置し、それらが時間発展に伴って起こす散乱の回数や散乱時のエネルギーなどを計算する条件が設定された。また、結果以外にも、理論モデルを構成するアルゴリズムについても比較を行った。発表者は重イオン核反応モデルJQMD(JAERI Quantum Molecular Dynamics)を用いて計算を行い、世界で開発されている15の計算コードによる計算結果と比較した。コードアルゴリズムの比較では、JQMDは必ず陽子から 優先的に衝突確率を計算し、その後に中性子の衝突を計算するため、物理描像の妥当性が指摘された。一方、JQMDは他のモデルとほぼ同じ計算結果を出すことも判明した。衝突回数や運動量の計算値が平均から2倍以上乖離するモデルもある中で、JQMDは本計算条件で安定した性能を発揮することが確認された。
Ho, D. M. L.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; 大久保 綾子; Rameb ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; 片岡 修; et al.
ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; 片岡 修; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.353 - 363, 2018/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:18.26(Chemistry, Analytical)国際核鑑識作業グループが主催する第4回核鑑識共同試料分析演習には、過去最大の17か国からの参加があり、このうち7か国は初めての参加であった。本稿では、演習に初めて参加した5か国のラボラトリが、演習で実施した分析試料の準備および分析内容について情報を共有した。核鑑識共同試料分析演習は、各ラボラトリで確立した分析法のテスト、他の目的で確立した方法の核鑑識への適用化、分析技術の修練に非常に有用であることが確認された。また、演習実施後に開催されたレビュー会合によって、核鑑識シグネチャとその解釈に関する理解を深めることができた。