Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Izawa, Kazuhiko; Aoyama, Yasuo; Sono, Hiroki; Ogawa, Kazuhiko; Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-001, 40 Pages, 2007/02
A series of critical experiments is conducted in FY 2006 using a heterogeneous core of the Static Experiment Critical Facility (STACY) in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). In the experiment, the core is composed of uranyl nitrate solution ( U enrichment 6wt%) containing soluble poison (gadolinium) and 333 pins of uranium dioxide (
U enrichment 6wt%) containing soluble poison (gadolinium) and 333 pins of uranium dioxide ( U enrichment 5wt%) loaded at a latticepitch of 1.5cm. Prior to the experiment, the following neutronic characteristics were analyzed to assess safety of the core and operation parametor limits: criticality, reactivity and reactor shutdown margins. In the analyses, a Monte Carlo code, MVP, and a neutronics code system, SRAC, were used with an evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-3.3. From these analyses, it was confirmed that the reactor shutdown margins would comply with the safety criteria under all conditions of the fuel used in the experiments. Simplified formulas for criticality and reactivity were also evaluated based on the analyzed values which are utilized to confirm the operation parameter limits during operations of the core.
U enrichment 5wt%) loaded at a latticepitch of 1.5cm. Prior to the experiment, the following neutronic characteristics were analyzed to assess safety of the core and operation parametor limits: criticality, reactivity and reactor shutdown margins. In the analyses, a Monte Carlo code, MVP, and a neutronics code system, SRAC, were used with an evaluated nuclear data library, JENDL-3.3. From these analyses, it was confirmed that the reactor shutdown margins would comply with the safety criteria under all conditions of the fuel used in the experiments. Simplified formulas for criticality and reactivity were also evaluated based on the analyzed values which are utilized to confirm the operation parameter limits during operations of the core.
Fukuda, Yoshihiro; Saito, Yuji; Yokoya, Akinari; Teraoka, Yuden
JAEA-Technology 2007-002, 35 Pages, 2007/03
JAEA(Japan Atomic Energy Agency) have newly introduced refocusing toroidal mirrors to upgrade a surface chemistry and biophysical spectroscopy stations of BL23SU (JAEA Actinide Science) in SPring-8. We demonstrate significant improvements in the efficiency of experiments. We report on the detail of the systems.
Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Umeda, Masayuki; Beddingfield, D. H.*; Menlove, H. O.*; Yamashita, Kiyonobu
JAEA-Technology 2007-003, 24 Pages, 2007/02
As of the safeguards approach in the HTTR facility, an unattended spent fuel flow monitor (UFFM) was applied to carry out an item counting of spent fuel blocks. The UFFM is so designed and fabricated as to be the compact and unique monitor system to verify a movement of spent fuel blocks in "difficult to access" area and reduce inspection efforts. This system consists of two detector packages, electronics and computer. One package consists of two ionization chambers and a He-3 counter. The IAEA acceptance tests were performed and it was confirmed the followings: (1) All the detectors were functioning properly to measure a spent fuel block flow. (2) The time difference between detector signals was sufficient to determine the direction of the spent fuel blocks. (3) The UFFM was useful to carry out the item counting. The UFFM was approved as the IAEA safeguards equipment in the safeguards approach in the HTTR.
Yamagishi, Hideshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-004, 15 Pages, 2007/02
Two-dimensional position sensitive neutron detectors that have performances of a fast response and a very small spatial resolution are required for various neutron scattering experiments using high-intensity pulse-neutron sources in a high-intensity proton accelerator facility. We put forward the development of a micro-pixel gas chamber (MPGC) filled with helium-3 gas as the two-dimensional position sensitive neutron detector. The MPGC provides fast responses and very small signals and requires more than 500 signal channels. Therefore, development of an application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is essential for processing of multi-channel signals from the MPGC. Design and study of the ASIC was performed.
Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Aoki, Hiromichi; Haga, Takahisa; Nishizawa, Hidetoshi; Sonoda, Takashi; Sakazume, Yoshinori; Shimizu, Kaori; Niitsuma, Yasushi*; Shirahashi, Koichi; Inoue, Takeshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-005, 27 Pages, 2007/03
Analysis of the uranyl nitrate solution fuel is carried out at the analytical laboratory of NUCEF (Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Research Facility), which provides essential data for operation of STACY (Static Experiment Critical Facility), TRACY (Transient Experiment Critical Facility) and the fuel treatment system. Analyzed in FY 2005 were uranyl nitrate solution fuel samples taken before and after experiments of STACY and TRACY, samples for the preparation of uranyl nitrate solution fuel, and samples for nuclear material accountancy purpose. Also analyzed were the samples from raffinate treatment and its preliminary tests. The raffinate was generated, since FY 2000, during preliminary experiments on U/Pu extraction-pulification to fix the operation condition to prepare plutonium solution fuel to be used for criticality experiments at STACY. This report summarizes work related to the analysis and management of the analytical laboratory in the FY 2005.
Homma, Hiroyuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Kasahara, Seiji; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Hara, Teruo; Kato, Ryoma; Sakaba, Nariaki
JAEA-Technology 2007-006, 60 Pages, 2007/02
At the present time, we are alarmed by depletion of fossil energy and adverse effect of rapid increase in fossil fuel burning on environment such as climate changes and acid rain, because our lives depend still heavily upon fossil energy. It is thus widely recognized that hydrogen is one of important future energy carriers in which it is used without emission of carbon dioxide greenhouse gas and atmospheric pollutants and that hydrogen demand will increase greatly as fuel cells are developed and applied widely in the near future. To meet massive demand of hydrogen, hydrogen production from water utilizing nuclear, especially by thermochemical water-splitting Iodine-Sulphur (IS) process utilizing heat from High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs), offers one of the most attractive zero-emission energy strategies and the only one practical on a substantial scale. However, to establish a technology based for the HTGR hydrogen production by the IS process, we should close several technology gaps through R&D with the High-Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), which is the only Japanese HTGR built and operated at the Oarai Research & Development Centre of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). We have launched design studies of the IS process hydrogen production system coupled with the HTTR (HTTR-IS system) to demonstrate HTGR hydrogen production. In designing the HTTR-IS system, it is necessary to consider preventive and breakdown maintenance against accidents occurred in the IS process as a chemical plant. This report describes case study on chemical plant accidents relating to the IS process plant and shows a proposal of accident protection measures based on above case study, which is necessary for flow-sheet design of the HTTR-IS System.
Fukuda, Yoshihiro; Takeda, Yukiharu; Okane, Tetsuo; Saito, Yuji; Kobayashi, Keisuke*
JAEA-Technology 2007-007, 23 Pages, 2007/03
We have introduced a "Nonstop absorption measurement system" into the XMCD station of BL23SU at SPring-8. This system allows us to shorten the measuring time by about 1/10 in comparison to conventional one. We report on the detail of the system.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Ida, Mizuho; Shimizu, Katsusuke*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-008, 28 Pages, 2007/03
This report describes results of thermo-structural analysis of a backwall in IFMIF lithium target performed during FY 2003-2006. The IFMIF is an accelerator-based intense neutron source for testing candidate materials for fusion reactors. Intense neutrons are emitted inside the Li flow through a backwall. The backwall is made of 316L stainless steel or RAFM. Since the backwall is operating under a severe neutron irradiation of 50 dpa/year and a maximum nuclear heating rate of 25 W/cm , thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Thermal stress was calculated using the ABAQUS code. In a case of the 316L stainless steel backwall, the maximum thermal stress was beyond the permissible stress. On the other hand, in a case of the F82H backwall, a maximum thermal stress was 289 MPa below the permissible stress (455 MPa). Therefore, F82H is recommended as the backwall material.
, thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Thermal stress was calculated using the ABAQUS code. In a case of the 316L stainless steel backwall, the maximum thermal stress was beyond the permissible stress. On the other hand, in a case of the F82H backwall, a maximum thermal stress was 289 MPa below the permissible stress (455 MPa). Therefore, F82H is recommended as the backwall material.
Ozawa, Takayuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-009, 18 Pages, 2007/03
The increase of linear power and burn-up is considered as one of measures for the utility of fast reactor in future, and then the application of annular fuels is under consideration. In this study, we developed the probabilitsic code BORNFREE-CEPTAR code to develop the reasonable design method for annular fuels. As the results of probability evaluation of fuel melting at the transient, the melting probability for annular fuels was estimated to be approximately two figures lower than that for solid fuels, and the remarkable decrease of melting probability was seen in the estimation results for solid fuels. On the other hand, the results for annular fuels indicated that this effect was comparably small. In addition, the permissive linear power for annular fuels tended to enhance from that for solid fuels under the similar fuel melting probability condition. This indicated the possibility of higher linear power operation for high-density annular fuels than low-density solid fuels.
Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Ozawa, Takayuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-010, 44 Pages, 2007/03
We developed MOX Fuel Database, which included valuable data from several irradiation tests in FUGEN and Halden reactor, for help of LWR MOX use. This database includes the data of fabrication and irradiation, and the results of post-irradiation examinations for seven fuel assemblies, i.e. P06, P2R, E03, E06, E07, E08 and E09, irradiated in FUGEN. The highest pellet peak burn-up reached  48 GWd/t in MOX fuels, of which the maximum plutonium content was
48 GWd/t in MOX fuels, of which the maximum plutonium content was  6 wt%, irradiated in E09 fuel assembly without any failure. Also the data from the instrumented MOX fuels irradiated in HBWR to study the irradiation behavior of BWR MOX fuels under the steady state condition (IFA-514/565 and IFA-529), under the load-follow operation condition (IFA-554/555) and under the transit condition (IFA-591) are included in this database. The highest assembly burn-up reached
6 wt%, irradiated in E09 fuel assembly without any failure. Also the data from the instrumented MOX fuels irradiated in HBWR to study the irradiation behavior of BWR MOX fuels under the steady state condition (IFA-514/565 and IFA-529), under the load-follow operation condition (IFA-554/555) and under the transit condition (IFA-591) are included in this database. The highest assembly burn-up reached  56 GWd/t in IFA-565 steady state irradiation test, and the maximum linear power of MOX fuel rods was 58.3-68.4 kW/m without any failure in IFA-591 ramp test. In addition, valuable instrument data, i.e. cladding elongation, fuel stack elongation, fuel center temperature and rod inner pressure were obtained from IFA-554/555 load-follow test.
56 GWd/t in IFA-565 steady state irradiation test, and the maximum linear power of MOX fuel rods was 58.3-68.4 kW/m without any failure in IFA-591 ramp test. In addition, valuable instrument data, i.e. cladding elongation, fuel stack elongation, fuel center temperature and rod inner pressure were obtained from IFA-554/555 load-follow test.
Ochs, M.*; Saito, Yoshihiko; Kitamura, Akira; Shibata, Masahiro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Yui, Mikazu
JAEA-Technology 2007-011, 342 Pages, 2007/03
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed the sorption database (SDB) for bentonite and rocks in order to assess the retardation property of important radioactive elements in natural and engineered barriers in the H12 report. The database includes distribution coefficient (K ) of important radionuclides. The K
) of important radionuclides. The K values in the SDB are about 20,000 data. The SDB includes a great variety of K
values in the SDB are about 20,000 data. The SDB includes a great variety of K and additional key information from many different literatures. Accordingly, the following classification guideline and classification system were developed in order to evaluate the reliability of each K
and additional key information from many different literatures. Accordingly, the following classification guideline and classification system were developed in order to evaluate the reliability of each K value (Th, Pa, U, Np, Pu, Am, Cm, Cs, Ra, Se, Tc on bentonite). The reliability of 3740 K
value (Th, Pa, U, Np, Pu, Am, Cm, Cs, Ra, Se, Tc on bentonite). The reliability of 3740 K values are evaluated and categorized.
values are evaluated and categorized.
Baba, Shinichi; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Matsui, Yoshinori; Ishihara, Masahiro; Sawa, Kazuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2007-012, 142 Pages, 2007/03
The creep test under irradiation with thermal gradient for the cylindrical carbon fiber reinforced carbon composites (c/c composite) are carried out in the Japan Material Testing Reactor (JMTR). This report described 4-items; first item is design/evaluation of the capsule for the irradiation test, second is before irradiation measurements for the residual strain due to manufactured cylindrical c/c composite, and third is also before irradiation measurements of the distance between 2-holes of predrilled in the specimen and last item is examination of analysis for the irradiation creep with thermal gradient by VIENUS Code.
Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Ozawa, Takayuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-013, 38 Pages, 2007/03
The following generation MONJU core fuel is considered using the high density solid pellet. Although the fuel design code "CEPTAR" was developed for annular fuel pellet, CEPTAR code was not verified with the data of high density solid pellet. In this study, CEPTAR code was verified with irradiation data of JOYO Mk-II driver fuel that used high density solid pellet. To estimate irradiation behavior of JOYO Mk-II driver fuel, the following new equations were added to CEPTAR code; The swelling equation and irradiation creep equation of PNC316. The pellet swelling equation evaluated with the PIE data of JOYO Mk-II driver fuel. As a result of verification by using the irradiation data of JOYO Mk-II driver fuel, the calculated values with CEPTAR code were in agreement with the observed values from the result of PIEs up to pellet peak burn-up  76,000MW d/t.
76,000MW d/t.
Tochio, Daisuke; Watanabe, Shuji; Motegi, Toshihiro; Kawano, Shuichi; Kameyama, Yasuhiko; Sekita, Kenji; Kawasaki, Kozo
JAEA-Technology 2007-014, 62 Pages, 2007/03
The rise-to-power test of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) was begun in April 2000. The reactor thermal power of 30 MW, which is the maximum thermal power of the HTTR, and the reactor outlet coolant temperature of 850 C in normal operation was achieved in middle of December 2001. After that reactor thermal power of 30 MW a reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950
C in normal operation was achieved in middle of December 2001. After that reactor thermal power of 30 MW a reactor outlet coolant temperature of 950 C was achieved in the final rise-to-power test at April 2004. After receiving the operation permit, the safety demonstration tests were conducted to demonstrate inherent safety features of the HTGRs. This paper summarizes the HTTR operating experiences for five years since rise-to-power test that were catalogued into three categories, (1) Operating experience pertaining to new gas cooled reactor design, (2) Operating experience for improvement of the performance, (3) Operating experience due to fail of system and components.
C was achieved in the final rise-to-power test at April 2004. After receiving the operation permit, the safety demonstration tests were conducted to demonstrate inherent safety features of the HTGRs. This paper summarizes the HTTR operating experiences for five years since rise-to-power test that were catalogued into three categories, (1) Operating experience pertaining to new gas cooled reactor design, (2) Operating experience for improvement of the performance, (3) Operating experience due to fail of system and components.
Yagyu, Junichi; Sasajima, Tadayuki; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Kawamata, Yoichi
JAEA-Technology 2007-015, 27 Pages, 2007/03
The feedback control of the plasma position and shape based on signals of magnetic probes is performed on JT-60. The fabrication cost of these magnetic probes is very high. Therefore, the cost reduction is required for the use in a next device. On the other hand, the magnetic field measurement in three axial directions with the advanced technology (AT) probes is simultaneously made on LHD of NIFS. The AT-probe has been developed at a low fabrication cost and in compact size and light weight. The possibility of application of the AT-probe in a Tokamak device (JT-60U) has been investigated in collaboration between JAEA and NIFS. We designed and fabricated the casing and interface for the AT-probe, and installed it under the first wall of JT-60U. A comparison of output signals between the installed AT-probe and a existing magnetic probe was made. Tests have been carried out to evaluate the vibration resistance and the radioactive resistance through about two thousand shots with high performance plasmas including one hundred disruption shots in JT-60U. As a result, the AT-probe has a good performance and an enough usable prospect in environment of the Tokamak device.
Miyashita, Makoto; Yutani, Toshiaki*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-016, 62 Pages, 2007/03
This report describes investigation on structure of a high neutron flux test module (HFTM) for the International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facilities (IFMIF). The HFTM is aimed for neutron irradiation of a specimen in a high neutron flux domain of the test cell for irradiation ground of IFMIF. We investigated the overall structure of the HFTM that was able to include specimens in a rig and thermocouple arrangement, an interface of control signal and support structure. Moreover, pressure and the amount of the bend in the module vessel (a rectangular section pressure vessel) were calculated. The module vessel did a rectangular section from limitation of a high neutron flux domain. Also, we investigated damage of thermocouples under neutron irradiation, which was a temperature sensor of irradiation materials temperature control demanded high precision. Based on these results, drawings on the HTFM structure.
Ishikuro, Yasuhiro
JAEA-Technology 2007-017, 91 Pages, 2007/03
JRR-4, a light-water-moderated and cooled, swimming pool type research reactor using high-enriched uranium plate-type fuels had been operated from 1965 to 1996. In order to convert to low-enriched -uranium-silicied fuels, modification work had been carried out for 2 years, from 1996 to 1998. After the modification, the first criticality of low-enriched-uranium-silicied core was achieved on 14th July 1998, and the operation has been carried out since 6th October 1998. In this report, the core characteristics have been analyzed with SRAC code system. SRAC was verified compared with the experiment value. The core characteristics were analyzed such as excess reactivity, control rod worth, neutron flux distribution, the peaking factor of initial core, as well as excess reactivity of burn -up core. As a result, in the initial core, against the experiment value, excess reactivity was an error of about 1% k/k, the peaking factor was an error of about 1%, control rod worth was an error of about 14%. SRAC code was confirmed that it was able to evaluate with accuracy in low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuel.
k/k, the peaking factor was an error of about 1%, control rod worth was an error of about 14%. SRAC code was confirmed that it was able to evaluate with accuracy in low-enriched-uranium-silicied fuel.
Yokoo, Kenji; Horiguchi, Hironori; Yagi, Masahiro; Nagadomi, Hideki; Yamamoto, Kazuyoshi; Sasajima, Fumio; Oyama, Koji; Ishikuro, Yasuhiro; Sasaki, Tsutomu; Hirane, Nobuhiko; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2007-018, 104 Pages, 2007/03
Reactor operation training using JRR-4 (Japan Research Reactor No.4) was started in FY 1969, one of the curriculums of Nuclear Technology and Education Center (NuTEC). After that, the program was updated and carried out for reactor operation training, control rod calibration, and measurement of various kind of characteristics. JRR-4 has been contributed for nuclear engineer training that is over 1,700 trainees from bother domestic and foreign countries. JRR-4 can be used for experiment from zero power to 3500kW, and the trainees can make experience to operate the reactor from start up to shut down, not only zero-power experiments (critical approach, control rod calibration, reactivity measurement, etc.) but also other experiments under high power operation (xenon effect, temperature effects, reactor power calibration, etc.). This report is based on various kinds of guidance texts using for training, and collected for operation and experiments for reactor physics.
Nozawa, Yukio; Koya, Toshio; Sekino, Hajime
JAEA-Technology 2007-019, 23 Pages, 2007/03
However, RHL is the one of target "A midterm decommissioning plan of Tokai Research Establishment" as the rationalization program for a decrepit facility in JAERI. This program has been taking over in JAEA. Therefore, all PIEs had been finished in March 2003 and the destruction works of hot cells have been started. The contents of these works are to remove out the apparatus from the hot cell and to transfer the irradiated samples and disposal of radioactive waste. The authorization work of the destruction program for regulation committee is in progress. The 18 lead cells had been destructed. The examinations performed in RHL will be succeeding to the RFEF and the WASTEF. The partial area of RHL facility will be used for the temporary storage of un- irradiated fuel samples used for our previous research works and radioactive device generated in proton accelerator facility (called J-PARC which is under constructing in Tokai site).
Sato, Takahiko
JAEA-Technology 2007-020, 18 Pages, 2007/03
In the MOX fuels irradiated in FBR, the enhanced concentration of plutonium and americium together with fuel restructuring caused by the steep temperature gradient in the radial direction is observed around the central void. The atoms transport caused by thermal diffusion and the pore migration toward the pellet center due to evaporation-condensation is considered as Pu redistribution mechanism. Since the redistribution mechanism for Am is expected to be similar to that for Pu, assuming that their redistribution would be caused by the similar mechanism, we developed the redistribution model for Pu and Am. In order to verify the redistribution model for Pu and Am, the computed radial distribution of Pu and Am concentration was compared with the results of SXMA measurements for MOX fuels, of which initial Am concentration was 0.9 wt%, irradiation in JOYO. As a result, it was confirmed that the computed radial distribution of Pu and Am would be in good agreement with the observed one.
Kurokochi, Naohiro; Takada, Shoji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-021, 72 Pages, 2007/03
In order to acquire the fundamental data which is necessary for the approximation model construction of rotor which is used in the design of control system of the magnetic bearing which supports the gas turbine generator for GTHTR300, this paper shows 3 dimensional finite element analysis, the bearing rigid dependency of rotor eigen value was made clear, and axial direction amplitude distribution was made clear. In addition, it made also the higher-order bending vibration eigen value of each bearing rigidity clear. With the comparison and the examination of this numerical analysis result and the test result, it could verify propriety. This numerical analysis model was applied to GTHTR300, rotor eigen value and axial direction amplitude distribution was estimated. It is the plan that this numerical analysis result is made to reflect on the construction of the beam model that is the approximate model of rotor which is for the design of control system of the magnetic bearing indispensable.
Kato, Michio; Hayashi, Koji; Aita, Hideki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Takada, Shoji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-022, 209 Pages, 2007/03
The mock-up test facility was fabricated to investigate performance of the steam generator for mitigation of the temperature fluctuation of helium gas and transient behavior of the hydrogen production system for HTTR and to obtain experimental data for verification of a dynamic analysis code. The test facility has an approximate hydrogen production capacity of 120Nm /h and the steam reforming process of methane; CH
/h and the steam reforming process of methane; CH +H
+H O=3H
O=3H +CO, was used for hydrogen production of the test facility. An electric heater was used as a heat source instead of the reactor in order to heat helium gas up to 880
+CO, was used for hydrogen production of the test facility. An electric heater was used as a heat source instead of the reactor in order to heat helium gas up to 880  C (4MPa) at the chemical reactor inlet which is the same temperature as the HTTR hydrogen production system. Fabrication of the test facility was completed in February in 2002, and seven cycle operations were carried out from March in 2002 to December in 2004. This report describes the structure and main specifications of the test facility.
C (4MPa) at the chemical reactor inlet which is the same temperature as the HTTR hydrogen production system. Fabrication of the test facility was completed in February in 2002, and seven cycle operations were carried out from March in 2002 to December in 2004. This report describes the structure and main specifications of the test facility.
Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Kazawa, Minoru; Hanada, Masaya; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
JAEA-Technology 2007-023, 41 Pages, 2007/03
In JT-60 Super Advanced (JT-60 SA) where the first plasma will be in 2014, D beams of 10 MW are designed to be injected for 100 s. The negative-ion-based neutral beam injection (N-NBI) system in JT-60U will be upgraded from existing JT-60U N-NBI system while the modification of existing components should be minimized. The feasibility on the further long pulse operation of the existing beamline components in the JT-60U N-NBI system, which has successfully injected 3.2 MW for 21 s, has been studied. The thermal characteristic of the beamline components during long pulse operation was estimated by a three-dimension analysis code (AMPS). As the result, it is found that most of the beamline components except for the 4th beam limiter without water cooling and a plasma grid and acceleration grids in the negative ion source are to be available without modification in the JT-60 SA N-NBI system. For the 4th beam limiter, the water cooling is required to withstand the power loading. For the acceleration grids, the power loading of the grounded grid should be reduced to a half of the present value to realize a 10 MW injection for 100 s.
beams of 10 MW are designed to be injected for 100 s. The negative-ion-based neutral beam injection (N-NBI) system in JT-60U will be upgraded from existing JT-60U N-NBI system while the modification of existing components should be minimized. The feasibility on the further long pulse operation of the existing beamline components in the JT-60U N-NBI system, which has successfully injected 3.2 MW for 21 s, has been studied. The thermal characteristic of the beamline components during long pulse operation was estimated by a three-dimension analysis code (AMPS). As the result, it is found that most of the beamline components except for the 4th beam limiter without water cooling and a plasma grid and acceleration grids in the negative ion source are to be available without modification in the JT-60 SA N-NBI system. For the 4th beam limiter, the water cooling is required to withstand the power loading. For the acceleration grids, the power loading of the grounded grid should be reduced to a half of the present value to realize a 10 MW injection for 100 s.
Usui, Katsutomi; Noto, Katsuya; Kawai, Mikito; Oga, Tokumichi*; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
JAEA-Technology 2007-024, 32 Pages, 2007/03
The JT-60 positive ion-based NBI (P-NBI) system is required to extend the pulse duration from 30 s to 100 s for JT-60SA, which is the modification of JT-60U to a fully superconducting coil tokamak. The JT-60SA NBI system will have 12 P-NBI units, each of which will inject 2 MW at 85 keV. The present power supply system is to be upgraded to operate for 100 s with minimum modification. The modification of the power supply has been studied in view of the protective characteristic and the thermal capacities of main power supply components. The design study is based on the results of the first modification of 30 s operation which was done in 2003. It has been confirmed that the long pulse operation of 100 s is possible by with partial modification of the power supply components such as enhancement of the water-cooled resistance of the acceleration power supply.
Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Kazawa, Minoru; Komata, Masao; Kawai, Mikito; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Otsuki, Shinichi*; Sato, Fujio*
JAEA-Technology 2007-025, 37 Pages, 2007/03
The modification of the beamline components for JT-60SA NBI heating system has been preliminarily studied by means of three-dimensional Computer Aided Design (CAD) technique, such as the connection between positive ion-based NBI (P-NBI) port and the cryostat of JT-60SA vacuum vessel, an additional magnetic shielding plate, the down-shift of the negative ion-based NBI (N-NBI), and disassembly of the present NBI system. The length of drift duct for JT-60SA is to be shorted because the cryostat is to be inserted between the JT-60SA vacuum vessel and the P-NBI beamline. It is found that the removal of the fast shutter and a newly designed connection flange made of FRP is a solution to keep the same function in the shorten drift duct. The position interference with the 3D CAD indicates that the available space between the neutralizer cell and the ion tank is 30 mm, which is enough space to install a thick mild steel to avoid the magnetic saturation. On the N-NBI, the down-shift of 0.6 m is realized by shorting the basement of ion tank, reversing the shaft of the movable calorimeter and exchanging the support structure of the neutralizer cell. Moreover, the minimum dissection components and the disassembly procedure have been proposed to effectively disassemble the present NBI system.
Honda, Atsushi; Okano, Fuminori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Oshima, Katsumi; Numazawa, Susumu*; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
JAEA-Technology 2007-026, 19 Pages, 2007/03
The modification of the JT-60U to a fully superconducting coil tokamak, JT-60SA (Super Advanced), has been programmed as the satellite devise for the ITER (International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor) and as the national centralized tokamak. The present positive-ion-based NBI system (P-NBI), which has been operated for 20 years and will be the main heating system on JT-60SA, is required to manage the long pulse injection extended from 30 s to 100 s at the power of 24 MW with 12 units. To realize such a requirement, the original control system handling more than 4000 digital data is to be fully remodeled. Design study of the new control system has been conducted from viewpoint of market availability, system extensibility, cost-effectiveness and independent development in programming. It has been concluded that a distributed control system using PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) could be applied to the large-scale control system for 100-s operations with satisfaction of the evaluation viewpoints.
Kikuchi, Katsumi; Akino, Noboru; Hanada, Masaya; Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Kamada, Masaki; Kawai, Mikito; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; Noto, Katsuya; Usui, Katsutomi
JAEA-Technology 2007-027, 17 Pages, 2007/03
Voltage holding capability of the 500 kV accelerator in the JT-60 negative ion source that is one of the key issues for high performance of the JT-60 negative-ion-based NBI system was investigated. The achieved voltage holding capabilities with and without the beam acceleration were 400 kV and 455 kV, respectively. To understand a poor voltage holding capability of the negative ion source, correlation between the voltage holding capability and the light emitted inside the ion source was carefully examined. The acceleration voltage was stably applied at  400kV, where the light intensity was almost zero. Increasing the acceleration voltage beyond 400 kV, the voltage holding become very unstable where the light intensity increases in proportion to the acceleration voltage. The spectroscopy measurement showed that the light spectrum was a broad wavelength of 360 - 500 nm peaked at 420 nm. There was no line spectrum due to the gas discharge such as hydrogen, oxygen, carbon. From these results, it is seemed that the origin of the light emission is a cathode luminescence from the FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) insulator in JT-60 negative ion source due to the electron impact. Moreover, breakdown phenomena at inside and outside of the ion source were examined by using photo-multipliers with fast data acquisition system. When the breakdown occurred inside the ion source, the breakdowns sequentially occurred at the spark gap switches outside of the ion source, which protect the FRP insulator from the flashover on its surface. Once the spark gap was turned on after the breakdown inside the ion source, the breakdowns at the spark gap occurred at lower voltage than the normal set value when the high voltage was applied again after
400kV, where the light intensity was almost zero. Increasing the acceleration voltage beyond 400 kV, the voltage holding become very unstable where the light intensity increases in proportion to the acceleration voltage. The spectroscopy measurement showed that the light spectrum was a broad wavelength of 360 - 500 nm peaked at 420 nm. There was no line spectrum due to the gas discharge such as hydrogen, oxygen, carbon. From these results, it is seemed that the origin of the light emission is a cathode luminescence from the FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic) insulator in JT-60 negative ion source due to the electron impact. Moreover, breakdown phenomena at inside and outside of the ion source were examined by using photo-multipliers with fast data acquisition system. When the breakdown occurred inside the ion source, the breakdowns sequentially occurred at the spark gap switches outside of the ion source, which protect the FRP insulator from the flashover on its surface. Once the spark gap was turned on after the breakdown inside the ion source, the breakdowns at the spark gap occurred at lower voltage than the normal set value when the high voltage was applied again after  70 ms interval. This result indicates that the voltage holding capability was limited by the spark gap switches in this operational sequence.
70 ms interval. This result indicates that the voltage holding capability was limited by the spark gap switches in this operational sequence.
Muramatsu, Yasuyuki; Okawara, Masami; Suzuki, Toshiyuki; Shibata, Isao; Fuketa, Toyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-028, 47 Pages, 2007/03
As a part of Advanced LWR Fuel Performance and Safety Research Program, irradiation experiments are conducted with high burnup uranium dioxide fuel and uranium-plutonium mixed oxide (MOX) fuel in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor. When an irradiation capsule is transferred and loaded to the reactor core, a capsule loader is used. The previous capsule loader, however, could not have enough shielding capability against neutron flux from high burnup MOX fuel. In order to fulfill the requirement and to handle a new high pressure water capsule, accordingly, a type-B capsule loader was developed.
Suto, Shinya; Nakabayashi, Hiroki; Yao, Kaoru*
JAEA-Technology 2007-029, 73 Pages, 2007/03
The cooling examination was executed by using the simulated fuel assembly to obtain the basic data of the most effective cooling system in the laser disassembling process of the spent fuel assembly of prototype fast breeder reactor "Monju". As a result, the following have been understood. (1) Before the laser disassembling (there is not any duct tube cutting), it is possible to cool enough by the amount of the wind of 20m /h or more flowing from the handling head side. (2) After the laser disassembling begins (duct tube is cut), 1kW or more of the heat generation cannot be cooled by ventilation from the handling head side. (3) Cooling by the flow across fuel pin is required during laser disassembling. The basic data of the cooling system was obtained from these examination results. However, for cooling across fuel pin during the laser disassembling, it is necessary to examine shape of the side cooling nozzle, spraying angle, and flow velocity at the nozzle exit, etc. enough.
/h or more flowing from the handling head side. (2) After the laser disassembling begins (duct tube is cut), 1kW or more of the heat generation cannot be cooled by ventilation from the handling head side. (3) Cooling by the flow across fuel pin is required during laser disassembling. The basic data of the cooling system was obtained from these examination results. However, for cooling across fuel pin during the laser disassembling, it is necessary to examine shape of the side cooling nozzle, spraying angle, and flow velocity at the nozzle exit, etc. enough.
Yamazaki, Dai; Moriai, Atsushi; Tamura, Itaru; Maruyama, Ryuji; Ebisawa, Toru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Soyama, Kazuhiko
JAEA-Technology 2007-030, 21 Pages, 2007/03
A new neutron reflectometer "SUIREN" has been developed and started its operation at the research reactor JRR-3 of JAEA in 2006. SUIREN (Apparatus for Surface and Interface investigations with Reflection of Neutrons) provides monochromatic neutron beam with wavelength of 3.8  and vertical sample geometry, which is suitable for studies on interfaces involving solid layers of soft materials, magnetic materials, neutron mirrors and many other things. Collimated neutron intensity is about 2.1
and vertical sample geometry, which is suitable for studies on interfaces involving solid layers of soft materials, magnetic materials, neutron mirrors and many other things. Collimated neutron intensity is about 2.1 10
10
 2.6
2.6 10
10 n/s/cm
n/s/cm with =0.08 deg at the sample position. Background is as low as 4.5
with =0.08 deg at the sample position. Background is as low as 4.5 10
10 n/s when a local beam shutter is closed. A demonstration experiment showed that specular reflectivity of a silicon substrate of 3 inches in diameter can be measured down to 10
n/s when a local beam shutter is closed. A demonstration experiment showed that specular reflectivity of a silicon substrate of 3 inches in diameter can be measured down to 10 over 0
over 0  Qz
Qz  0.22
0.22 
 in 27 hours. This paper describes the beam-line and components of the SUIREN reflectometer, some results of test measurements and future plans.
in 27 hours. This paper describes the beam-line and components of the SUIREN reflectometer, some results of test measurements and future plans.
Shibata, Akira; Takada, Fumiki
JAEA-Technology 2007-031, 24 Pages, 2007/03
The fracture toughness which represents resistance for brittle or ductile fracture is one of the most important material property concerning linear and non-linear fracture mechanics analyses. In order to respond to needs of collecting data relating to fracture toughness of pressure vessel and austenitic stainless steels, fracture toughness test for irradiated materials has been performed in JMTR Hot Laboratory. On the other hand, there has been no computer program for analysis of fracture toughness using the test data obtained from the test apparatus installed in the hot cell. Therefore, only load-displacement data have been provided to users to calculate fracture toughness of irradiated materials. Recently, request of analysis of fracture toughness have been increased. Thus a computer program, which calculates the amount of the crack extension, the compliance and the fracture toughness from the data acquired from the test apparatus installed in the hot cell, has been developed. In the program unloading elastic compliance method is applied based on ASTM E1820-01. Through the above development, the request for the fracture toughness analysis can be satisfied and the fracture toughness of irradiated test specimens can be provided to users.
Kakudate, Satoshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-032, 18 Pages, 2007/05
Remote maintenance of the ITER blanket composed of about 400 modules in the vessel is required by a maintenance robot due to high  radiation of
radiation of  500Gy/h in the vessel. A concept of rail-mounted vehicle manipulator system has been developed to apply to the maintenance of the ITER blanket. The most critical issue of the vehicle manipulator system is the feasibility of the deployment of the articulated rail composed of eight rail links into the donut-shaped vessel without any driving mechanism in the rail. To solve this issue, a new driving mechanism and procedure for the rail deployment has been proposed, taking account of a repeated operation of the multi-rail links deployed in the same kinematical manner. The new driving mechanism, which is deferent from those of a usual articulated arm equipped with actuator in the every joint for movement, is composed of three mechanisms. To assess the feasibility of the kinematics of the articulated rail for rail deployment, a kinematical model composed of three rail links related to a cycle of the repeated operation for rail deployment was considered. The determinant det J of the Jacobian matrix J was solved so as to estimate the existence of a singular point of the transformation during rail deployment. As a result, it is found that there is a singular point due to det J =0. To avoid the singular point of the rail links, a new location of the second driving mechanism and the related rail deployment procedure are proposed. As a result of the rail deployment test based on the new proposal using a full-scale vehicle manipulator system, the respective rail links have been successfully deployed within 6 h less than the target of 8 h in the same manner of the repeated operation under a synchronized cooperation among the three driving mechanisms. It is therefore concluded that the feasibility of the rail deployment of the articulated rail composed of simple structures without any driving mechanism has been demonstrated.
500Gy/h in the vessel. A concept of rail-mounted vehicle manipulator system has been developed to apply to the maintenance of the ITER blanket. The most critical issue of the vehicle manipulator system is the feasibility of the deployment of the articulated rail composed of eight rail links into the donut-shaped vessel without any driving mechanism in the rail. To solve this issue, a new driving mechanism and procedure for the rail deployment has been proposed, taking account of a repeated operation of the multi-rail links deployed in the same kinematical manner. The new driving mechanism, which is deferent from those of a usual articulated arm equipped with actuator in the every joint for movement, is composed of three mechanisms. To assess the feasibility of the kinematics of the articulated rail for rail deployment, a kinematical model composed of three rail links related to a cycle of the repeated operation for rail deployment was considered. The determinant det J of the Jacobian matrix J was solved so as to estimate the existence of a singular point of the transformation during rail deployment. As a result, it is found that there is a singular point due to det J =0. To avoid the singular point of the rail links, a new location of the second driving mechanism and the related rail deployment procedure are proposed. As a result of the rail deployment test based on the new proposal using a full-scale vehicle manipulator system, the respective rail links have been successfully deployed within 6 h less than the target of 8 h in the same manner of the repeated operation under a synchronized cooperation among the three driving mechanisms. It is therefore concluded that the feasibility of the rail deployment of the articulated rail composed of simple structures without any driving mechanism has been demonstrated.
Hirose, Akira; Wada, Shigeru; Kusunoki, Tsuyoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-033, 87 Pages, 2007/03
Neutron-Transmutation-Doped Silicon Semiconductor (NTD-Si) has good properties for the power device. In recent years the demand of NTD-Si has increased significantly due to mass production of hybrid-cars. We have been investigated the expansion technology of the NTD-Si productivity using the research reactors JRR-3, JRR-4 and JMTR of JAEA in order to meet the demand. The conceptual design of the automated silicon irradiation device using the JRR-3 Uniformity Irradiation System was carried out as one of the effective measures. After a Si ingot is irradiated once, it is turned over manually and irradiated again in order to irradiate the ingot uniformly. With the conventional equipment, it is necessary to wait radioactivity of the ingot decrease less than the permissible level with holding the ingot in the irradiation equipment. The waiting procedure takes 48 hours or more. Because the automated NTD-Si irradiation device reduces the manual operation process and the waiting time, it is effective to shorten the waiting period. This report is concerning the conceptual design of the automated silicon irradiation device for the JRR-3 Uniformity Irradiation System.
Totsuka, Toshiyuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-034, 41 Pages, 2007/05
The Man-Machine Interfacing System for JT-60 remote experiment was developed using the Java language which doesn't depend to a computer. The purpose is construction of environment that can do participation of experiment on JT-60 via the network from an outside. This report deals with the technical devices in this development and the equipped functions.
Matsumoto, Toshiyuki; Yoshida, Eiichi; Suzuki, Shigeaki*; Yasu, Tomohisa*
JAEA-Technology 2007-035, 35 Pages, 2007/03
In the future, a large amount of sodium (Na) containing radioactive wastes must be processed at the time of final shutdown/ decommissioning of FBR plant or radioactive sodium facilities in Japan. Therefore, its disposal technology should be established in consideration of economical efficiency, safety, etc. In the existing technology, since the method of processing sodium directly into radioactive waste is not established, conversion of sodium into chemically stable material can be considered. Then, basic experiments in which sodium was injected at 10 kg/h into solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) were conducted, with the improved Sodium Conversion Test Apparatus (SCOT). The conditions of NaOH solution were temperature of 100 C, and NaOH concentration of 45-50 wt%. Consequently, the injected sodium reacted completely in the NaOH solution, and NaOH temperature, NaOH concentration, etc. were controlled properly. It validated that the system of this apparatus was appropriate. Moreover, in case sodium is injected into NaOH solution, a nozzle blockades sometimes. Therefore, the methods to eliminate the cause of nozzle blockage were examined.
C, and NaOH concentration of 45-50 wt%. Consequently, the injected sodium reacted completely in the NaOH solution, and NaOH temperature, NaOH concentration, etc. were controlled properly. It validated that the system of this apparatus was appropriate. Moreover, in case sodium is injected into NaOH solution, a nozzle blockades sometimes. Therefore, the methods to eliminate the cause of nozzle blockage were examined.
Ishii, Kazuhiro; Seki, Masami; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Hiranai, Shinichi; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Sato, Fumiaki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Yokokura, Kenji
JAEA-Technology 2007-036, 30 Pages, 2007/07
The lower hybrid (LH) antenna in JT-60U has interaction with plasmas because it should be close to them in order to inject effectively radio frequency (RF) power into them. As a result, it has been a serious problem that the antenna mouth made of stainless steels was damaged due to excessive heat loads of plasmas and RF breakdowns. To solve the problem, a heat-resistant LH antenna was developed tipping carbon grills with fairly high heat resistance on the antenna mouth, and therefore reduction in damages on the mouth was expected. Power injection into plasmas was firstly performed with the heat-resistant antenna. RF conditioning was done carefully in the initial phase because RF breakdown due to outgassing from the grills might be occurred. After sufficient degassing was done through RF conditioning, RF power of about 1.6 MW  10 sec injection was successfully injected to plasmas. Moreover it was demonstrated that it had comparably high plasma current drive capability (about 1.6
10 sec injection was successfully injected to plasmas. Moreover it was demonstrated that it had comparably high plasma current drive capability (about 1.6  10
10 A/W/m
A/W/m ), required as a current drive LH antenna.
), required as a current drive LH antenna.
Ichige, Hisashi; Honda, Masao; Sasaki, Shunichi; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Matsuzawa, Yukihiro; Haga, Saburo; Ishige, Yoichi
JAEA-Technology 2007-037, 16 Pages, 2007/07
In JT-60U, pellet injector has been developed for improvement of density controllability and long operation duration consistent with a long pulse discharge ( 65 s) started from FY2003. The injection frequency and operation duration were limited by extrusion speed and volume of the piston type pellet extruder, respectively, in the previous system. The screw type pellet extruder made in Russian company was newly installed in the system, which can continuously extrude the pellet at high speed and has been used in other fusion devices. After parts of the pellet injector system moved from JT-60 torus hall for efficient work, the previous piston type pellet extruder was changed to the new screw type pellet extruder and the tests for continuous pellet extrusion were performed. In the extrusion test using deuterium gas as a working gas, continuous pellet extrusion up to 330s was achieved, which is sufficient performance for applying it to JT-60U experiments.
65 s) started from FY2003. The injection frequency and operation duration were limited by extrusion speed and volume of the piston type pellet extruder, respectively, in the previous system. The screw type pellet extruder made in Russian company was newly installed in the system, which can continuously extrude the pellet at high speed and has been used in other fusion devices. After parts of the pellet injector system moved from JT-60 torus hall for efficient work, the previous piston type pellet extruder was changed to the new screw type pellet extruder and the tests for continuous pellet extrusion were performed. In the extrusion test using deuterium gas as a working gas, continuous pellet extrusion up to 330s was achieved, which is sufficient performance for applying it to JT-60U experiments.
Higuchi, Hidekazu; Osugi, Takeshi; Nakashio, Nobuyuki; Momma, Toshiyuki; Tohei, Toshio; Ishikawa, Joji; Iseda, Hirokatsu; Mitsuda, Motoyuki; Ishihara, Keisuke; Sudo, Tomoyuki; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2007-038, 189 Pages, 2007/07
The Advanced Volume Reduction Facilities (AVRF) is constructed to manufacture the waste packages of radioactive waste for disposal in the Nuclear Science Research Institute of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The AVRF is constituted from two facilities. The one is the Waste Size Reduction and Storage Facility (WSRSF) which is for reducing waste size, sorting into each material and storing the waste package. The other is the Waste Volume Reduction Facility (WVRF) which is for manufacturing the waste package by volume reducing treatment and stabilizing treatment. WVRF has an induction melting furnace, a plasma melting furnace, an incinerator, and a super compactor for treatment. In this report, we summarized about the basic concept of constructing AVRF, the constitution of facilities, the specifications of machineries and the state of trial operation until March of 2006.
Sakata, Shinya; Kiyono, Kimihiro; Oshima, Takayuki; Sato, Minoru; Ozeki, Takahisa
JAEA-Technology 2007-039, 27 Pages, 2007/07
JT-60 data processing system (DPS) possesses three-level hierarchy. At the top level of hierarchy is JT-60 inter-shot processor (MSP-ISP), which is a mainframe computer, provides communication with the JT-60 supervisory control system and supervises the internal communication inside the DPS. The middle level of hierarchy has minicomputers and the bottom level of hierarchy has individual diagnostic subsystems, which consist of the CAMAC and VME modules. To meet the demand for advanced diagnostics, the DPS has been progressed in stages from a three-level hierarchy system, which was dependent on the processing power of the MSP-ISP, to a two-level hierarchy system, which is decentralized data processing system (New-DPS) by utilizing the UNIX-based workstations and network technology. This replacement had been accomplished, and the New-DPS has been started to operate in October 2005.
Kasahara, Seiji; Kubo, Shinji; Sato, Hiroyuki; Sakaba, Nariaki
JAEA-Technology 2007-040, 31 Pages, 2007/07
Purification methods of hydrogen and oxygen as products of thermochemical hydrogen production iodine sulphur (IS) process thermally connected with the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) was investigated and evaluated. Present state of R&D of membrane separation method, pressure swing adsorption (PSA) method and cryogenic distillation method was researched and their applicability to the HTTR-IS system was evaluated. At present, PSA method was the most effective due to its feasibility, soundness and reliability with past performance. In addition, hydrogen purification systems by using PSA and membrane separation method were described in this paper.
Noguchi, Hiroki; Ota, Hiroyuki*; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kubo, Shinji; Onuki, Kaoru; Hino, Ryutaro
JAEA-Technology 2007-041, 34 Pages, 2007/07
Thermo-chemical IS process produces large amount of hydrogen effectively. Since the IS process uses strong acids such as sulfuric acid and hydriodic acid, it is necessary to develop large-scale chemical reactors featuring materials that exhibit excellent heat and corrosion resistance. A sulfuric acid decomposer is one of the key components of the IS process. The decomposer is exposed to severe corrosion condition of sulfuric acid boiling flow, where only the SiC ceramics shows good corrosion resistance. However, at the current status, it is very difficult to manufacture the large-scale SiC ceramics structure required in the commercial plant. Therefore, we devised a new concept of the decomposer, which featured a counter flow type heat exchanger consisting of cylindrical blocks made of SiC ceramics. This paper describes results of the design work and the test-fabrication study of the sulfuric acid decomposer, which was carried out in order to confirm its feasibility.
 C discharged from Tokai reprocessing plant into rice plant; Monitoring data and a simple modeling approach
C discharged from Tokai reprocessing plant into rice plant; Monitoring data and a simple modeling approachKoarashi, Jun; Fujita, Hiroki; Onuma, Toshimitsu*; Mikami, Satoshi; Akiyama, Kiyomitsu; Takeishi, Minoru
JAEA-Technology 2007-042, 32 Pages, 2007/07
Carbon-14 is one of the most important radionuclides from the perspective of dose estimation due to the nuclear fuel cycle. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted the careful monitoring of  C in airborne release from Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP), atmospheric CO
C in airborne release from Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP), atmospheric CO and rice grains around TRP. This report reviewed the
and rice grains around TRP. This report reviewed the  C monitoring data obtained over ten years from 1991 to 2001. A simple mathematical model for transfer of TRP-derived
C monitoring data obtained over ten years from 1991 to 2001. A simple mathematical model for transfer of TRP-derived  C into rice plant was tested using the data set. The model-calculated
C into rice plant was tested using the data set. The model-calculated  C concentrations in atmospheric CO
C concentrations in atmospheric CO and rice grain agreed well with the observations, suggesting an applicability of the simple modeling approach to environmental assessment for atmospheric
and rice grain agreed well with the observations, suggesting an applicability of the simple modeling approach to environmental assessment for atmospheric  C discharge under steady-state conditions.
C discharge under steady-state conditions.
 decomposer for thermochemical hydrogen production by IS process; Basic design of SiC plate-type SO
decomposer for thermochemical hydrogen production by IS process; Basic design of SiC plate-type SO decomposer and catalyst test results
decomposer and catalyst test resultsKanagawa, Akihiro; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Onuki, Kaoru; Hino, Ryutaro
JAEA-Technology 2007-043, 54 Pages, 2007/09
Thermo-chemical Iodine-Sulfur (IS) process has a potential to produce large amount of hydrogen without CO emission by using thermal energy of a high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR). In SO
emission by using thermal energy of a high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR). In SO decomposer of IS process, SO
decomposer of IS process, SO gas is catalytically decomposed into O
gas is catalytically decomposed into O and SO
and SO under high temperature condition up to 850
under high temperature condition up to 850 C using the sensible heat of He gas. The decomposer is exposed to the severe corrosive condition. We proposed a new concept of the decomposer, which featured a plate-type heat exchanger made of SiC ceramics and revealed the results of thermal-hydraulic and mechanical strength analysis. To examine the fabricability of the proposed concept, a mock-up model was test-fabricated and issues on the fabricability of large-sized decomposer were clarified. Also, preliminary catalyst tests were carried out to clarify catalyst bed specification of the SO
C using the sensible heat of He gas. The decomposer is exposed to the severe corrosive condition. We proposed a new concept of the decomposer, which featured a plate-type heat exchanger made of SiC ceramics and revealed the results of thermal-hydraulic and mechanical strength analysis. To examine the fabricability of the proposed concept, a mock-up model was test-fabricated and issues on the fabricability of large-sized decomposer were clarified. Also, preliminary catalyst tests were carried out to clarify catalyst bed specification of the SO decomposer.
decomposer.
Oshima, Katsumi; Okano, Fuminori; Honda, Atsushi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Usui, Katsutomi; Noto, Katsuya; Kawai, Mikito; Ikeda, Yoshitaka
JAEA-Technology 2007-044, 27 Pages, 2007/06
In the positive ion based NBI (P-NBI) system, we have developed a protection system to protect the power supply facilities from over load during long pulse operation. The protection system monitors the voltage (V) and current (I) in the power supply facilities, and calculates the parameters of V2t and I2t in real-time, where T is the pulse duration. It turns off the power supply facilities when V2t and I2t are beyond the critical values. After two development stages, we have completed the protection system using a package typed PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) which has a high expandability of multi-unit operation. Moreover, we have constructed a user-friendly system by using a SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system.
Yokokura, Kenji; Moriyama, Shinichi; Hasegawa, Koichi; Suzuki, Sadaaki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Ishii, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Fumiaki
JAEA-Technology 2007-045, 22 Pages, 2007/07
A power measuring device using a dielectric disk for a high power millimeter waves is investigated. In the device, a high power wave is transmitted in a waveguide and then heats a dielectric installed in the waveguide. The transmitted power is estimated from the temperature rise of the dielectric disk. It is a new type of power measurement device, which is not sensitive to higher modes or change of their polarization in time. It also can measure the wide power range of kW to MW levels flexibly by choosing dielectric material proper to the power level as a detector. In the report, materials that have small dielectric loss for millimeter wave are chosen, and their properties of temperature rise and millimeter wave power capacity are estimated. On the basis of these results, design of the power measurement device and fabrication of its prototype are described for practical use in the electron cyclotron heating systems for the JT-60U and JT-60SA.
Izumo, Hironobu; Kato, Tomoaki; Kinase, Masami; Torii, Yoshiya; Murayama, Yoji
JAEA-Technology 2007-046, 23 Pages, 2007/07
JRR-3 (Japan Research Reactor No.3) has been operated for about 15 years after the modification, without significant troubles by carrying out maintenance such as the preventive maintenance (mainly Time-Based Maintenance: TBM) for the safety-grade equipments and the breakdown maintenance for the non-safety-grade equipments. Recently, numbers of unscheduled shutdowns caused by aging of the non-safety-grade equipment have been increasing, but resources for both maintenances have been decreasing year by year. In such a situation, new JRR-3 maintenance program is studying and reviewed considering safety, reliability and economical. In the evaluation, the maintenance data (i.e. vibration, measurement, etc.) which accumulated on JRR-3 is applied effectively. This report offers the policy on the maintenance review at JRR-3 and the future direction of JRR-3 maintenance programs.
Oyama, Sunao*; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Kaneshiro, Noriyuki*; Nemoto, Takahiro; Sekita, Kenji; Isozaki, Minoru; Emori, Koichi; Ito, Yoshiteru*; Yamamoto, Hideo*; Ota, Yukimaru; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2007-047, 40 Pages, 2007/08
High-Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) built by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has commonly used reciprocating compressor to extract helium gas and discharge helium gas into primary/secondary coolant helium loop from helium purification system. Rod-seal structure of the compressor is complicated from a prevention coolant leak standpoint. Because of frequently leakage of seal oil in operation, Rod seal structure isn't as reliable as it should be sustainable in the stable condition during long term operation. As a result of investigations, leakage's root is found in that seal were used in a range beyond limit sliding properties of seal material. Therefore a lip of the seal was worn and transformed itself and was not able to sustain a seal function. Endurance test using materials testing facility and verification test using a actual equipment on candidate materials suggest that a seal of fluorine contained resin mixed graphite is potentially feasible material of seal.
Chida, Teruo; Ida, Mizuho; Nakamura, Hiroo; Sato, Toru*; Sugimoto, Masayoshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-048, 40 Pages, 2007/08
This report describes results of thermo-structural analysis of a backwall in international fusion material irradiation facilities (IFMIF) lithium target preformed during FY2007. The IFMIF is an accelerator-based intense neutron source for testing candidate materials for fusion reactors. Since the backwall is operating under a severe neutron irradiation of 50 dpa/year and a maximum nuclear heating rate of 25 W/cm , thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Since previous model included only the backwall, a model including a part of target assembly is applied. In this analysis, three models were calculated. First model is a basic geometry adding a part of the target assembly to the backwall. Second model is a modified geometry which has a thin backwall. In a third model, a lip seal with a stress mitigation structure was applied to the second model. Calculation results showed that, in the third model, a thermal stress at a center of the backwall was 146 MPa below a permissible stress of F82H (455MPa: an yield strength at 300
, thermo-structural design is one of critical issues in a target design. Since previous model included only the backwall, a model including a part of target assembly is applied. In this analysis, three models were calculated. First model is a basic geometry adding a part of the target assembly to the backwall. Second model is a modified geometry which has a thin backwall. In a third model, a lip seal with a stress mitigation structure was applied to the second model. Calculation results showed that, in the third model, a thermal stress at a center of the backwall was 146 MPa below a permissible stress of F82H (455MPa: an yield strength at 300 C) and maximum stress was 286 MPa below a permissible stress of SUS316L (328MPa: 3Sm value at 300
C) and maximum stress was 286 MPa below a permissible stress of SUS316L (328MPa: 3Sm value at 300 C). These results showed a prospect of the present backwall configuration.
C). These results showed a prospect of the present backwall configuration.
Seimiya, Munetaka; JT-60 Operation Team
JAEA-Technology 2007-049, 54 Pages, 2007/08
Since the first plasma in JT-60 was achieved in April 1985, various experimental challenges have been successfully conducted, and currently producing many new findings. These achievements have been realized by large modifications for lower X-point divertor in 1987, for large plasma current upgrade in 1989-1991, for W-shaped divertor in 1997, and for long pulse discharge in 2002. Such developments contribute to have established JT-60 as the leading tokamak in the world. As a consequence of the 22-year operation, we have accumulated many operational and experimental data. This reports the operational records including troubles and availability, the outline of planning management, the safety control and the promotion procedure of operation in JT-60.
Kato, Tomoaki; Araki, Masaaki; Izumo, Hironobu; Kinase, Masami; Torii, Yoshiya; Murayama, Yoji
JAEA-Technology 2007-050, 39 Pages, 2007/08
On the conversion from aluminide fuel to silicide fuel, burnable absorbers were introduced for decreasing excess reactivity. The burnable absorbers influence reactivity during reactor operation. So, the burning of the burnable absorbers was studied and the influence on reactor operation was made cleared. Furthermore, necessary excess reactivity on beginning of operation cycle and the time limit for restart after unplanned reactor shutdown was calculated. After the conversion, the fuel exchange procedure was changed from the six-batch dispersion procedure to the fuel burn-up management procedure. The previous estimation of fuel burn-up was required for the planning of fuel exchange, so that the estimation was carried out by means of past operation data. Finally, a new fuel exchange procedure was proposed for effective use of fuel elements. The average length of fuel-staying in the core can be increased by two percent on the procedure.
Nagao, Yoshiharu; Sato, Masashi; Niimi, Motoji
JAEA-Technology 2007-051, 73 Pages, 2007/09
An evaluation procedure using Monte Carlo method has been introduced to evaluate  dose in neutron-
dose in neutron- mixing field of nuclear reactor. Benchmark calculations of the
mixing field of nuclear reactor. Benchmark calculations of the  heating rate experiments in JMTRC and the nuclear heating rate measurements by the nuclear heating rate measurement capsule in JMTR were conducted by the procedure. As the results, it was confirmed that the procedure was applicable to evaluate
heating rate experiments in JMTRC and the nuclear heating rate measurements by the nuclear heating rate measurement capsule in JMTR were conducted by the procedure. As the results, it was confirmed that the procedure was applicable to evaluate  /nuclear heating rate of JMTR. The nuclear heating distribution of JMTR core was analyzed, and the nuclear heating data maps were prepared. The values of the data maps were comparison with the results of irradiation tests by the nuclear heating rate measurement capsule. As the results, the values of the data map were within -27 to +35 % in comparison with the irradiation tests. The data maps are therefore utilizable for thermal design of irradiation capsule with more accurate temperature control, after refurbishment of the JMTR.
/nuclear heating rate of JMTR. The nuclear heating distribution of JMTR core was analyzed, and the nuclear heating data maps were prepared. The values of the data maps were comparison with the results of irradiation tests by the nuclear heating rate measurement capsule. As the results, the values of the data map were within -27 to +35 % in comparison with the irradiation tests. The data maps are therefore utilizable for thermal design of irradiation capsule with more accurate temperature control, after refurbishment of the JMTR.
Ikekame, Yoshinori; Ouchi, Satoshi; Suwa, Masayuki; Isaka, Koji; Goto, Shingo; Murayama, Yoji
JAEA-Technology 2007-052, 47 Pages, 2007/08
In order to sustain safe and stable operation of JRR-3, it is necessary to measure and indicate appropriately the process values such as flow rate of coolant with the process instrumentation facilities of JRR-3. Whenever reactor facilities such as cooling pump or measuring device are maintained or refurbished, the process instrumentation facilities are calibrated with the appropriate criteria established by considering overall accuracy of the facilities. In this report, for all of the safety protection system, a part of the process instrumentation facilities, accuracy of each component and overall accuracy of the system are compiled. Using these date, the process instrumentation facilities would be maintained more effectively and objectively.
Terakado, Masayuki; Shimono, Mitsugu; Sawahata, Masayuki; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Igarashi, Koichi; Sato, Fumiaki; Wada, Kenji; Seki, Masami; Moriyama, Shinichi
JAEA-Technology 2007-053, 28 Pages, 2007/09
The electron cyclotron heating (ECH) system at 110 GHz are injected to JT-60U plasmas with pulse modulation at dozens to hundreds of Hz in order to measure heat conductivity of the plasma to investigate plasma confinement. The JT-60U ECH system has a unique feature to realize the pulse modulation by controlling the anode voltage of the triode gyrotron without chopping the main acceleration voltage. The typical depth of the modulation is 80 % at the modulation frequency range of 12.2 Hz to 500 Hz. However in the JT-60SA, higher modulation frequency of some kHz will be required to stabilize neoclassical tearing mode (NTM). The modulation techniques have been investigated and the modulation frequency of 3.5 kHz with the modulation depth of 84 % has been achieved. The modulation frequency up to 3 kHz is available in the pulse widths of the practical operation. As a next step, replacement of the parts in the anode voltage divider circuit is planned to achieve higher modulation frequency.
Noguchi, Hiroki; Ota, Hiroyuki*; Terada, Atsuhiko; Kubo, Shinji; Onuki, Kaoru; Hino, Ryutaro
JAEA-Technology 2007-054, 31 Pages, 2007/09
JAEA has been conducting R&D on thermo-chemical water splitting hydrogen production technology by an iodine-sulfur cycle (IS process) aiming to establish the technology with high-temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs). The IS process uses sulfuric acid as a process fluid, which is a very corrosive fluid. For development of the sulfuric-acid decomposer in the pilot plant, the sulfuric-acid flow test loop (SFTL) was constructed to obtain flow boiling characteristics, and to confirm applicability of components such as pipelines, pumps and instrumentations. The SFTL consists of a sulfuric-acid boiling heat transfer test loop and a high temperature component test loop, whose maximum flow rates are 2.5 L/min and 20 L/min, respectively. This report presents outline of the SFTL and shakedown test results.
Suzuki, Sadaaki; Seki, Masami; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Sato, Fumiaki; Hiranai, Shinichi; Ishii, Kazuhiro*; Hasegawa, Koichi; Moriyama, Shinichi
JAEA-Technology 2007-055, 27 Pages, 2007/09
In the experiments featuring lower hybrid range of frequency (LHRF) system in JT-60U, carbon grills were attached to the plasma-facing part of the antenna in order to avoid the damage by the excessive heat load from the plasma. However some electric discharge traces were found there in the observation after the experiments. To avoid such discharges, improvements of the arc detector and the protection interlock by visible picture detection were tackled. In the arc detector, the amplification circuit was improved in order to obtain shorter response time and higher resolution of optical detection. Moreover, in visible picture detection, a new function of RF-on/off control utilizing PC image processing was added to distinguish the light of the arc from one of the plasma. This report summarizes improvement of the protection interlock device in a LHRF heating system.
Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Tochio, Daisuke; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Goto, Minoru
JAEA-Technology 2007-056, 51 Pages, 2007/09
The three gas circulators trip test and the vessel cooling system stop test as the safety demonstration test by using the HTTR are under planning to demonstrate inherent safety features of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor. All three gas circulators to circulate the helium gas as the coolant are stopped to simulate the loss of forced cooling in the three gas circulators trip test. The stop of the vessel cooling system located outside the reactor pressure vessel to remove the core residual heat follows the stop of all three gas circulators in the vessel cooling system stop test. The analysis of the reactor transient for such tests and abnormal events postulated during the test was performed. From the result of analysis, it was confirmed that the three gas circulators trip test and the vessel cooling system stop test can be performed within the region of the normal operation in the HTTR and the safety of the reactor facility is ensured even if the abnormal events would occur.
Shiraishi, Kunio; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Ishigami, Tsutomu; Tomii, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-057, 46 Pages, 2007/09
The method for evaluating efficiently decommissioning cost in a short time was made based on the features of various types of nuclear facilities where the feature of nuclear facilities was arranged. The evaluation method can calculate decommissioning cost using conversion factors corresponding to weight of components and structures of nuclear facilities, etc. The conversion factors were made based on the experience of the JPDR decommissioning projects in the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and of improvements of the reprocessing plant of the Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC). In this report, the decommissioning cost evaluation method of nuclear facilities that had been made before unification of JAERI and JNC was revaluated as a new decommissioning cost evaluation method to reasonably advance decommissioning plans of various nuclear facilities.
Suguro, Toshiyasu; Nishikawa, Yoshiaki*; Komuro, Takashi*; Kagawa, Akio; Kashiwazaki, Hiroshi; Yamada, Kazuo
JAEA-Technology 2007-058, 20 Pages, 2007/11
For safety assessment of TRU waste disposal, data on sorption data of plutonium on Tuff have been obtained by a static batch-type experiment. Because the repository condition will be reducing and be affected by considerable amount of nitrate in waste, the authors carried out the experiments using Tuff under the reducing (Na S
S O
O as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
as added as reductant) and anoxic condition (O
 1 ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO
1 ppm) and solution of 0 to 0.5 M NaNO . The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (Kd) ranges 0.2 to 0.7 m
. The experimental results suggest that distribution coefficient (Kd) ranges 0.2 to 0.7 m kg
kg in case of L/S=0.1 m
in case of L/S=0.1 m kg
kg . Similarly the Kd ranges, 1 to 7 m
. Similarly the Kd ranges, 1 to 7 m kg
kg at L/S=1 m
at L/S=1 m kg
kg . However, almost samples of the solution after experiments were plutonium solubility less than detection limit(10
. However, almost samples of the solution after experiments were plutonium solubility less than detection limit(10 mol/dm
mol/dm ) of alpha spectrometer. The reason, it is guessed plutonium coprecipitation with calcium hydroxide, because experiments using saturated calcium hydroxide in the liquid.
) of alpha spectrometer. The reason, it is guessed plutonium coprecipitation with calcium hydroxide, because experiments using saturated calcium hydroxide in the liquid.
Saito, Kenji; Sekita, Kenji; Kawasaki, Kozo; Yamamoto, Kazuhiko*; Matsuura, Makoto*
JAEA-Technology 2007-059, 36 Pages, 2007/11
The Wide-Range Monitoring neutron detectors of HTTR are used under 450  C in normal operation and 550
C in normal operation and 550  C in the accidents. When the WRM detectors are used under the high temperature for a long time, characteristics of the detector might be degraded, because of the decrease of the nitrogen concentration in the ionization gas caused by adsorbtion of nitrogen into the electrode material. Consequently, the nitrogen gas adsorption test was carried out to clarify the quantity of absorbed nitrogen gas in electrode material under the high temperature. Then, the performance evaluation test of the prototype detector was carried out, and it was confirmed that degradation of the prototype detector characteristics didn't arise under the high temperature anvironment. This report describes the results of consideration about the life-extension of WRM detectors. As a result, it was confirmed that the WRM detectors are usable for 5 years under 450
C in the accidents. When the WRM detectors are used under the high temperature for a long time, characteristics of the detector might be degraded, because of the decrease of the nitrogen concentration in the ionization gas caused by adsorbtion of nitrogen into the electrode material. Consequently, the nitrogen gas adsorption test was carried out to clarify the quantity of absorbed nitrogen gas in electrode material under the high temperature. Then, the performance evaluation test of the prototype detector was carried out, and it was confirmed that degradation of the prototype detector characteristics didn't arise under the high temperature anvironment. This report describes the results of consideration about the life-extension of WRM detectors. As a result, it was confirmed that the WRM detectors are usable for 5 years under 450  C in normal operation and 550
C in normal operation and 550  C in the accidents.
C in the accidents.
Kanagawa, Akihiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Ishikura, Shuichi; Onuki, Kaoru; Hino, Ryutaro
JAEA-Technology 2007-060, 31 Pages, 2007/11
Thermo-chemical Iodine-Sulfur (IS) process can produce large amount of hydrogen effectively without emission of greenhouse effect gas such as carbon dioxide, where nuclear thermal energy of a high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) is adopted as a heat source. The IS process uses strong acids such as sulfuric acid and hydriodic acid in high temperature and pressure conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to develop large-size chemical reactors featuring materials that exhibit high temperature and corrosion resistance. A SO decomposer, which is one of key components of the IS process, consists of a pressure vessel for high temperature and high pressure helium gas and an internal structure for SO
decomposer, which is one of key components of the IS process, consists of a pressure vessel for high temperature and high pressure helium gas and an internal structure for SO decomposition by the latent heat of the helium gas. Since joints of the internal structure will be heated up to 700
decomposition by the latent heat of the helium gas. Since joints of the internal structure will be heated up to 700 C, we designed a high-temperature joint coupled with coned-disk springs and SiC bolts (coned-disk springs assembly) so as to keep seal performance under high temperature condition. This report presents applicability examination results of designed coned-disk springs assembly as well as seal performance test results of candidate gaskets.
C, we designed a high-temperature joint coupled with coned-disk springs and SiC bolts (coned-disk springs assembly) so as to keep seal performance under high temperature condition. This report presents applicability examination results of designed coned-disk springs assembly as well as seal performance test results of candidate gaskets.
Kanagawa, Akihiro*; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Onuki, Kaoru; Fukui, Hiroshi*; Nishibayashi, Toshiki*
JAEA-Technology 2007-061, 32 Pages, 2007/12
Separation of hydrogen iodide from HIx solution (HI-I -H
-H O mixture) is one of the technical issues in the development of thermochemical IS process. Application of pervaporation (PV) to the concentration of HIx solution in the IS process pilot test plant was discussed from the viewpoints of process heat mass balance, conceptual design of the apparatus, and the corrosion resistance of the membrane module. Compared with the electro-electrodialysis system, the PV system enables the downsizing of apparatus by using hollow fiber membranes, although it does not improve the thermal efficiency of IS process. Immersion tests of commercially available Nafion hollow fiber membrane module in the HIx solution at 100
O mixture) is one of the technical issues in the development of thermochemical IS process. Application of pervaporation (PV) to the concentration of HIx solution in the IS process pilot test plant was discussed from the viewpoints of process heat mass balance, conceptual design of the apparatus, and the corrosion resistance of the membrane module. Compared with the electro-electrodialysis system, the PV system enables the downsizing of apparatus by using hollow fiber membranes, although it does not improve the thermal efficiency of IS process. Immersion tests of commercially available Nafion hollow fiber membrane module in the HIx solution at 100 C indicated the necessity of improving the corrosion resistance of bundle materials.
C indicated the necessity of improving the corrosion resistance of bundle materials.
Ishikawa, Masao; Kondoh, Takashi; Hayakawa, Atsuro*; Nishitani, Takeo; Kusama, Yoshinori
JAEA-Technology 2007-062, 57 Pages, 2007/12
The microfission chambers (MFC)provide time-resolved measurements of the global neutron source strength and fusion power from ITER. In the previous work, it was found that combination of the MFC for low power operation and for high power operation can cover the target measurement requirement of ITER. Signals from the MFC are transferred by double coaxial mineral cable (MI) cable. These MFC will be installed in the vacuum vessel, so that the MI cables should be placed in the vacuum vessel. In this design work, the placing route of the MI cables from the installation position of the microfission chamber to the feed-through in the upper port is designed. As far placing of the MI cable, since the MI cable is filled with Ar gas at 14.6 atom, the double pipe structure that the outer pipe covers the MI cable is adopted in order to prevent the gas leak into the vacuum vessel. The exhaust system of the double pipe is also designed for detection and exhaust of the leaked Ar gas.
Sone, Tomoyuki; Nonaka, Kazuharu; Sasaki, Toshiki; Yamaguchi, Hiromi
JAEA-Technology 2007-063, 42 Pages, 2008/01
Steam reforming method has been developed for the treatment of organic wastes which are not suitable materials (tributyl phosphate, halogenated oil) for the incineration due to large quantities of secondary wastes generation. Process demonstration tests were conducted with the demonstration scale steam reforming system to examine the feasibility of treatment of simulated waste solvent (TBP and n-dodecane mixture) and simulated waste oils (halogenated oils and mineral oil mixture). These tests were also conducted to optimize the process conditions. The results of these studies are as follows: (1)More than 98wt% of the simulated wastes were evaporated in the gasification process. Solid residues removed from the gasification process as secondary wastes were inorganic compounds. (2)While the simulated waste oils were treated, the stacking of the filter is reduced by increasing the feed rate of steam from 1.5 kg/h to 3.0 kg/h. (3)Most of phosphoric acids produced by thermal decomposition of TBP were vaporized in the gasification process at 600 650
650 C. This result shows that volume of radioactive secondary waste can be effectively reduced.
C. This result shows that volume of radioactive secondary waste can be effectively reduced.
Kajita, Shin; Hatae, Takaki; Katsunuma, Atsushi*; Kusama, Yoshinori
JAEA-Technology 2007-064, 60 Pages, 2008/01
The design of the collection optics for edge Thomson scattering diagnostics for ITER is provided. Since the neutron and  ray radiation fluxes generated by the nuclear fusion reaction are considerably high near the plasma in ITER, available optical components are limited. Near the plasma, namely in the front-end optics, only metal mirrors can be used; moreover, optical fiber may be used only outside the vacuum window, which is located far from the front-end optics. In this design, three metal mirrors are used for the front-end optics, and the light ray is transmitted in the slender port plug through a relay optical system. To compensate the aberrations and increase the coupling efficiency to the fibers, two types of optical system with Catadioptric system are proposed for fiber-coupling optical system. It has been revealed that refraction type and reflection type system are not adequate for the fiber-coupling optical system. The image qualities are discussed based on the spot diagram and so on for the Catadioptric optical system.
ray radiation fluxes generated by the nuclear fusion reaction are considerably high near the plasma in ITER, available optical components are limited. Near the plasma, namely in the front-end optics, only metal mirrors can be used; moreover, optical fiber may be used only outside the vacuum window, which is located far from the front-end optics. In this design, three metal mirrors are used for the front-end optics, and the light ray is transmitted in the slender port plug through a relay optical system. To compensate the aberrations and increase the coupling efficiency to the fibers, two types of optical system with Catadioptric system are proposed for fiber-coupling optical system. It has been revealed that refraction type and reflection type system are not adequate for the fiber-coupling optical system. The image qualities are discussed based on the spot diagram and so on for the Catadioptric optical system.
 -ray emitting nuclides (Joint research)
-ray emitting nuclides (Joint research)Ishimori, Kenichiro; Oki, Keiichi; Takaizumi, Hirohide; Kameo, Yutaka; Oki, Yoshiyuki*; Nakashima, Mikio
JAEA-Technology 2007-065, 20 Pages, 2008/01
In order to prepare a reference material which is used for radiochemical analysis of solidified products made from non-metallic miscellaneous low level radioactive solid wastes by melting in Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the preparation method of the reference material was investigated. Under the optimum melting conditions obtained in this report, the reference material containing  Np,
Np,  Am and
Am and  Cm as
Cm as  -ray emitting nuclides was successfully prepared. From radiochemical analysis of the reference material, the radioactive concentration of respective nuclides was determined to be 0.188
-ray emitting nuclides was successfully prepared. From radiochemical analysis of the reference material, the radioactive concentration of respective nuclides was determined to be 0.188 0.001 Bq/g for
0.001 Bq/g for  Np, 0.368
Np, 0.368 0.004 Bq/g for
0.004 Bq/g for  Am, 0.402
Am, 0.402 0.010 Bq/g for
0.010 Bq/g for  Cm.
Cm.
Furusawa, Takayuki; Saikusa, Akio; Hamamoto, Shimpei; Nemoto, Takahiro; Shinohara, Masanori; Isozaki, Minoru
JAEA-Technology 2007-066, 38 Pages, 2008/01
In the HTTR rise-to-power test which was performed from April in 2000 as phase 1 up to 10MW, nitrogen gas remained in the air cooler which release the heat to atmosphere. This residence nitrogen gas causes the reduction of the thermal performance of the air cooler. So, it was impossible that heat generated reactor core could not remove when reactor operated full power operation. A mockup test was carried out to investigate the occurrence mechanism of the residence nitrogen gas. From a result of the mockup test, we clarified that the marked wave rise in the water pressurizer and the melting velocity of the nitrogen gas into the pressurized water is thought to be higher than expected. Therefore, we installed a hollow type plate, multi-hole type plate and so on in the water pressurizer. As a result, it was confirmed that no residence nitrogen gas in the air cooler during rise-to-power test and normal operation. Consequently, the hollow type plate and multi-hole type plate were effective for prevention of the residence nitrogen gas in the air cooler. This paper describes the results of the mockup test and the improvement of the water pressurizer.
Seki, Yohji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Tsuru, Daigo; Enoeda, Mikio; Akiba, Masato; Ezato, Koichiro; Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Nishi, Hiroshi; Hirose, Takanori; Homma, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2007-067, 34 Pages, 2008/01
This report is result of one-dimensional nuclear and thermal analyses on Test Blanket Module (TBM) for ITER emphasizing on optimized layer structures of a ceramic tritium breeder (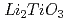 ) and a beryllium neutron multiplier
) and a beryllium neutron multiplier 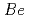 . Taking into account increment of Tritium Breeding Ratio (TBR), the radial widths of the breeder and multiplier layers are optimized. The main results of our study are as follows: (1) In multilayered structures of pebble beds, the peak of the TBR exists within the range of the volume ratio
. Taking into account increment of Tritium Breeding Ratio (TBR), the radial widths of the breeder and multiplier layers are optimized. The main results of our study are as follows: (1) In multilayered structures of pebble beds, the peak of the TBR exists within the range of the volume ratio 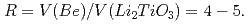 (2) In the case of the single packing, the R stayed in the range of
(2) In the case of the single packing, the R stayed in the range of 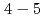 by setting the two layers of Be behind a layer of
by setting the two layers of Be behind a layer of 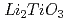 . This database of TBR for optimized layer structures contributes to the estimation of TBR at the design stage of the TBM and demonstration blanket.
. This database of TBR for optimized layer structures contributes to the estimation of TBR at the design stage of the TBM and demonstration blanket.
 )
)Kutsukake, Kenichi; Matsuda, Makoto; Hanashima, Susumu; Obara, Kenjiro*
JAEA-Technology 2007-068, 52 Pages, 2008/01
Many measurement and control equipment is installed inside of a high voltage terminal of the JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator and operated under pressurized sulfur hexafluoride (SF ) of 0.5 MPa. This screening test has been carried out to select a relay, which is usable under the SF
) of 0.5 MPa. This screening test has been carried out to select a relay, which is usable under the SF for turn on and off a power supply of the devices, from commercial relays used in the atmospheric condition. Four kinds of relay were tested: electromechanical relay (EMR), magnet contactor (MAG), solid-state relay (SSR) and hybrid relay (HYB). Temperature of the relay, change of appearance of the relay including contact surface using the SEM and EDS were measured and observed. The EMR and the MAG showed irregular contact because of the sulfide or fluoride, and these compounds which are formed by chemical reaction between metals and sulfur or hydrogen fluoride due to dissociation of SF
for turn on and off a power supply of the devices, from commercial relays used in the atmospheric condition. Four kinds of relay were tested: electromechanical relay (EMR), magnet contactor (MAG), solid-state relay (SSR) and hybrid relay (HYB). Temperature of the relay, change of appearance of the relay including contact surface using the SEM and EDS were measured and observed. The EMR and the MAG showed irregular contact because of the sulfide or fluoride, and these compounds which are formed by chemical reaction between metals and sulfur or hydrogen fluoride due to dissociation of SF in electric arcs. Solid-state relay and hybrid relay are available in the pressurized SF
in electric arcs. Solid-state relay and hybrid relay are available in the pressurized SF of 0.5 MPa.
of 0.5 MPa.
Sakazume, Yoshinori; Aoki, Hiromichi; Haga, Takahisa; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Sonoda, Takashi; Shimizu, Kaori; Niitsuma, Yasushi*; Ito, Mitsuo; Inoue, Takeshi
JAEA-Technology 2007-069, 44 Pages, 2008/02
Analysis of the uranyl nitrate solution fuel is carried out at the analytical laboratory of NUCEF (Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Research Facility), which provides essential data for operation of STACY (Static Experiment Critical Facility), TRACY (Transient Experiment Critical Facility) and the fuel treatment system. Analyzed in FY 2006 were uranyl nitrate solution fuel samples taken before and after experiments of STACY and TRACY, samples for the preparation of uranyl nitrate solution fuel, and samples for nuclear material accountancy purpose. The total number of the samples analyzed in FY 2006 was 254. This report summarizes work related to the analysis and management of the analytical laboratory in the FY 2006.
Ikusawa, Yoshihisa; Ozawa, Takayuki
JAEA-Technology 2007-070, 27 Pages, 2008/03
IFA-554/555 load-follow tests were performed in HALDEN reactor to study the MOX fuel behavior under the daily-load-follow operation condition in the framework of ATR-MOX fuel development in JAEA. In this report, FP gas release behavior of MOX fuel rod was evaluated under the daily-load-follow operation condition with the examination data from IFA-554/555 by using the computation code FASTGRASS. As the computation results of FASTGRASS code, which could compute the FP gas release behavior under the transient condition, it could be concluded that FP gas would release due to the relaxation of fuel pellet inner stress, which were caused by the cyclic power change during the daily-load-follow operation. In addition, since the amount of released FP gas would decrease during the steady operation after the daily-load-follow, it could be mentioned that the total of FP gas release at the end of life with the daily-load-follow would not be so much different from that without the daily-load-follow.